The Neo-Babylonian Empire: A Map of Revival and Power
Related Articles: The Neo-Babylonian Empire: A Map of Revival and Power
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Neo-Babylonian Empire: A Map of Revival and Power. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Neo-Babylonian Empire: A Map of Revival and Power
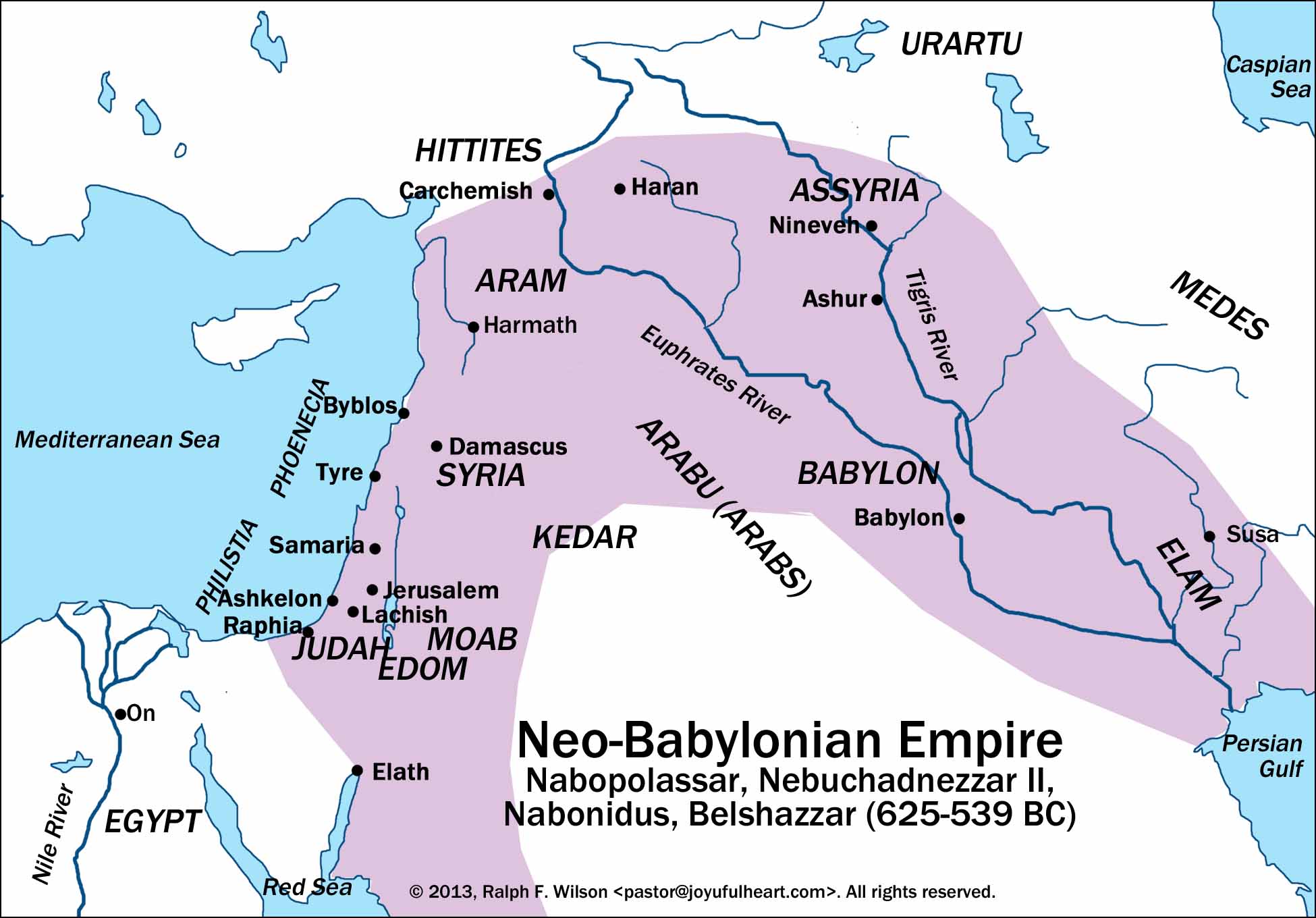
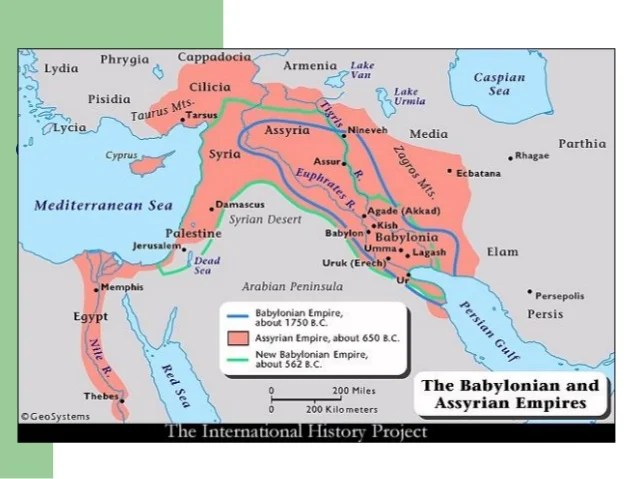
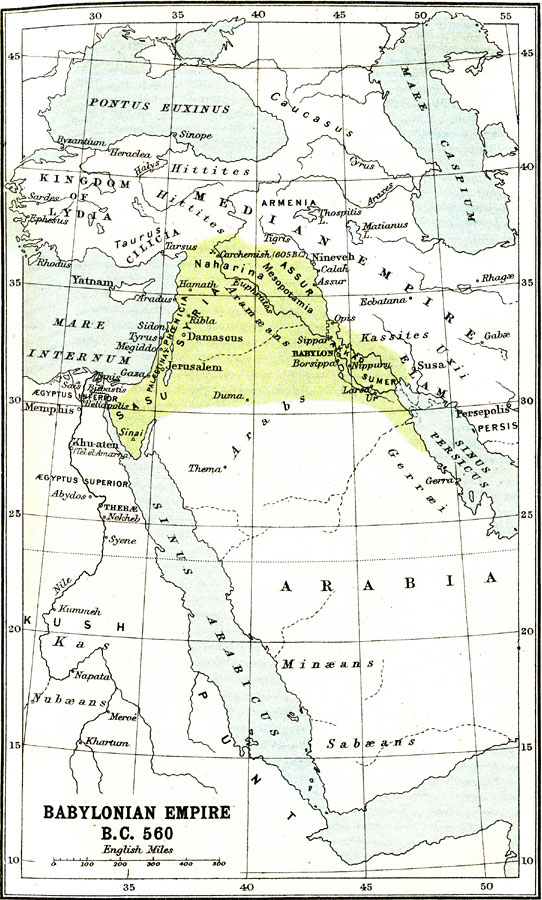
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, a resurgence of Babylonian power in the ancient world, stands as a testament to the resilience and dynamism of ancient civilizations. Emerging from the ashes of the Assyrian Empire, the Neo-Babylonians carved a distinct and influential mark on the map of the ancient Near East. Understanding the geographical extent and political landscape of this empire requires a careful examination of its map.
The Geographic Scope of the Neo-Babylonian Empire:
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, established by the Chaldean dynasty under Nabopolassar in the 7th century BCE, reached its zenith under the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II (605-562 BCE). Its territorial expanse encompassed a vast swathe of the ancient Near East, stretching from the Persian Gulf in the east to the Mediterranean Sea in the west.
Key Regions and Cities:
- Mesopotamia: The heartland of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, Mesopotamia, a fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, served as the cradle of Babylonian civilization. Key cities within this region included Babylon, the imperial capital, Borsippa, a religious center, and Sippar, a significant economic hub.
- Syria and Palestine: The Neo-Babylonians expanded their influence westwards, conquering key cities in Syria and Palestine, including Damascus, Tyre, and Jerusalem. This expansion brought the empire into direct contact with the burgeoning Phoenician and Israelite civilizations.
- Egypt: The Neo-Babylonian Empire’s reach extended to Egypt during the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II. While the empire did not permanently conquer Egypt, the Babylonian forces managed to capture and sack Memphis, the Egyptian capital, in 567 BCE.
- Eastern Anatolia: The Neo-Babylonian Empire also extended its influence eastward, incorporating parts of eastern Anatolia into its domain. This expansion brought the empire into contact with the powerful Medes and Persians, who would eventually rise to challenge Babylonian dominance.
The Significance of the Neo-Babylonian Map:
The map of the Neo-Babylonian Empire is a powerful visual representation of the empire’s political and economic influence. It highlights the strategic importance of Mesopotamia as a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange. The empire’s vast territory facilitated the flow of goods, ideas, and people, contributing to a vibrant and dynamic cultural landscape.
Understanding the Neo-Babylonian Map:
To fully appreciate the significance of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, it is essential to understand the map in relation to its historical context. The map reveals:
- The Rise of a New Power: The Neo-Babylonian Empire emerged as a successor to the declining Assyrian Empire, signifying a shift in the balance of power in the ancient Near East.
- The Importance of Trade and Commerce: The Neo-Babylonian Empire controlled key trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods and resources across the ancient world. This economic prosperity contributed to the empire’s cultural and artistic flourishment.
- The Interplay of Cultures: The empire’s geographical expanse brought together diverse cultures, fostering a vibrant and cosmopolitan society. This interaction between different civilizations led to the exchange of ideas, religions, and artistic traditions.
- The Legacy of Nebuchadnezzar II: The reign of Nebuchadnezzar II marked the zenith of Neo-Babylonian power. His ambitious building projects, including the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, left an enduring legacy on the ancient world.
FAQs about the Neo-Babylonian Empire Map:
1. What were the main geographical features of the Neo-Babylonian Empire?
The Neo-Babylonian Empire encompassed Mesopotamia, Syria, Palestine, parts of Egypt, and eastern Anatolia. The empire’s strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes contributed to its economic prosperity.
2. What were the key cities of the Neo-Babylonian Empire?
Babylon, the imperial capital, was the most important city. Other significant cities included Borsippa, Sippar, Damascus, Tyre, and Jerusalem.
3. How did the Neo-Babylonian Empire’s map change over time?
The empire’s territorial extent fluctuated during its existence. Its boundaries expanded under Nebuchadnezzar II but contracted after his death. The empire’s ultimate collapse came at the hands of the Persians under Cyrus the Great in 539 BCE.
4. What was the impact of the Neo-Babylonian Empire on the ancient world?
The Neo-Babylonian Empire left a lasting legacy on the ancient world. Its economic prosperity, cultural dynamism, and architectural achievements influenced subsequent civilizations. The empire’s conquest of Jerusalem and the subsequent exile of the Israelites also had a profound impact on Jewish history and culture.
5. How does the map of the Neo-Babylonian Empire help us understand its history?
The map provides a visual representation of the empire’s geographical extent, its strategic importance, and its influence on surrounding civilizations. It helps us understand the empire’s political, economic, and cultural context.
Tips for Studying the Neo-Babylonian Empire Map:
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map with key cities and geographical features marked is essential for understanding the empire’s scope and significance.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical context of the Neo-Babylonian Empire is crucial for interpreting the map. Factors like the rise and fall of other empires, the development of trade routes, and the cultural interactions between different civilizations are important considerations.
- Focus on key cities: Pay attention to the key cities within the empire, such as Babylon, Borsippa, Damascus, and Jerusalem, as they played significant roles in the empire’s history and development.
- Analyze the empire’s borders: The empire’s borders provide insights into its strategic goals and its relationship with neighboring civilizations.
- Connect the map to other sources: Use the map as a starting point for further research. Consult historical texts, archaeological evidence, and other sources to gain a deeper understanding of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
Conclusion:
The map of the Neo-Babylonian Empire is a valuable tool for understanding the history and significance of this ancient civilization. It reveals the empire’s geographical extent, its political and economic influence, and its impact on the ancient world. By studying the map and its historical context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the legacy of the Neo-Babylonian Empire and its enduring contribution to the development of human civilization.
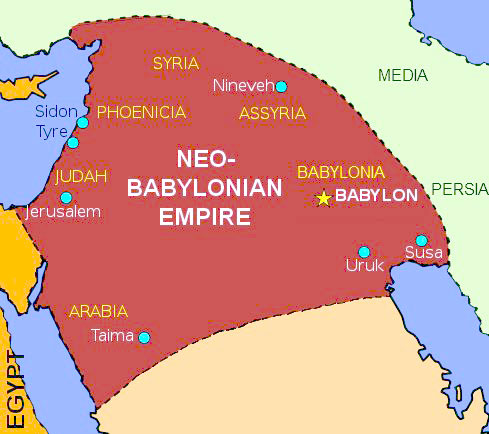


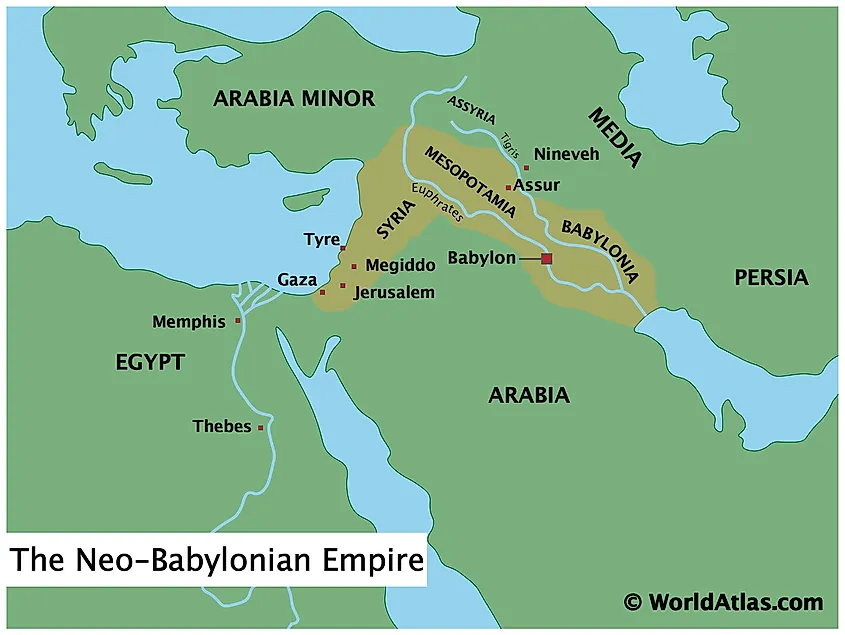

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Neo-Babylonian Empire: A Map of Revival and Power. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!