Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map
Related Articles: Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map
- 3.1 A Visual Representation of Iceland’s Geological History
- 3.2 Benefits and Applications of the Icelandic Geologic Map
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions about the Icelandic Geologic Map
- 3.4 Tips for Utilizing the Icelandic Geologic Map
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map
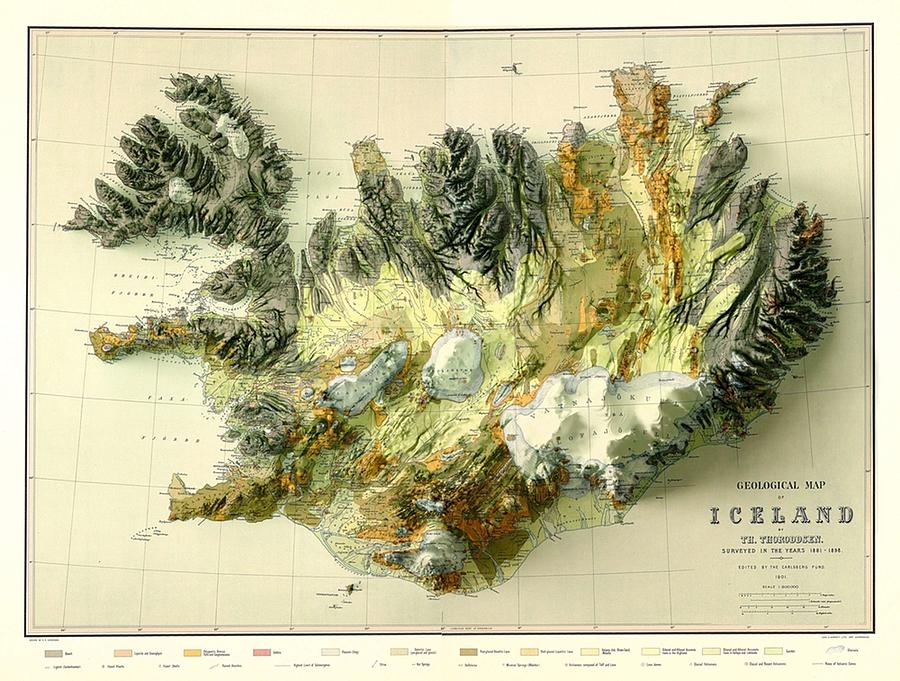
Iceland, the "Land of Fire and Ice," is a geological marvel, boasting a landscape sculpted by volcanic activity, glaciers, and tectonic forces. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its geological formations is crucial for various disciplines, from resource management and disaster preparedness to tourism and scientific research. This article delves into the significance and utility of the Icelandic geologic map, providing a comprehensive overview of its key features and applications.
A Visual Representation of Iceland’s Geological History
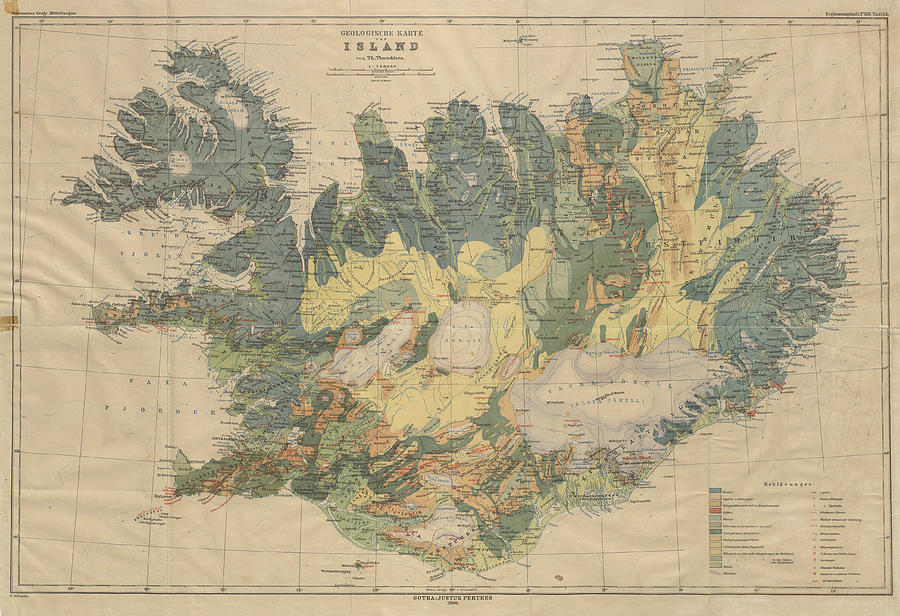
The Icelandic geologic map serves as a visual representation of the country’s geological history, depicting the distribution and characteristics of various rock types, geological formations, and structures. It provides a detailed snapshot of the island’s complex geological evolution, encompassing:
- Volcanic Activity: Iceland’s landscape is dominated by volcanic activity, with numerous volcanoes, lava fields, and geothermal areas. The map clearly distinguishes between different volcanic zones, including the active volcanic zones along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the central volcanic zone, and the northern volcanic zone. It also highlights the distribution of various volcanic rocks, such as basalt, rhyolite, and andesite, providing insights into the composition and history of volcanic eruptions.
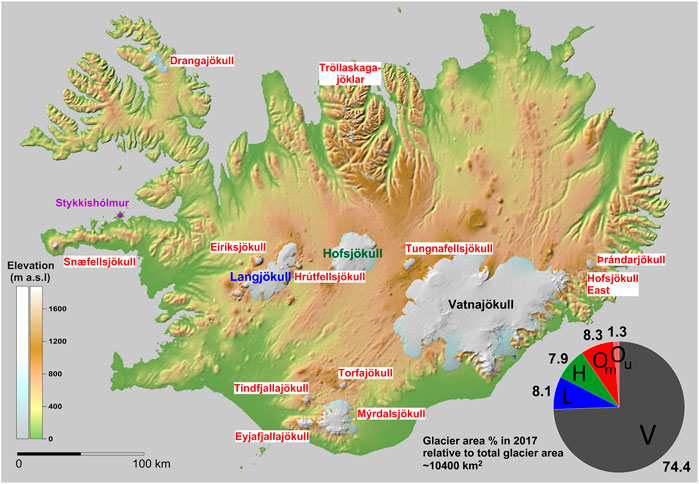
- Glacial Erosion: Iceland’s glaciers have played a significant role in shaping its landscape, leaving behind vast glacial valleys, fjords, and moraines. The geologic map effectively showcases the extent of glacial erosion, highlighting the distribution of glacial deposits, such as till and outwash plains, and the presence of glacial features like eskers and drumlins.
- Tectonic Forces: Iceland sits atop the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates are pulling apart. This tectonic activity has resulted in the formation of a rift valley, characterized by numerous faults and fissures. The geologic map clearly depicts the location and orientation of these faults, providing insights into the ongoing tectonic processes shaping the island.
- Geothermal Activity: Iceland is renowned for its abundant geothermal resources, fueled by the volcanic activity and tectonic forces. The geologic map indicates the distribution of geothermal areas, showcasing the location of hot springs, geysers, and geothermal power plants.
Benefits and Applications of the Icelandic Geologic Map
The Icelandic geologic map is an invaluable tool for various sectors, offering a wealth of information and insights:
- Resource Management: The map aids in identifying and managing natural resources, including geothermal energy, mineral deposits, and groundwater resources. By understanding the distribution of different rock types and geological formations, resource exploration and extraction can be optimized.
- Disaster Preparedness: The map plays a crucial role in mitigating natural hazards, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and floods. Identifying areas prone to volcanic activity, seismic events, or landslides allows for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Infrastructure Development: The map provides essential information for planning and developing infrastructure projects, ensuring that construction activities are carried out in areas with minimal geological risks. It helps identify suitable locations for roads, bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure elements, minimizing potential geological hazards.
- Tourism and Recreation: The map is a valuable resource for promoting tourism and recreational activities. Understanding the geological features of the island, including volcanoes, glaciers, and waterfalls, enables the development of sustainable tourism practices and the creation of engaging and informative visitor experiences.
- Scientific Research: The geologic map serves as a foundational tool for scientific research, facilitating investigations into various geological processes, including plate tectonics, volcanism, and glacial erosion. It provides a detailed framework for studying the evolution of the island and understanding the underlying geological processes.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Icelandic Geologic Map
1. What is the scale of the Icelandic geologic map?
The Icelandic geologic map is available at various scales, depending on the level of detail required. The most commonly used scale is 1:500,000, providing a comprehensive overview of the island’s geology. However, more detailed maps at scales like 1:100,000 or even 1:25,000 are available for specific regions or areas of interest.
2. Where can I access the Icelandic geologic map?
The Icelandic Geologic Survey (ÍSOR) is the primary source for the Icelandic geologic map. Their website provides access to various digital and printed versions of the map, along with accompanying geological data and information. The map is also available through other online resources and geological databases.
3. Is the Icelandic geologic map updated regularly?
The Icelandic geologic map is constantly being updated and revised as new geological data becomes available. The Icelandic Geologic Survey actively conducts geological research and mapping projects, incorporating new findings and insights into the map.
4. What are the different geological units depicted on the Icelandic geologic map?
The Icelandic geologic map depicts a wide range of geological units, including:
- Volcanic Rocks: Basalt, rhyolite, andesite, tuff, and breccia.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Glacial deposits, fluvial deposits, and marine deposits.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Schists, gneisses, and amphibolites.
- Intrusive Rocks: Gabbro, diorite, and granite.
- Geological Structures: Faults, folds, and unconformities.
5. How does the Icelandic geologic map contribute to sustainable development?
The Icelandic geologic map plays a vital role in promoting sustainable development by:
- Identifying and managing natural resources: Ensuring responsible utilization of geothermal energy, mineral deposits, and groundwater resources.
- Mitigating natural hazards: Preventing potential risks associated with volcanic activity, earthquakes, and floods.
- Planning and developing infrastructure: Minimizing geological risks during construction projects, ensuring long-term sustainability of infrastructure.
- Promoting sustainable tourism: Facilitating responsible tourism practices and minimizing environmental impact.
Tips for Utilizing the Icelandic Geologic Map
- Understand the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols, colors, and abbreviations used on the map to effectively interpret the geological information.
- Identify key geological features: Focus on understanding the distribution of volcanoes, glaciers, faults, and other significant geological features.
- Analyze the geological context: Consider the relationship between different geological units and their influence on the overall landscape.
- Use the map in conjunction with other data: Integrate the geologic map with other relevant data, such as topographic maps, satellite imagery, and geological reports, for a comprehensive understanding of the area.
- Consult with experts: Seek guidance from geologists or other experts for interpreting the map and applying its information to specific projects or research.
Conclusion
The Icelandic geologic map is a valuable resource for understanding the complex geological history and characteristics of this unique island nation. Its applications extend across various disciplines, including resource management, disaster preparedness, infrastructure development, tourism, and scientific research. By providing a comprehensive visual representation of Iceland’s geological tapestry, the map serves as a foundation for informed decision-making and sustainable development, ensuring the preservation of this remarkable natural heritage for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Iceland’s Geological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Icelandic Geologic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!