Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Dual Axis Maps
- 3.2 Key Benefits of Dual Axis Maps
- 3.3 Practical Applications of Dual Axis Maps
- 3.4 Steps to Create a Dual Axis Map in Tableau
- 3.5 FAQs about Dual Axis Maps in Tableau
- 3.6 Tips for Creating Effective Dual Axis Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
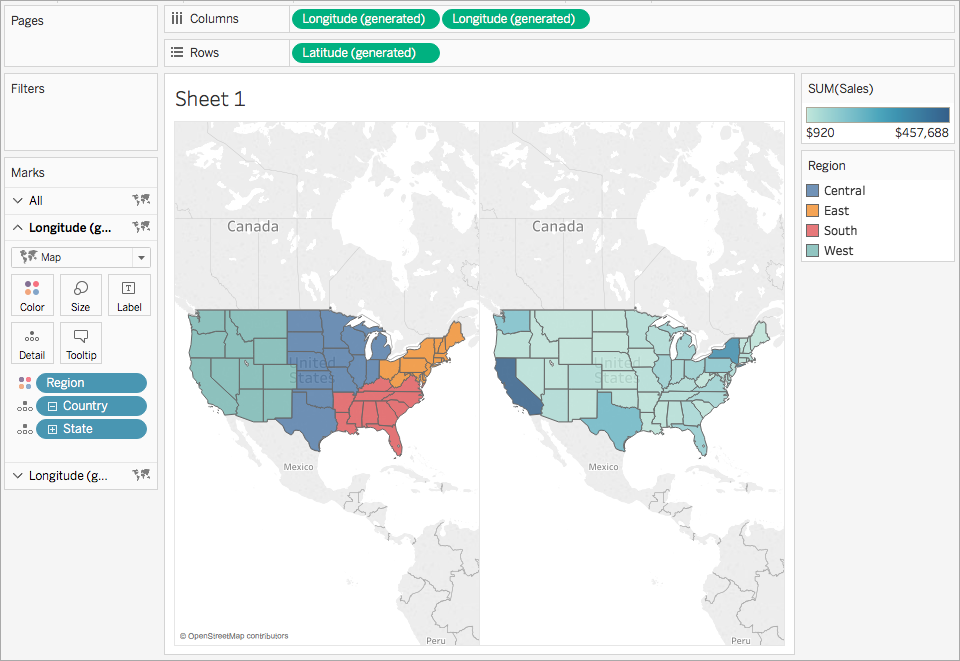
Tableau, a leading data visualization platform, offers a powerful suite of tools for creating insightful and engaging dashboards. Among these, dual axis maps stand out as a particularly versatile and informative visualization technique. This guide delves into the intricacies of dual axis maps in Tableau, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and potential applications.
Understanding the Essence of Dual Axis Maps
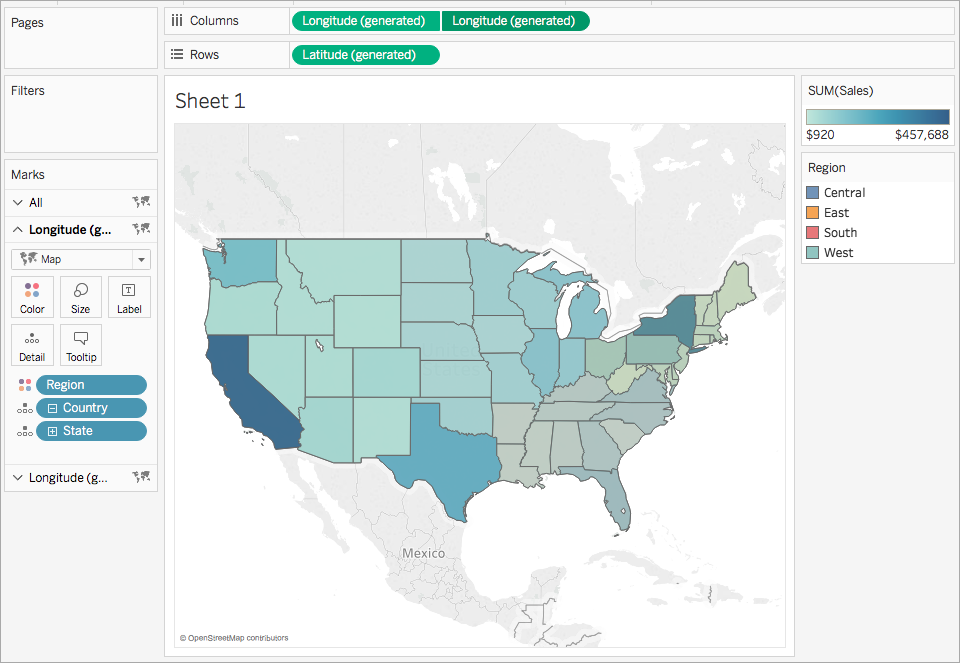
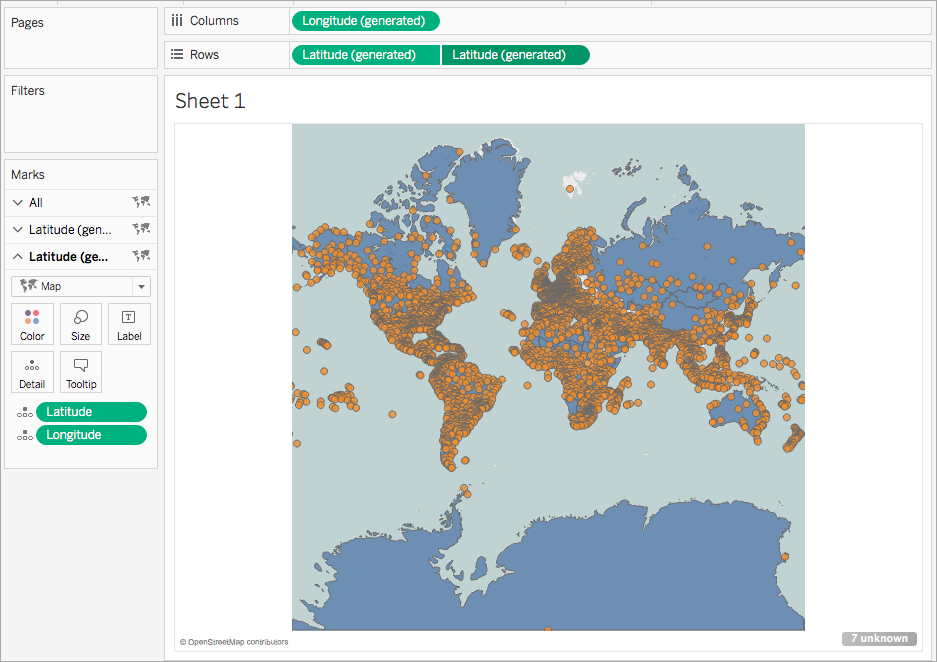
Dual axis maps, as the name suggests, utilize two separate axes to represent two distinct datasets on a single map. Each axis is linked to a specific data dimension, allowing for the simultaneous display of two different data sets on a geographical backdrop. This layered approach enables users to visualize relationships, trends, and comparisons between different data points within a geographical context.
Key Benefits of Dual Axis Maps
The power of dual axis maps lies in their ability to offer a multifaceted view of data, revealing insights that might otherwise be hidden. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Contextual Understanding: By overlaying two datasets on a map, dual axis maps provide a clear visual representation of how data points relate to each other geographically. This contextual understanding is crucial for identifying spatial patterns, correlations, and potential trends.
- Comparative Analysis: Dual axis maps facilitate direct comparisons between two different datasets. For instance, one axis could display sales figures, while the other shows customer demographics. This comparison can reveal valuable insights into factors influencing sales performance across different geographical regions.
- Trend Identification: By visualizing data over time, dual axis maps can highlight evolving trends and patterns. For example, one axis could represent population growth, while the other displays crime rates, enabling analysis of potential correlations between these factors across different regions.
- Interactive Exploration: Tableau’s interactive features allow users to explore data in detail. Users can zoom in on specific regions, filter data based on various criteria, and interact with the map to gain deeper insights.
- Effective Communication: Dual axis maps provide a visually compelling way to communicate complex data to a wider audience. Their intuitive nature makes it easy for users to understand the relationships between data points and draw meaningful conclusions.
Practical Applications of Dual Axis Maps
The versatility of dual axis maps makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Some common use cases include:
- Sales and Marketing: Analyzing sales performance by region, identifying customer demographics, and understanding market trends.
- Real Estate: Visualizing property prices, crime rates, and school district boundaries to understand real estate market dynamics.
- Healthcare: Mapping disease outbreaks, identifying healthcare access disparities, and visualizing patient demographics.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing air quality, mapping pollution levels, and visualizing deforestation patterns.
- Finance: Understanding stock market trends, identifying investment opportunities, and analyzing financial performance across different regions.
Steps to Create a Dual Axis Map in Tableau
Creating a dual axis map in Tableau is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Connect to Data: Begin by connecting your data source to Tableau. This can be a spreadsheet, database, or any other data source compatible with Tableau.
- Create Map: Drag the geographical dimension (e.g., state, city, county) to the "Rows" shelf. Tableau will automatically recognize the geographical data and create a map.
- Add First Data Set: Drag the first data dimension (e.g., sales, population) to the "Columns" shelf. This will display the first dataset on the map.
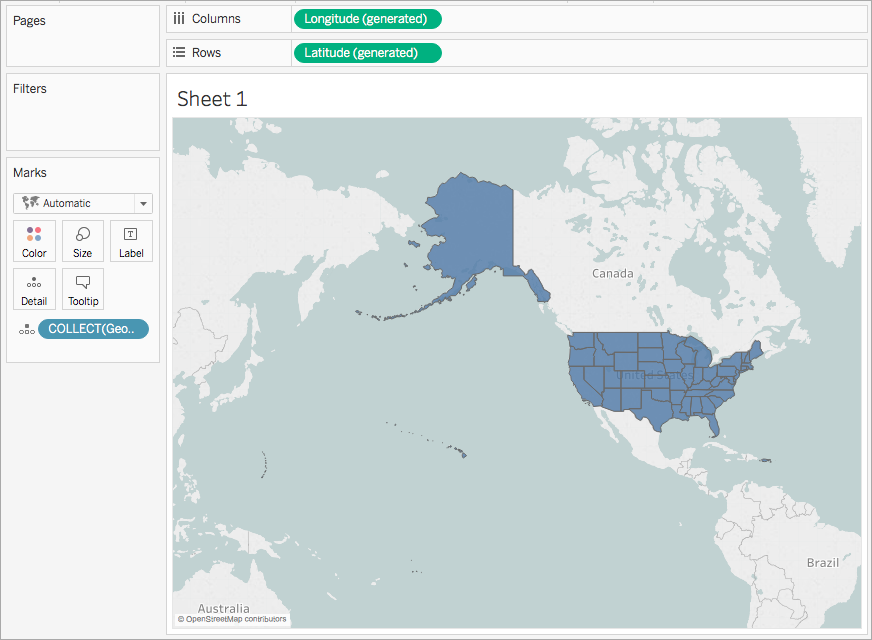
- Add Second Data Set: Right-click on the existing axis and select "Dual Axis." Then, drag the second data dimension to the "Columns" shelf on the newly created axis. This will overlay the second dataset on the map.
- Customize Appearance: Adjust the map’s appearance by changing colors, shapes, sizes, and labels to enhance visual clarity and communication.
- Add Interactions: Utilize Tableau’s interactive features to allow users to filter data, zoom in on specific regions, and explore the map in detail.
FAQs about Dual Axis Maps in Tableau
Q1: What types of data can be visualized on a dual axis map?
A: Dual axis maps can visualize any data that can be mapped to a geographical location. This includes numerical data (e.g., sales, population, crime rates) and categorical data (e.g., customer demographics, product categories).
Q2: How do I choose the appropriate data for each axis?
A: The choice of data for each axis depends on the specific insights you are trying to uncover. Consider the relationship between the datasets and the questions you are seeking to answer.
Q3: Can I use multiple data sets on a single dual axis map?
A: While Tableau allows for two axes, it’s generally recommended to focus on two key datasets to avoid visual clutter. However, you can use color or size variations within each dataset to represent additional dimensions.
Q4: How can I ensure clarity and readability in a dual axis map?
A: Use distinct colors, shapes, and sizes for each dataset to avoid confusion. Keep the map’s design clean and uncluttered. Consider using legends and tooltips to provide additional information.
Q5: Can I use dual axis maps for dynamic data?
A: Yes, Tableau allows you to create interactive dual axis maps that update in real-time. This enables you to explore data trends and patterns as they evolve.
Tips for Creating Effective Dual Axis Maps
- Choose Relevant Datasets: Select data that is relevant to the insights you wish to communicate.
- Maintain Data Balance: Ensure that the data scales on both axes are balanced to avoid one dataset overshadowing the other.
- Use Color Effectively: Choose distinct colors for each dataset to enhance visual clarity.
- Consider Map Projection: Select a map projection that accurately represents the geographical area being visualized.
- Test and Refine: Experiment with different visualizations and refine the map’s design to ensure optimal communication of insights.
Conclusion
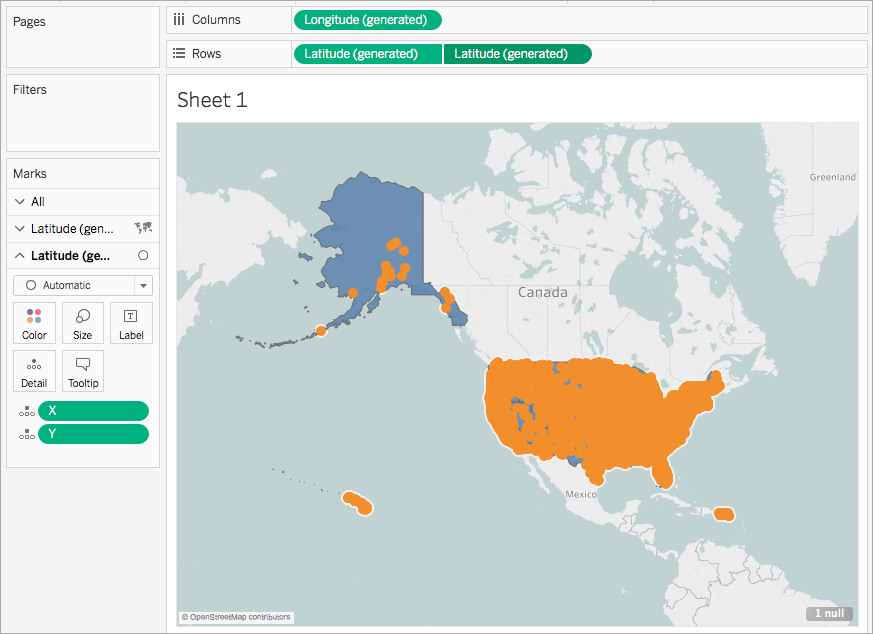
Dual axis maps in Tableau offer a powerful and versatile visualization technique for revealing insightful relationships and trends within geographical contexts. By leveraging the combined power of two datasets, dual axis maps provide a multifaceted view of data, enabling users to explore complex relationships, identify patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions. As a user-friendly and highly interactive tool, Tableau’s dual axis maps empower data analysts, researchers, and decision-makers to gain a deeper understanding of their data and make informed decisions based on visual insights.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Dual Axis Maps in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!