Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Shaping the Landscape
Related Articles: Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Shaping the Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Shaping the Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Shaping the Landscape
The world is a tapestry of diverse terrain, from rolling hills to deep valleys. As human civilization expands, it often necessitates altering the natural landscape to accommodate infrastructure, housing, and other development needs. This process, known as earthwork, involves the careful manipulation of soil and rock, and a fundamental technique within this realm is cut and fill.
Cut and Fill: A Fundamental Concept
Cut and fill refers to the process of excavating earth from one area (cut) and transporting it to another area (fill) to modify the existing terrain. This technique is employed to create level surfaces for roads, buildings, and other structures, or to create slopes that facilitate drainage and stability.
Visualizing Cut and Fill on Maps
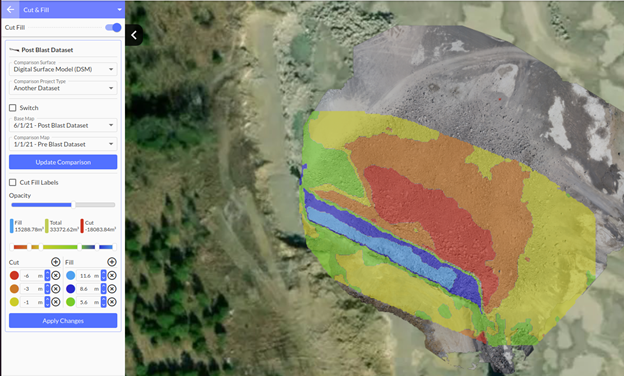
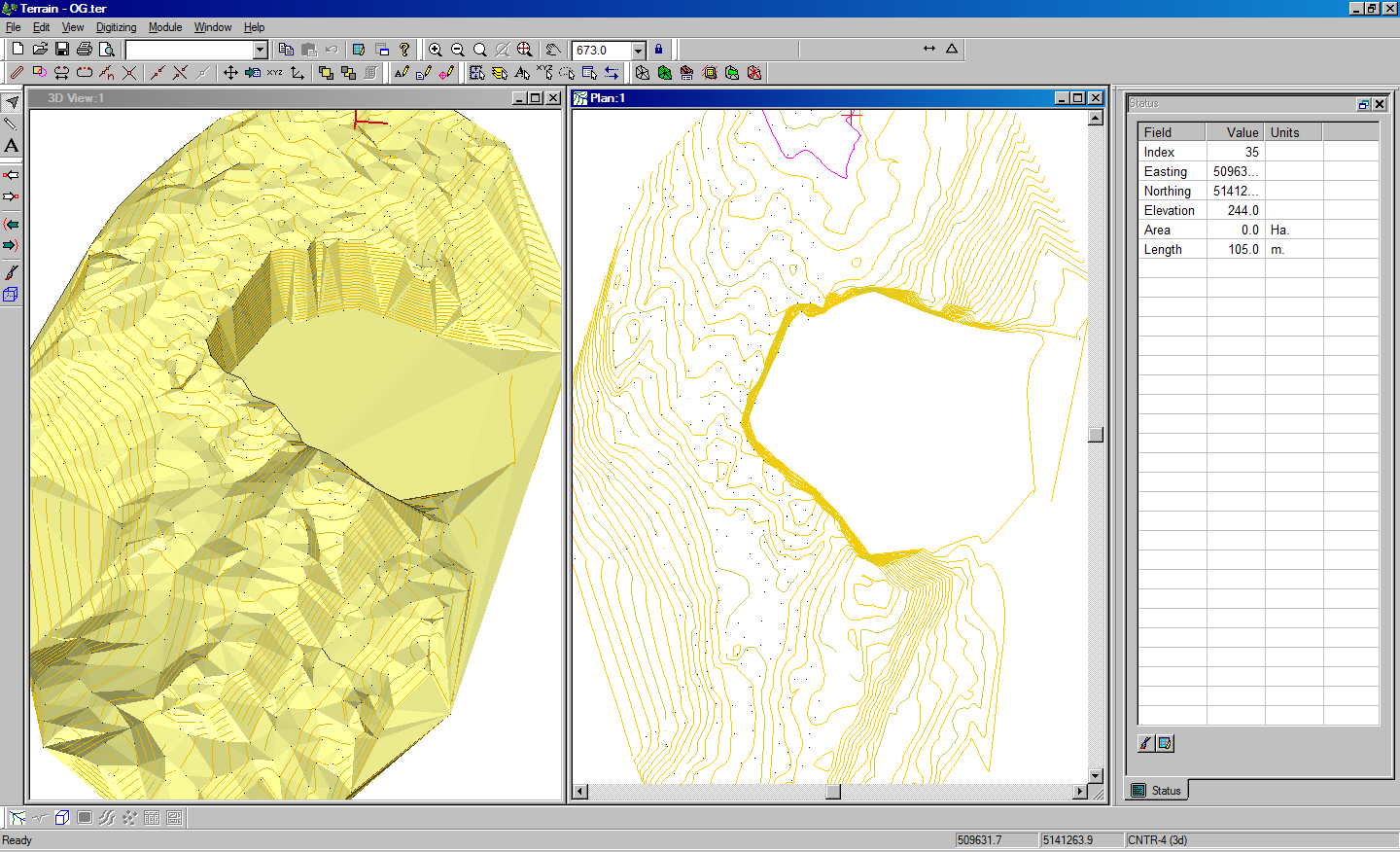
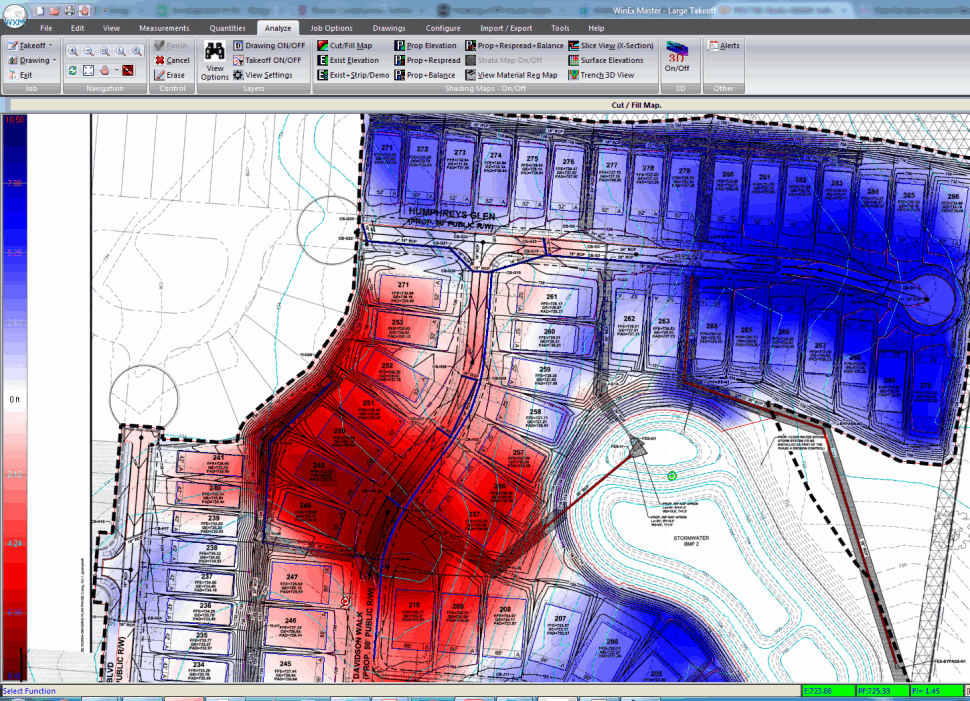
Maps play a crucial role in visualizing and understanding cut and fill operations. These maps, often referred to as topographic maps, depict the Earth’s surface with contour lines, which represent points of equal elevation. By examining these lines, engineers and planners can identify areas that need to be excavated (cut) and areas that require additional material (fill) to achieve the desired grade.
The Process of Cut and Fill
-
Site Survey and Design: The first step involves conducting a thorough site survey to gather data on existing terrain, soil conditions, and any potential obstacles. This information is then used to create a detailed plan that outlines the cut and fill operations.
-
Excavation (Cut): Excavation involves removing soil and rock from designated areas using various heavy equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and loaders. The excavated material is then transported to the fill areas.
-
Hauling and Placement (Fill): The excavated material is transported to the designated fill areas using trucks, dump trucks, or conveyor belts. The material is then carefully placed and compacted to ensure stability and prevent settling.
-
Compaction: Compaction is a crucial step in cut and fill operations. It involves using heavy rollers or other compaction equipment to compress the fill material, reducing voids and increasing its density. This process helps to ensure the stability of the fill and prevent future settling.
Benefits of Cut and Fill
-
Leveling the Landscape: Cut and fill allows for the creation of level surfaces for roads, buildings, and other structures, providing a stable foundation for construction.
-
Improving Drainage: By creating slopes and drainage channels, cut and fill can effectively manage water runoff, preventing erosion and flooding.
-
Creating Aesthetics: Cut and fill techniques can be used to create aesthetically pleasing landscapes, such as terraces, retaining walls, and sculpted slopes.
-
Optimizing Land Use: By altering the terrain, cut and fill enables the efficient use of land for various purposes, maximizing its potential.
Challenges and Considerations
-
Environmental Impact: Cut and fill operations can have significant environmental impacts, including soil erosion, habitat destruction, and potential pollution. Careful planning and mitigation measures are essential to minimize these impacts.
-
Cost and Time: Cut and fill operations can be expensive and time-consuming, particularly for large-scale projects.
-
Material Availability: The availability of suitable fill material can be a challenge, especially in areas with limited resources.
-
Safety: Cut and fill operations involve heavy equipment and hazardous materials, making safety a paramount concern.
FAQs about Cut and Fill on Maps
Q: How are cut and fill areas represented on maps?
A: Cut and fill areas are typically represented on maps using different colors or symbols to distinguish them from the existing terrain. For example, cut areas might be shown in blue or green, while fill areas might be represented in red or yellow.
Q: What are some common applications of cut and fill?
A: Cut and fill is widely used in various projects, including:
- Road Construction: Creating level surfaces for roads and highways.
- Building Construction: Preparing sites for buildings and other structures.
- Landscaping: Creating terraces, retaining walls, and sculpted slopes.
- Flood Control: Building levees and floodwalls to protect against flooding.
- Mining Operations: Creating access roads and processing areas for mining operations.
Q: How does cut and fill affect the surrounding environment?
A: Cut and fill operations can impact the surrounding environment in various ways:
- Soil Erosion: Excavation and fill placement can lead to soil erosion, particularly in areas with steep slopes.
- Habitat Destruction: Clearing land for cut and fill operations can destroy habitats for wildlife and plants.
- Water Pollution: Runoff from cut and fill sites can carry pollutants into nearby waterways.
- Noise and Dust: Cut and fill operations can generate significant noise and dust, which can be disruptive to nearby communities.
Tips for Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps
- Study Contour Lines: Pay close attention to the contour lines on topographic maps. These lines indicate changes in elevation and can help identify areas where cut and fill will be required.
- Identify Cut and Fill Areas: Look for areas on the map where the contour lines are spaced closely together, indicating steep slopes. These areas are likely to require cut and fill operations.
- Consider the Scale: The scale of the map is important for interpreting cut and fill operations. A larger-scale map will provide more detailed information about the terrain.
- Understand the Project’s Goals: Consider the purpose of the project and how cut and fill operations will contribute to achieving those goals.
Conclusion
Cut and fill is an essential technique in shaping the landscape for various development projects. Understanding the concepts of cut and fill, their representation on maps, and their potential impacts is crucial for successful planning and execution. By carefully considering the environmental, economic, and safety aspects of cut and fill operations, we can ensure that these projects are carried out responsibly and sustainably.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Cut and Fill on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Shaping the Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!