Unveiling the Power of Elastic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization and Analysis
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Elastic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization and Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Elastic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization and Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Elastic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization and Analysis
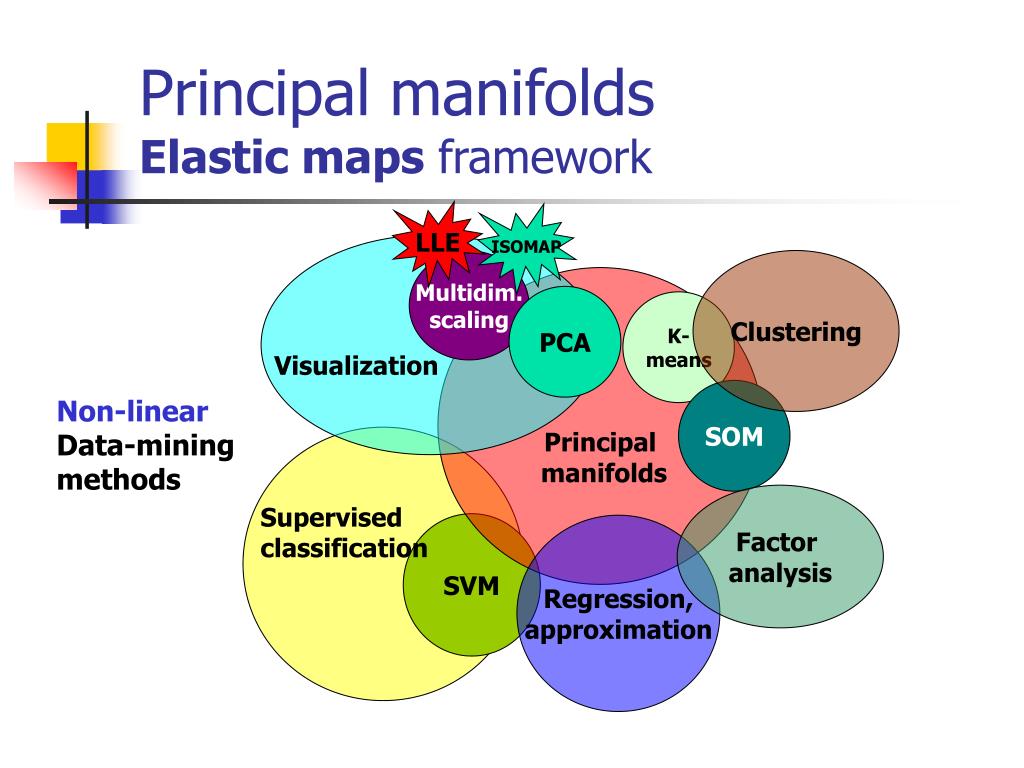
In the realm of data visualization and analysis, the ability to effectively represent complex relationships and patterns is paramount. While traditional static maps offer a valuable starting point, they often fall short in capturing the dynamic nature of real-world data. Enter elastic maps, a powerful tool that transcends the limitations of static representations, offering a flexible and interactive approach to data exploration.
Understanding the Essence of Elastic Maps
Elastic maps, also known as "rubber sheet maps" or "non-Euclidean maps," are a type of data visualization technique that utilizes a flexible, deformable canvas to represent data relationships. Unlike traditional maps, which adhere to fixed geographical coordinates, elastic maps allow for spatial distortions based on the underlying data. This flexibility enables the visualization of complex connections, patterns, and relationships that might otherwise be obscured by rigid geographical boundaries.
The Mechanics of Elastic Map Creation
The creation of an elastic map involves a series of steps that leverage computational algorithms to transform data into a visually compelling representation. The process typically involves:
-
Data Preparation: The initial step involves preparing the data by identifying relevant variables and relationships. This may include cleaning, transforming, and aggregating data to ensure consistency and relevance.
-
Distance Metric Selection: Choosing an appropriate distance metric is crucial for defining how data points are related and how the map will be deformed. Common distance metrics include Euclidean distance, Manhattan distance, and correlation distance, each emphasizing different aspects of data relationships.
-
Algorithm Application: A specific algorithm, such as multidimensional scaling (MDS) or Sammon mapping, is applied to the data based on the chosen distance metric. These algorithms aim to preserve the relationships between data points while minimizing distortions in the resulting map.
-
Visualization and Interpretation: The final step involves visualizing the resulting map and interpreting the spatial relationships represented. The map’s distortions provide insights into data clustering, outliers, and the relative importance of different variables.
Benefits of Utilizing Elastic Maps
The flexibility and adaptability of elastic maps offer a myriad of benefits for data analysis and visualization, including:
-
Enhanced Data Exploration: By allowing for spatial distortions, elastic maps enable users to discover hidden patterns and relationships that might be missed in traditional static representations. This interactive nature fosters a deeper understanding of the data and encourages exploration of different perspectives.
-
Improved Visualization of Complex Relationships: Elastic maps excel at visualizing complex data sets with multiple variables and intricate relationships. The ability to represent these relationships in a spatial context enhances comprehension and facilitates communication of insights.
-
Identification of Outliers and Clusters: The distortions in elastic maps highlight outliers and clusters within the data, providing valuable insights into data distribution and potential anomalies. This information can be crucial for identifying trends, making predictions, and understanding the underlying structure of the data.
-
Increased Data Accessibility: Elastic maps offer a visually intuitive and accessible way to present complex data to a wider audience, including those without specialized technical knowledge. This democratization of data insights fosters collaboration and informed decision-making.
Applications of Elastic Maps Across Diverse Fields
The versatility of elastic maps extends across various fields, providing valuable insights and aiding in decision-making processes. Some notable applications include:
-
Social Sciences: Elastic maps can be used to visualize social networks, analyzing relationships between individuals and groups, identifying influential nodes, and understanding the flow of information.
-
Business Analytics: Businesses can leverage elastic maps to analyze customer segmentation, market trends, and competitor analysis. The visualization of these relationships can inform strategic decision-making and optimize business processes.
-
Healthcare: In healthcare, elastic maps can be used to visualize patient data, identifying clusters of individuals with similar characteristics, understanding disease spread patterns, and optimizing resource allocation.
-
Environmental Science: Elastic maps are useful for visualizing environmental data, analyzing pollution patterns, understanding the impact of climate change, and monitoring ecological changes.
-
Genetics and Genomics: In the field of genomics, elastic maps can be used to analyze gene expression data, identify genes associated with specific diseases, and understand the complex interactions within the genome.
Addressing Common Questions About Elastic Maps
Q: What are the limitations of elastic maps?
A: While powerful, elastic maps have certain limitations. They can be challenging to interpret for complex datasets with numerous variables, and the distortions can sometimes obscure important details. Additionally, the choice of distance metric and algorithm can significantly impact the resulting map, requiring careful consideration and selection.
Q: How do I choose the right distance metric for my data?
A: The choice of distance metric depends on the nature of the data and the relationships you want to emphasize. Euclidean distance is suitable for measuring spatial distances, while Manhattan distance focuses on differences in absolute values. Correlation distance is useful for analyzing relationships between variables.
Q: What are some software tools for creating elastic maps?
A: Various software tools can be used to create elastic maps, including:
-
R: A statistical programming language with extensive packages for data visualization and analysis, including elastic map creation.
-
Python: A versatile programming language with libraries like Scikit-learn and Matplotlib for creating elastic maps.
-
Gephi: A free and open-source software specifically designed for network visualization and analysis, including elastic map capabilities.
-
Tableau: A powerful data visualization platform offering features for creating interactive elastic maps.
Tips for Effective Elastic Map Creation and Interpretation
-
Start with a Clear Objective: Before creating an elastic map, define the specific questions you want to answer and the relationships you aim to explore.
-
Choose the Right Distance Metric: Carefully select a distance metric that aligns with the nature of your data and the relationships you want to emphasize.
-
Experiment with Different Algorithms: Explore different algorithms and their parameters to find the best fit for your data and visualization goals.
-
Interpret the Distortions: Pay close attention to the distortions in the elastic map, as they reveal important insights into data clustering, outliers, and the relative importance of different variables.
-
Use Color and Labeling Effectively: Employ color and labeling techniques to enhance visual clarity and communication of insights.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Flexibility and Insight
Elastic maps offer a powerful and versatile approach to data visualization and analysis, surpassing the limitations of static representations by embracing flexibility and interactivity. By leveraging the power of spatial distortions, these maps enable the exploration of complex relationships, the identification of hidden patterns, and the communication of insights to a wider audience. As data complexity continues to increase, elastic maps will play an increasingly vital role in unlocking the potential of data and informing decision-making across diverse fields.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Elastic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization and Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!