Unpacking South Korea’s Population Density: A Visual Guide to a Nation in Transition
Related Articles: Unpacking South Korea’s Population Density: A Visual Guide to a Nation in Transition
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking South Korea’s Population Density: A Visual Guide to a Nation in Transition. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking South Korea’s Population Density: A Visual Guide to a Nation in Transition

South Korea, a nation known for its technological advancements and vibrant culture, is also characterized by a striking population distribution. Understanding the nuances of its population density is crucial for comprehending the country’s social, economic, and environmental landscape. This article delves into the complexities of South Korea’s population density map, exploring its historical evolution, current trends, and the implications for the nation’s future.
A Nation of Contrasts: Understanding South Korea’s Population Density
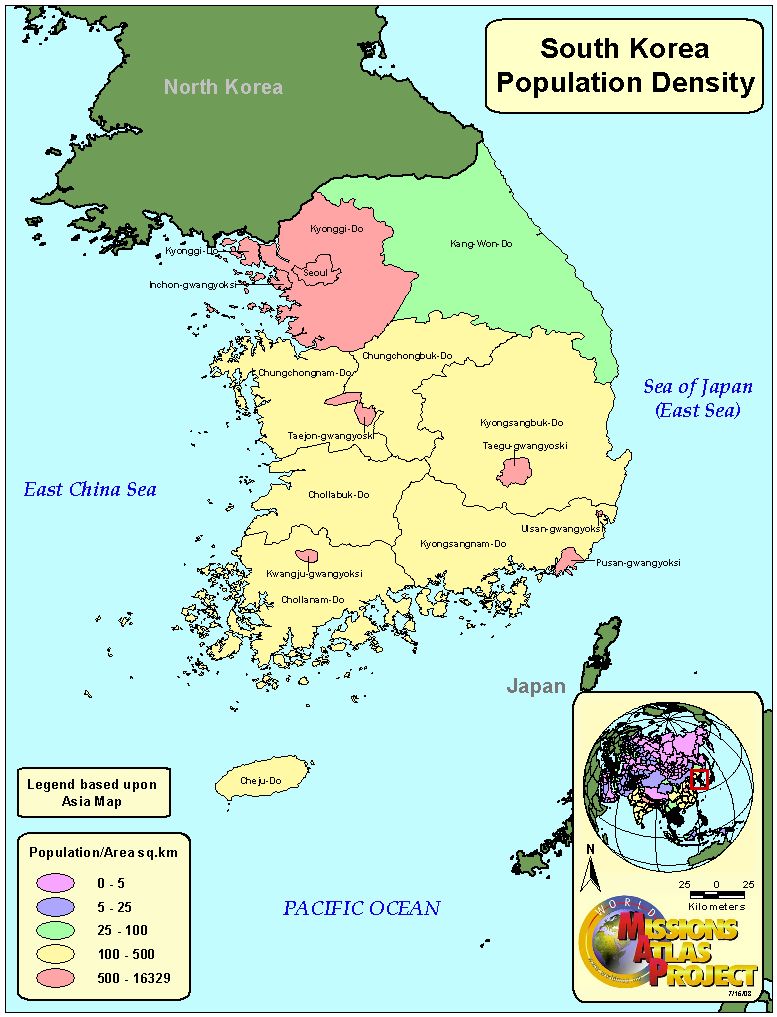
South Korea, despite its relatively small size, boasts a population exceeding 51 million, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world. However, population density is not uniformly distributed across the peninsula. The population density map reveals a stark contrast between the bustling urban centers and the sparsely populated rural areas.
The Urban Core: A Magnet for Population Growth
The map vividly illustrates the concentration of population in major metropolitan areas like Seoul, Busan, Daegu, Incheon, and Gwangju. These urban centers serve as economic hubs, attracting individuals seeking employment opportunities, educational institutions, and a vibrant cultural scene. The result is a densely populated core with a high concentration of infrastructure, businesses, and services.
Rural Outmigration: A Persistent Trend
In contrast to the urban centers, rural areas experience significantly lower population densities. This disparity is largely attributed to a persistent trend of outmigration from rural regions. Factors contributing to this phenomenon include limited job opportunities, a decline in traditional agricultural practices, and the allure of urban amenities.
The Impact of Population Density: Social, Economic, and Environmental Considerations
The uneven distribution of population in South Korea has profound implications for the nation’s social, economic, and environmental landscape.
Social Implications:
- Urban Sprawl and Housing Pressures: High population densities in urban centers create challenges related to housing affordability, infrastructure strain, and the potential for social inequalities.
- Aging Population and Labor Shortages: Rural outmigration contributes to an aging population in these areas, creating a shortage of young workers and placing strain on social services.
- Cultural and Social Dynamics: The concentration of population in urban areas fosters diverse cultural interactions, while rural areas grapple with maintaining traditional values and fostering community cohesion.
Economic Implications:
- Economic Concentration and Regional Disparities: Urban centers dominate economic activity, leading to regional disparities in wealth and development.
- Infrastructure Investment and Sustainability: Meeting the needs of densely populated areas requires significant investment in infrastructure, transportation, and public services.
- Competition for Resources: High population densities can strain resources, leading to competition for housing, employment, and essential services.
Environmental Implications:
- Urban Pollution and Environmental Strain: Densely populated urban areas face challenges related to air and water pollution, waste management, and the preservation of green spaces.
- Deforestation and Land Use Change: Rural outmigration can lead to land abandonment, potentially impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Climate Change Vulnerability: Coastal areas with high population densities are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Historical Perspective: Understanding the Evolution of Population Density
The current population density map is a product of historical and socio-economic factors.
- Post-Korean War Growth: Following the Korean War, South Korea experienced rapid economic growth and urbanization, leading to a significant shift in population distribution.
- Industrialization and Development: The rise of industrial centers in major cities attracted workers from rural areas, further contributing to urban population growth.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as infrastructure development and investment in urban centers, have influenced the distribution of population.
Future Trends: A Nation in Transition
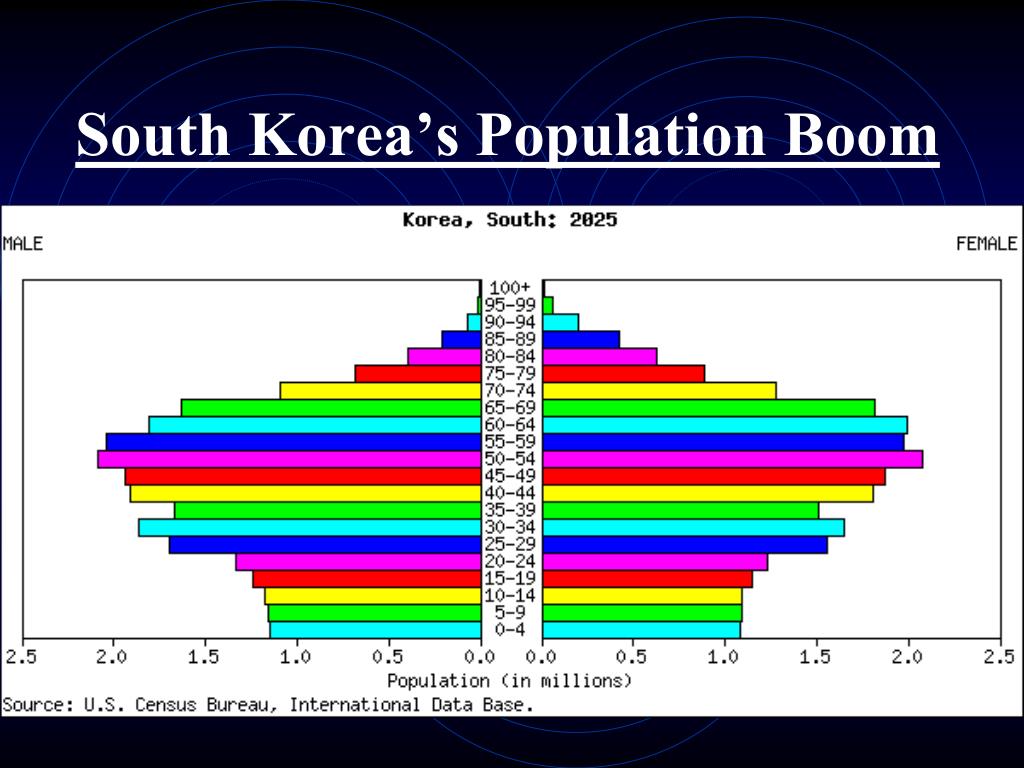
South Korea is experiencing demographic shifts, with a declining birth rate and an aging population. These trends are likely to impact the nation’s population density map in the coming decades.
- Urban Growth and Decentralization: While urban centers are expected to continue growing, government initiatives promoting regional development and decentralization may lead to a more balanced population distribution.
- Aging Population and Labor Shortages: An aging population could lead to a decline in the overall population density, particularly in rural areas.
- Sustainable Development and Urban Planning: Sustainable urban planning strategies will be crucial for managing population growth and mitigating environmental impacts.
FAQs about South Korea’s Population Density Map
Q: What is the average population density of South Korea?
A: The average population density of South Korea is approximately 528 people per square kilometer.
Q: What are the most densely populated areas in South Korea?
A: The most densely populated areas are the major metropolitan cities, including Seoul, Busan, Daegu, Incheon, and Gwangju.
Q: What are the factors contributing to the low population density in rural areas?
A: Factors contributing to low population density in rural areas include limited job opportunities, a decline in traditional agricultural practices, and the allure of urban amenities.
Q: How does South Korea’s population density compare to other countries?
A: South Korea is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with a higher density than countries like Japan, China, and India.
Q: What are the implications of South Korea’s aging population for population density?
A: An aging population could lead to a decline in the overall population density, particularly in rural areas, as people move to urban centers for access to healthcare and services.
Tips for Utilizing South Korea’s Population Density Map
- Understanding Regional Differences: The population density map provides valuable insights into regional differences in population distribution, economic activity, and social dynamics.
- Planning and Development: Urban planners and policymakers can utilize the map to inform infrastructure development, resource allocation, and social services planning.
- Environmental Management: The map helps identify areas with high population densities that require careful environmental management, such as pollution control and waste management.
- Tourism and Cultural Understanding: The population density map can guide tourists to areas with different cultural experiences and population densities.
- Research and Analysis: Researchers can use the map to analyze the relationship between population density and various social, economic, and environmental indicators.
Conclusion
South Korea’s population density map is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s social, economic, and environmental landscape. The map reveals a nation of contrasts, with densely populated urban centers and sparsely populated rural areas. Understanding the historical factors that have shaped this distribution and the future trends that will impact it is crucial for policymakers, urban planners, and anyone seeking to understand the complexities of this dynamic nation. By analyzing the population density map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities facing South Korea in the 21st century.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking South Korea’s Population Density: A Visual Guide to a Nation in Transition. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!