Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps
- 3.1 The Anatomy of a Weather Map
- 3.2 The Importance of Weather Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the World of Weather Maps
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Weather Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps
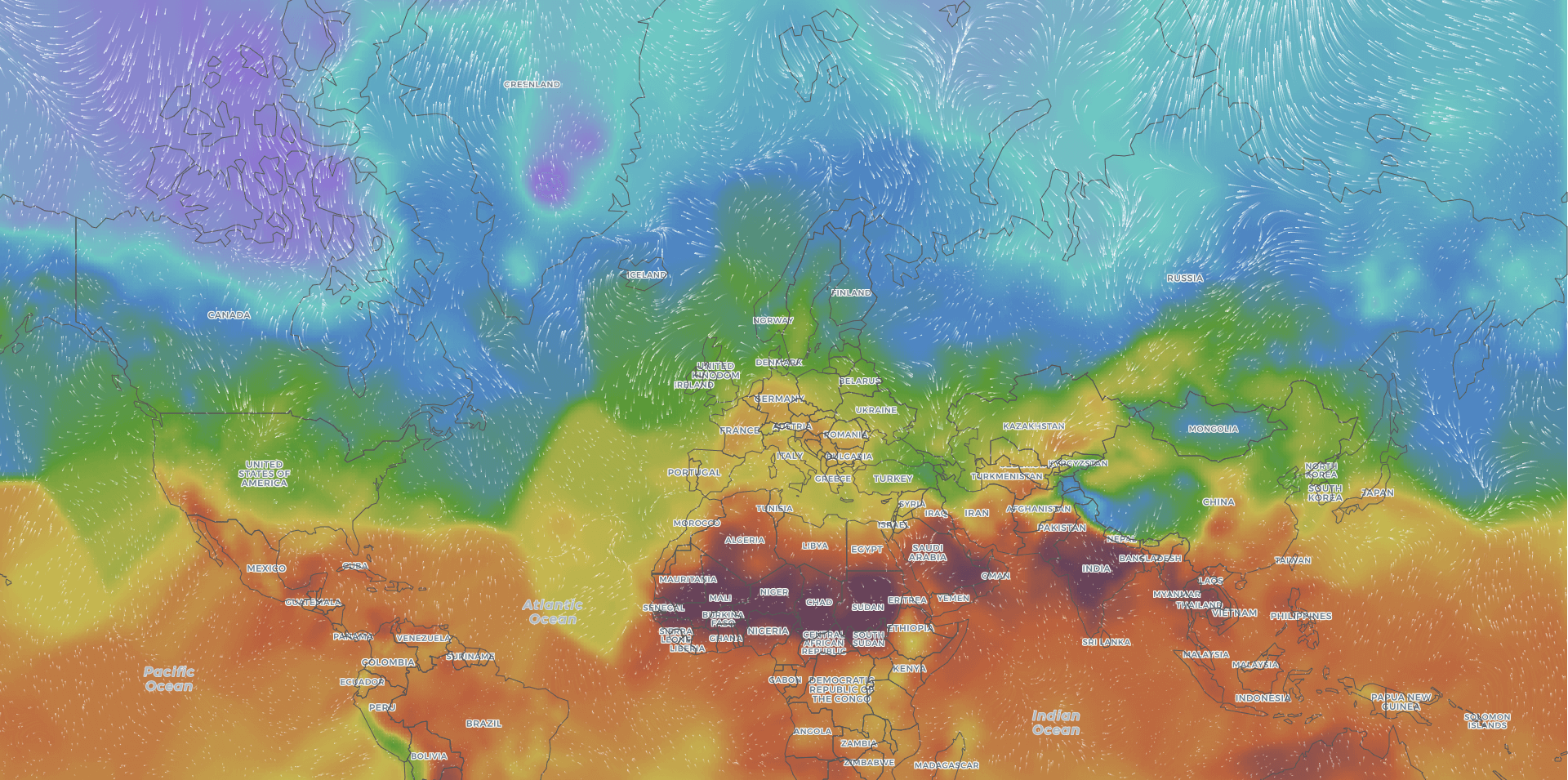
Weather maps, those colorful displays of swirling lines and symbols, are more than just aesthetically pleasing graphics. They are powerful tools that provide valuable insights into the current and future state of our atmosphere. Understanding how to read and interpret these maps empowers individuals, businesses, and organizations to make informed decisions, plan activities, and navigate the world’s diverse climate.
The Anatomy of a Weather Map
Weather maps are essentially visual representations of meteorological data, collected from various sources including weather stations, satellites, and radar systems. They typically depict key elements such as:
1. Temperature: Isotherms, lines connecting points of equal temperature, are used to show temperature variations across a region. Warmer areas are usually depicted in red or orange, while cooler areas are represented in blue or purple.
2. Precipitation: Areas experiencing precipitation are often indicated by shaded regions, with darker shades representing heavier rainfall. Symbols like rain drops, snowflakes, or lightning bolts denote specific types of precipitation.
3. Wind: Arrows on the map indicate wind direction, with the arrowhead pointing in the direction the wind is blowing. The length of the arrow often represents wind speed.
4. Pressure Systems: Isobars, lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, are vital for understanding weather patterns. High-pressure systems are typically associated with clear skies and calm conditions, while low-pressure systems often bring stormy weather.
5. Fronts: Boundaries between different air masses are known as fronts. These are represented by lines with symbols that indicate the type of front (e.g., cold front, warm front, stationary front). Fronts play a crucial role in determining weather changes.
The Importance of Weather Maps
Weather maps serve as a crucial tool for various sectors:
1. Public Safety: Emergency responders, disaster management agencies, and law enforcement agencies rely on weather maps to anticipate and prepare for extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, and snowstorms. This information enables timely warnings, evacuation procedures, and efficient resource allocation.
2. Agriculture: Farmers use weather maps to make critical decisions regarding planting, irrigation, and harvesting. Accurate weather forecasts help them optimize crop yields, mitigate risks, and plan for potential challenges.
3. Aviation: Pilots and air traffic controllers use weather maps to navigate safely, avoid turbulent conditions, and make informed decisions regarding flight routes and schedules. Weather maps provide information on wind patterns, precipitation, and visibility, crucial for flight safety.
4. Transportation: Road and rail transportation systems utilize weather maps to prepare for potential road closures, delays, and hazardous conditions. This allows them to implement preventive measures, reroute traffic, and ensure the safety of commuters.
5. Tourism and Recreation: Travelers and outdoor enthusiasts rely on weather maps to plan their activities, choose appropriate clothing, and anticipate potential hazards. Weather forecasts help them make informed decisions about outdoor adventures, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
6. Energy Production: Weather maps play a vital role in the energy sector, particularly in renewable energy production. Wind farms, solar power plants, and hydroelectric facilities use weather forecasts to optimize energy generation and manage resource allocation.
Navigating the World of Weather Maps
While weather maps are powerful tools, interpreting them effectively requires some understanding. Several resources can assist in this process:
1. National Weather Service (NWS): The NWS provides comprehensive weather maps and forecasts for the United States, offering a wide range of information from local forecasts to national outlooks.
2. Weather Underground: This website offers interactive weather maps, detailed forecasts, and historical weather data, allowing users to explore weather patterns in various regions.
3. AccuWeather: AccuWeather is another popular platform providing detailed weather maps, forecasts, and real-time weather updates for locations worldwide.
4. Weather.com: This website, part of the Weather Channel, offers a user-friendly interface with interactive weather maps, forecasts, and weather alerts for various locations.
5. Google Maps: Google Maps integrates weather information into its platform, providing users with current weather conditions, forecasts, and weather alerts for specific locations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Maps
1. What are the different types of weather maps?
Weather maps can be categorized based on their purpose and the data they display. Some common types include:
- Surface Maps: Depicting weather conditions at ground level, including temperature, pressure, wind, and precipitation.
- Upper Air Maps: Showing weather conditions at different altitudes, providing insights into atmospheric circulation and jet streams.
- Radar Maps: Using radar technology to detect precipitation, wind, and other atmospheric phenomena.
- Satellite Maps: Capturing images of the Earth’s atmosphere from space, providing a broader view of weather patterns.
2. How often are weather maps updated?
Weather maps are typically updated every few hours, depending on the source and the type of data being displayed. Some sources provide real-time updates, while others offer forecasts for specific intervals (e.g., hourly, daily).
3. How accurate are weather maps?
The accuracy of weather maps depends on various factors, including the quality of data, the complexity of weather systems, and the forecasting models used. While weather forecasts are constantly improving, they are not always perfect and can be subject to error.
4. What are the limitations of weather maps?
Weather maps can be limited in their ability to predict localized weather events, particularly those influenced by complex terrain or microclimates. Additionally, they may not always capture the full range of weather phenomena, such as lightning strikes, hailstorms, or tornadoes.
5. How can I improve my understanding of weather maps?
To enhance your understanding of weather maps, consider the following:
- Study basic meteorology: Familiarize yourself with key meteorological concepts like pressure systems, fronts, and wind patterns.
- Explore online resources: Utilize websites and apps that provide explanations, tutorials, and interactive weather maps.
- Practice interpreting maps: Regularly examine weather maps and try to identify key features and patterns.
- Engage with weather professionals: Seek out information from meteorologists, weather forecasters, and other experts.
Tips for Using Weather Maps Effectively
1. Understand the context: Consider the specific location, time of year, and any known weather patterns when interpreting a weather map.
2. Look for trends: Analyze the direction and movement of pressure systems, fronts, and other weather features to anticipate future weather changes.
3. Pay attention to details: Examine the symbols, colors, and lines on the map to understand specific weather elements and their intensity.
4. Compare multiple sources: Consult different weather sources to get a more comprehensive view of the weather situation and identify potential discrepancies.
5. Stay informed: Regularly check weather updates, forecasts, and alerts to stay informed about potential weather changes and hazards.
Conclusion
Weather maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the world’s diverse climate. By understanding the principles of weather map interpretation, individuals, businesses, and organizations can make informed decisions, plan activities, and mitigate risks associated with weather events. From public safety to agriculture, aviation, and tourism, weather maps play a vital role in various sectors, enhancing safety, efficiency, and informed decision-making. By utilizing these tools effectively, we can better prepare for, adapt to, and thrive within the ever-changing world of weather.





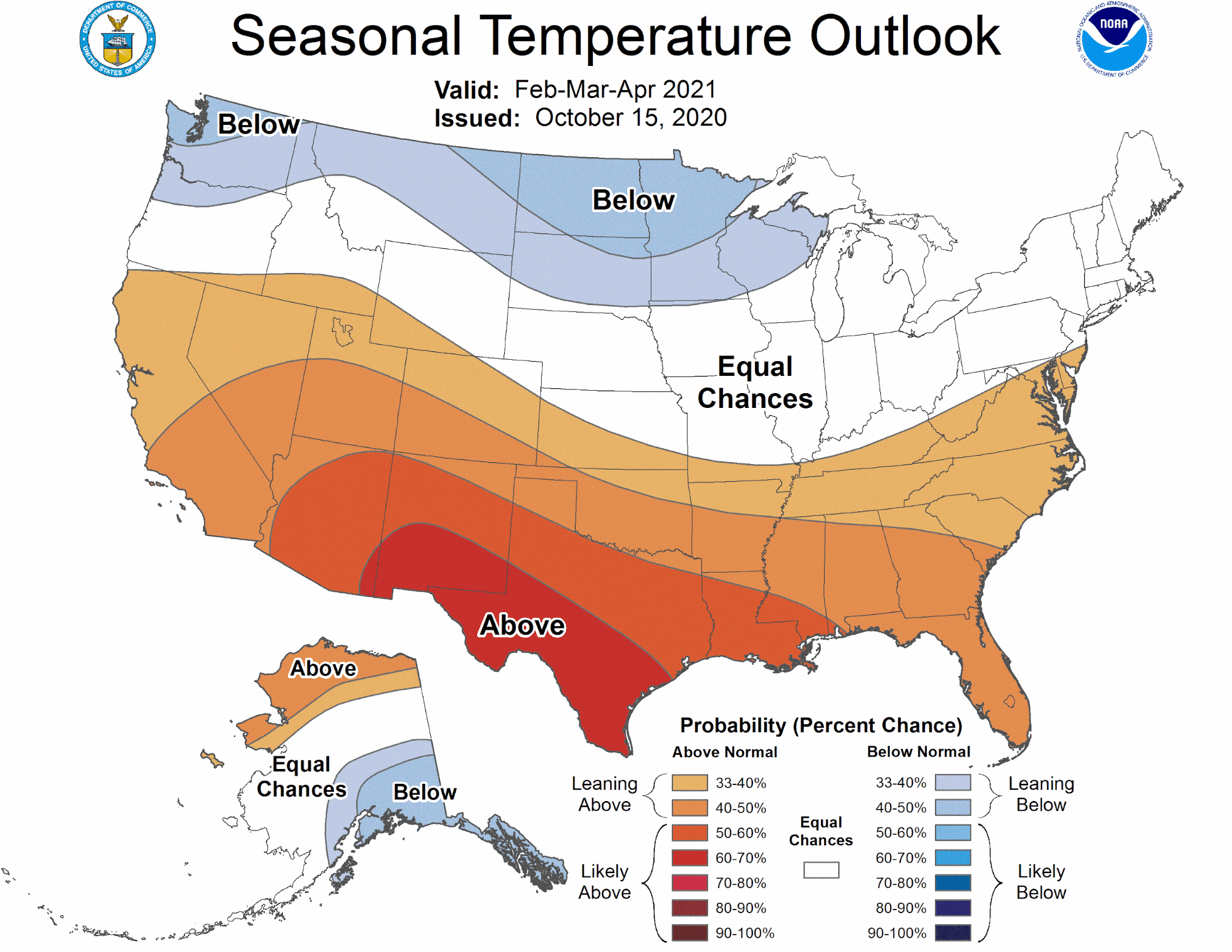
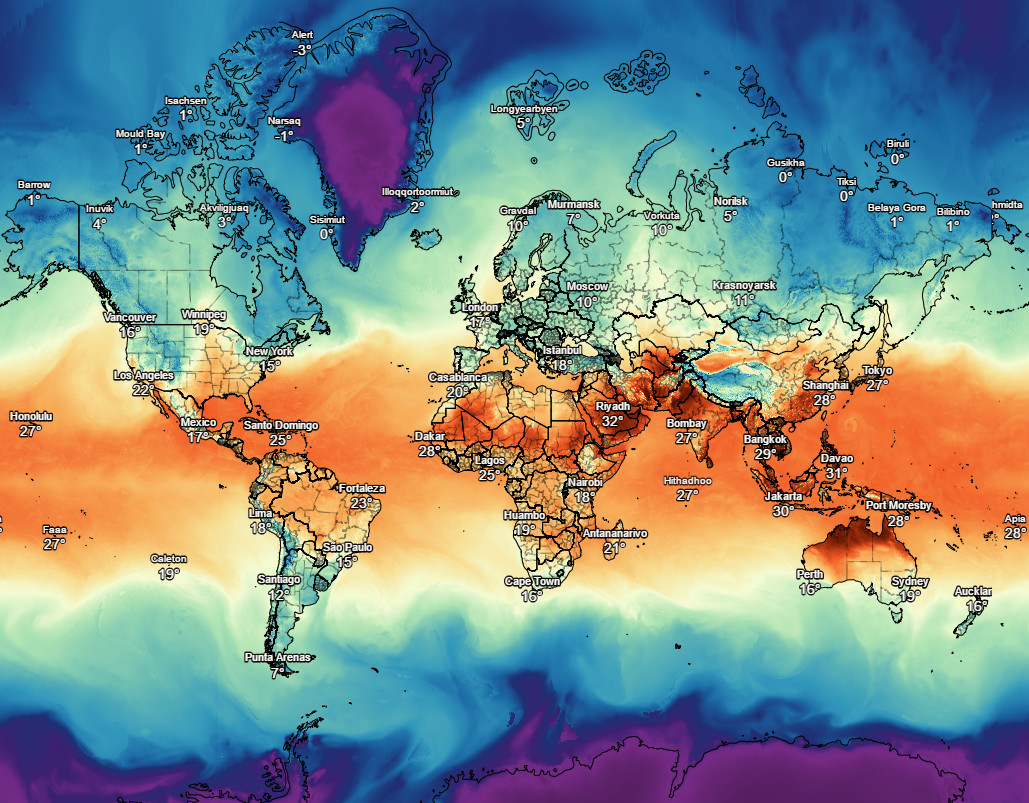

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World’s Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!