Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Look at Hydraulic Fracturing and its Geographic Distribution
Related Articles: Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Look at Hydraulic Fracturing and its Geographic Distribution
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Look at Hydraulic Fracturing and its Geographic Distribution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Look at Hydraulic Fracturing and its Geographic Distribution
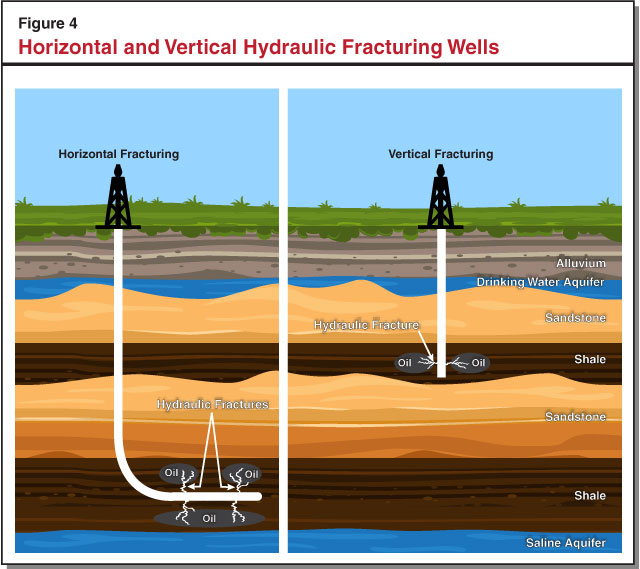
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, is a controversial but increasingly prevalent method of extracting natural gas and oil from shale formations. While California’s energy landscape is largely defined by its renewable energy sources, the state also has significant reserves of shale gas, particularly in the Central Valley and the San Joaquin Valley. Understanding the geographic distribution of fracking activity within California is crucial for comprehending its impact on the environment, economy, and public health.
The Geographical Landscape of Fracking in California
California’s fracking landscape is characterized by a complex interplay of geological formations, environmental concerns, and regulatory frameworks. The state’s shale gas deposits are concentrated in the following areas:
-
Central Valley: The Central Valley, known for its agricultural abundance, also harbors significant shale gas deposits. The Monterey Shale formation, extending from Monterey County to Kern County, is a key target for fracking operations. This region’s agricultural significance, coupled with its potential for natural gas extraction, raises concerns about the potential impact on groundwater resources and agricultural productivity.
-
San Joaquin Valley: The San Joaquin Valley, a vast agricultural region, also holds substantial shale gas reserves. The Monterey Shale formation extends into this region, making it another focal point for fracking activity. Similar to the Central Valley, concerns about groundwater contamination and potential damage to agricultural land are prominent in the San Joaquin Valley.
-
Other Areas: While the Central and San Joaquin Valleys are the primary areas for fracking, smaller shale gas deposits exist in other parts of California, including the Los Angeles Basin, the Ventura Basin, and the Sacramento Valley. These areas, while less prominent in terms of fracking activity, still present potential for future development.
A Visual Representation: Mapping California’s Fracking Activity
Visualizing the geographic distribution of fracking activity in California is essential for understanding its impact on the state’s environment, economy, and public health. Several resources provide interactive maps and data visualization tools, allowing users to explore the spatial patterns of fracking operations. These resources include:
-
California Department of Conservation, Division of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR): DOGGR provides an online map that tracks fracking permits and well locations, offering a comprehensive overview of fracking activity across the state.
-
FrackTracker Alliance: This non-profit organization maintains a map that tracks fracking activity, including well locations, permits, and environmental incidents, providing a citizen-driven perspective on fracking in California.
-
Environmental Defense Fund (EDF): EDF, a non-profit environmental advocacy group, offers a map that highlights areas with high potential for fracking, allowing users to visualize the potential impact of fracking on different regions.
Fracking’s Impact: A Multifaceted Perspective
The impact of fracking in California is multifaceted, encompassing environmental, economic, and public health considerations. Understanding these impacts is crucial for informed decision-making regarding fracking’s role in the state’s energy future.
Environmental Considerations:
-
Groundwater Contamination: Fracking involves injecting large volumes of water mixed with chemicals into the ground, raising concerns about potential contamination of groundwater resources. The chemicals used in fracking fluids can seep into aquifers, posing risks to drinking water supplies.
-
Air Quality: Fracking operations can release methane and other air pollutants, contributing to smog and greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of natural gas also releases carbon dioxide, a major contributor to climate change.
-
Seismic Activity: Fracking operations have been linked to induced seismicity, meaning they can trigger earthquakes. This is particularly relevant in California, a seismically active region.
-
Habitat Disruption: Fracking activities can disrupt natural habitats, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services. The clearing of land for fracking infrastructure can fragment wildlife corridors and disrupt ecological processes.
Economic Considerations:
-
Job Creation: Fracking operations create jobs in various sectors, including drilling, engineering, and transportation. These jobs can contribute to local economies, especially in rural areas.
-
Energy Security: Fracking can increase domestic energy production, reducing reliance on foreign imports and improving energy security. California’s reliance on imported natural gas makes fracking a potential source of domestic energy supply.
-
Tax Revenue: Fracking operations generate tax revenue for state and local governments, which can be used to fund public services and infrastructure projects.
Public Health Considerations:
-
Air Pollution: Air pollution from fracking operations can exacerbate respiratory problems and contribute to other health issues. The exposure to air pollutants can be particularly harmful for vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly.
-
Water Contamination: Contaminated drinking water from fracking operations can lead to various health problems, including gastrointestinal illnesses, skin irritation, and reproductive issues.
-
Noise Pollution: Fracking operations can generate significant noise pollution, disrupting communities and impacting sleep patterns. Noise pollution can also have negative effects on wildlife and ecosystems.
Navigating the Complexities of Fracking: FAQs
1. Is fracking legal in California?
Yes, fracking is legal in California, but it is subject to stringent regulations. The California Department of Conservation, Division of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR) oversees fracking operations and enforces regulations to minimize environmental impacts.
2. What are the main concerns about fracking in California?
The main concerns about fracking in California include potential groundwater contamination, air pollution, seismic activity, and habitat disruption. These concerns have led to ongoing debates and legal challenges regarding fracking practices in the state.
3. What are the potential benefits of fracking in California?
Fracking can create jobs, enhance energy security, and generate tax revenue. However, these benefits must be weighed against the potential environmental and public health risks associated with fracking operations.
4. How does California regulate fracking?
California has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for fracking, including requirements for well design, chemical disclosure, and environmental monitoring. The state’s regulatory framework aims to balance economic development with environmental protection.
5. What is the future of fracking in California?
The future of fracking in California remains uncertain. The state’s commitment to renewable energy and its stringent environmental regulations pose challenges for fracking operations. However, the potential economic benefits and the need for reliable energy sources continue to fuel the debate over fracking’s role in California’s energy future.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with Fracking in California
-
Stay Informed: Follow news and research on fracking in California. Reliable sources include the California Department of Conservation, DOGGR, environmental advocacy groups, and academic institutions.
-
Engage in Public Discourse: Participate in public hearings and community meetings related to fracking. Share your concerns and perspectives with policymakers and industry representatives.
-
Support Responsible Energy Policies: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and protect public health and the environment.
-
Consider Your Energy Consumption: Reduce your energy consumption by adopting energy-efficient practices, such as using public transportation, conserving water, and reducing waste.
Conclusion: A Complex and Evolving Landscape
Fracking in California presents a complex and evolving landscape, with significant implications for the state’s environment, economy, and public health. Balancing the potential benefits of fracking with its potential risks requires careful consideration, informed decision-making, and ongoing public engagement. As California continues to navigate its energy future, understanding the geographical distribution of fracking activity and its multifaceted impacts will remain crucial for shaping a sustainable and equitable energy future.

![]()



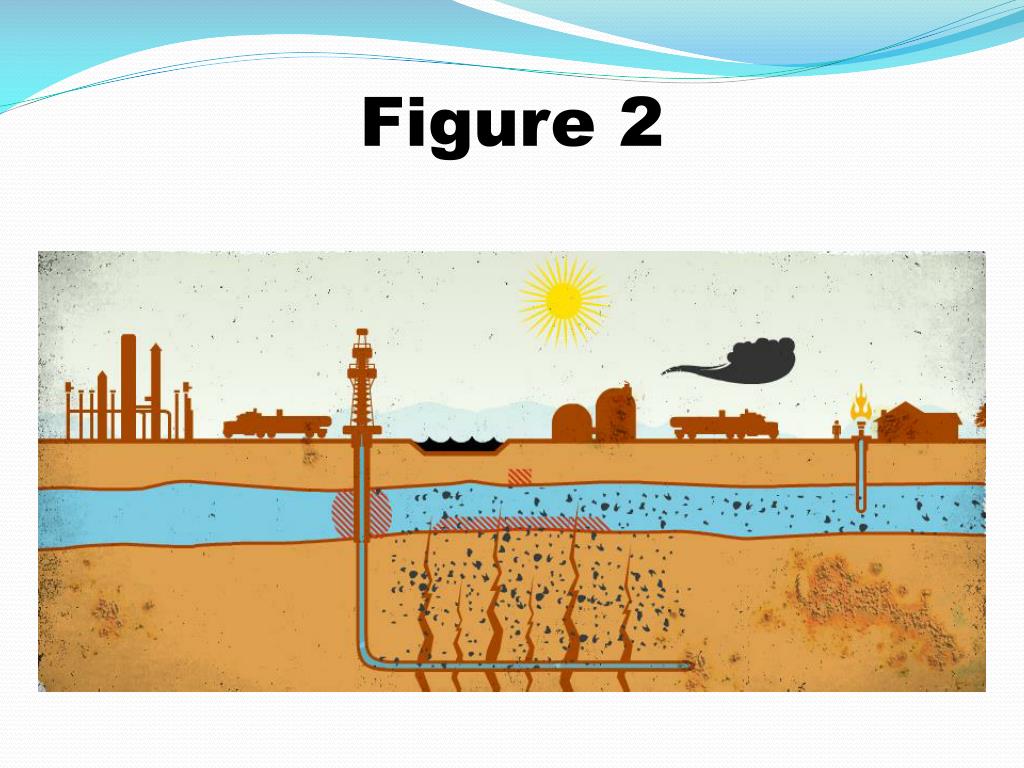


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Look at Hydraulic Fracturing and its Geographic Distribution. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!