The Geopolitical Landscape of Palestine: A Look at its Location on the World Map
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Landscape of Palestine: A Look at its Location on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Landscape of Palestine: A Look at its Location on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Landscape of Palestine: A Look at its Location on the World Map
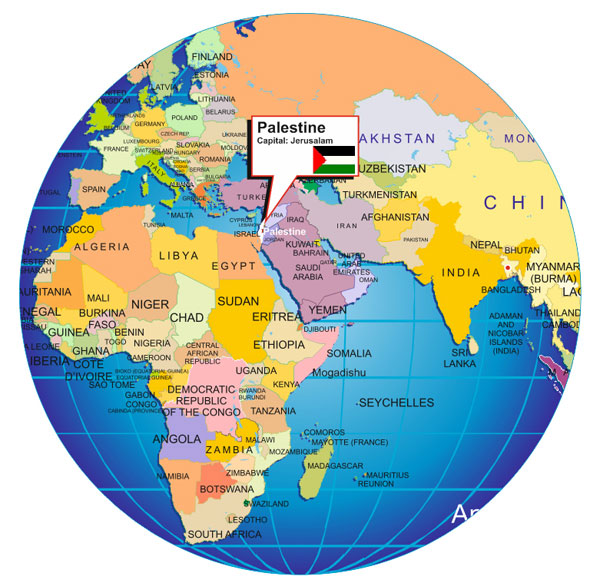
The Palestinian territories, a subject of intense global scrutiny and political debate, occupy a strategically vital location in the Middle East. Understanding this location is crucial to grasping the complex historical, political, and social realities that have shaped the region.
A Crossroads of History and Conflict:
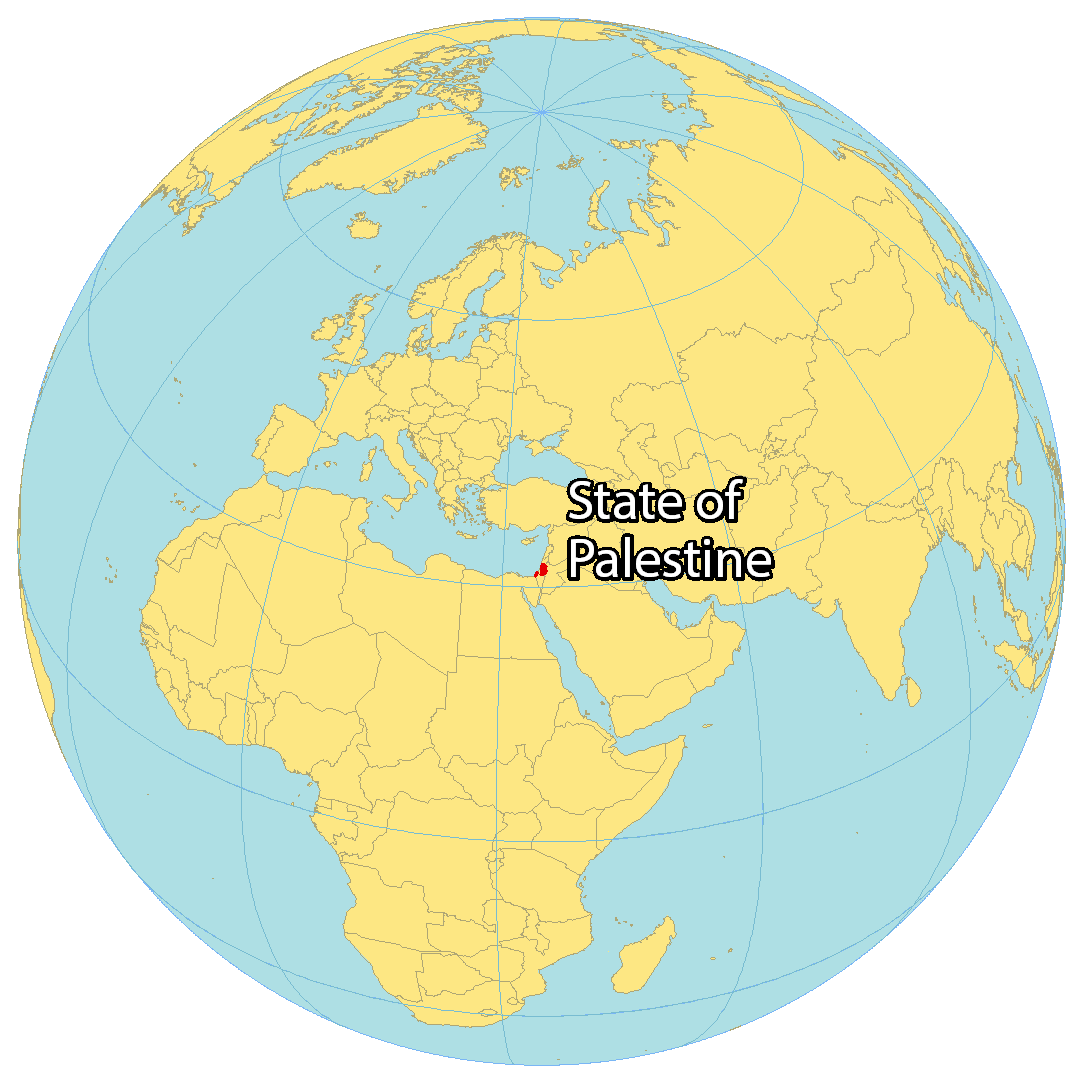
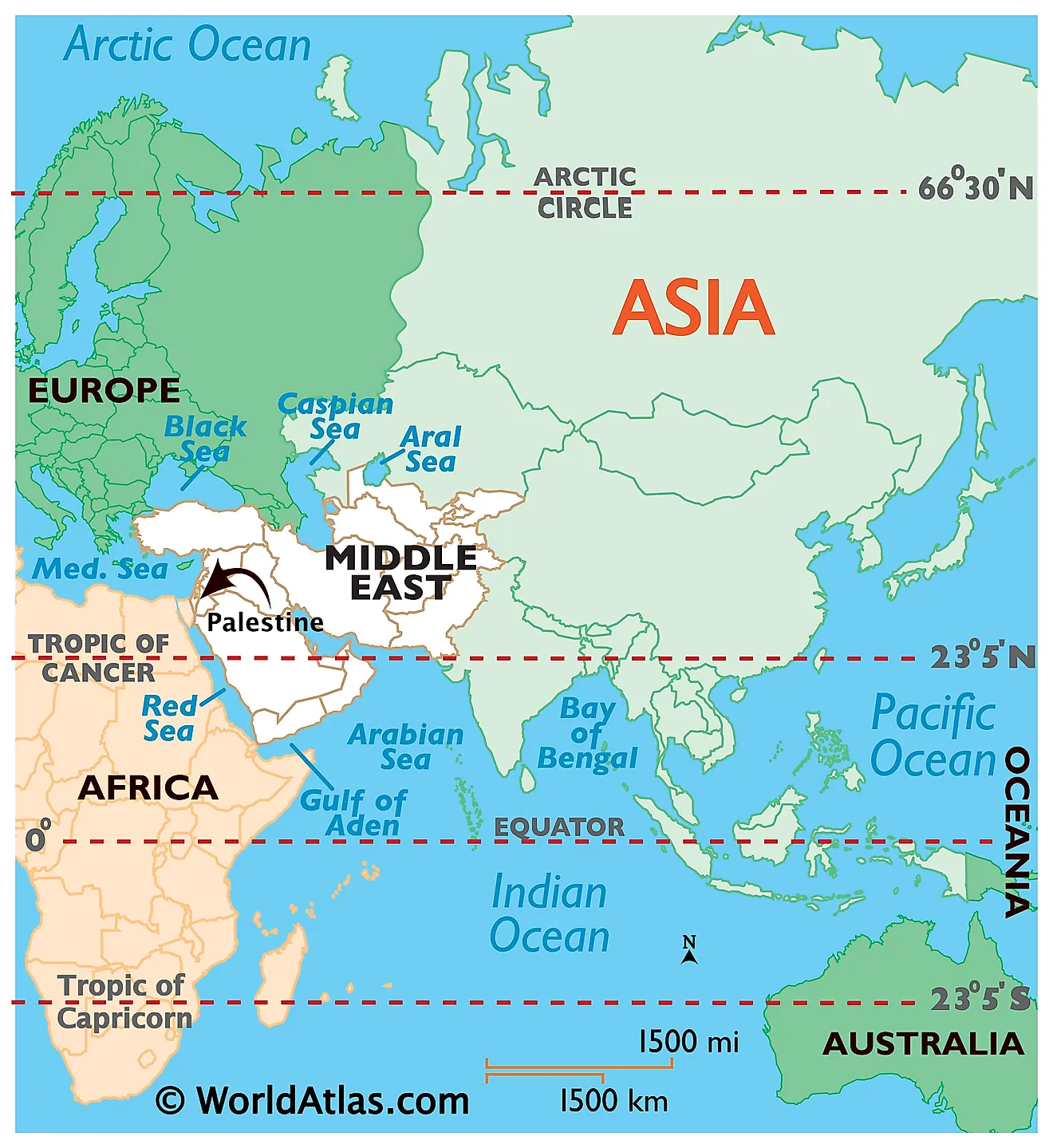
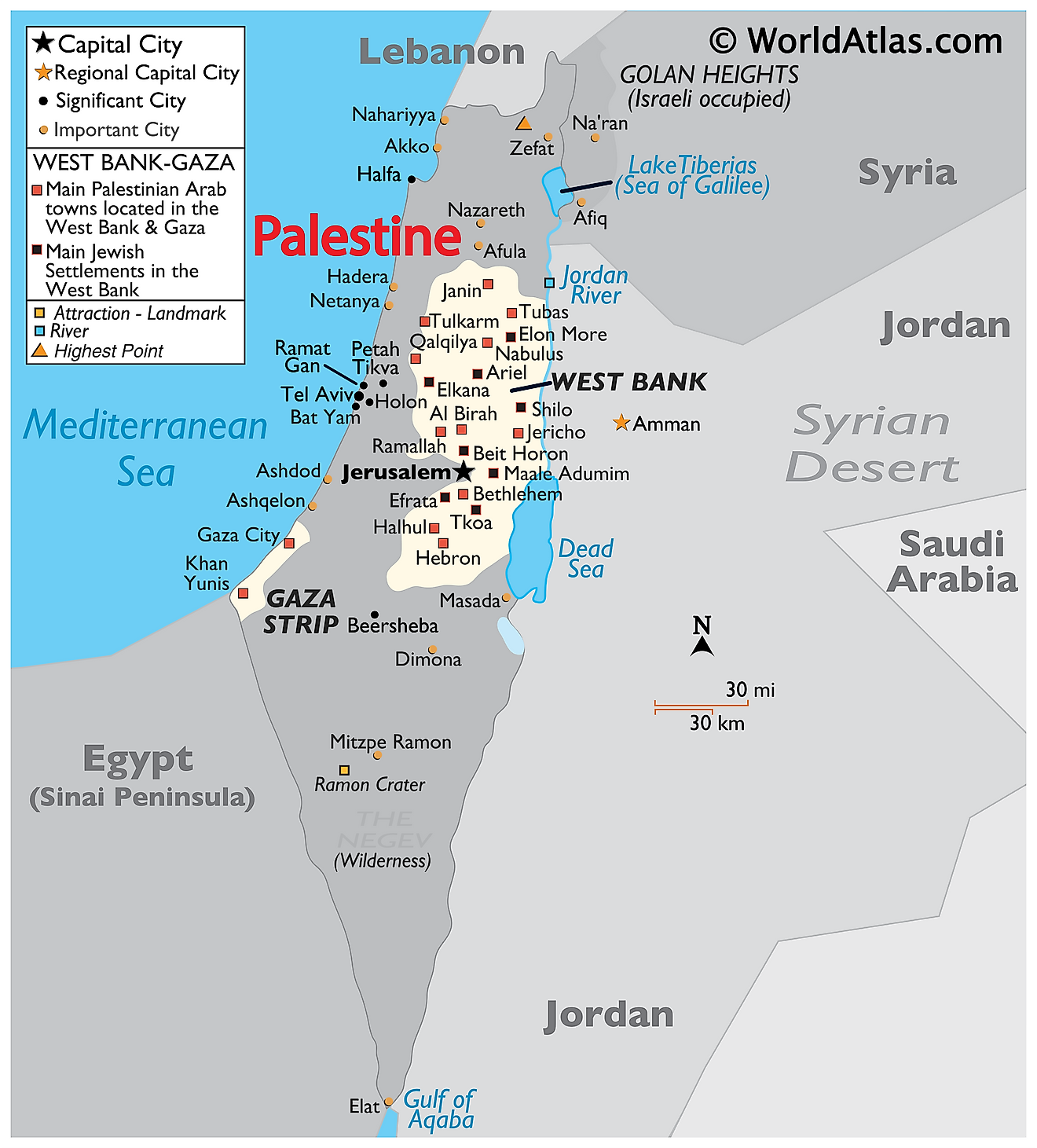
Palestine, as it exists today, encompasses the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. These territories are nestled between Israel to the east and south, Egypt to the southwest, and Jordan to the east. This geographic position has rendered Palestine a crossroads of civilizations, a land where diverse cultures have converged and clashed throughout history.
Historical Significance:
The region’s historical importance cannot be overstated. Palestine, often referred to as the "Holy Land," holds immense religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The presence of sacred sites such as Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Hebron has drawn pilgrims and conquerors alike for centuries, shaping the region’s cultural and political landscape.
The Modern Context:
The 20th century witnessed the establishment of the State of Israel, a development that fundamentally altered the political landscape of Palestine. The conflict between Israelis and Palestinians, rooted in competing claims to the land and its resources, has become a defining feature of the region. The ongoing struggle for Palestinian self-determination and the establishment of an independent state remain central to the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East.
Understanding the Geographic Reality:
The West Bank:
- Located west of the Jordan River, the West Bank is a mountainous region characterized by diverse landscapes, including fertile valleys and arid hills.
- It is home to major Palestinian cities such as Ramallah, Nablus, and Hebron.
- The West Bank is divided into Area A (under full Palestinian control), Area B (joint Israeli-Palestinian control), and Area C (under Israeli control).
The Gaza Strip:
- A narrow coastal strip bordering Egypt to the south and Israel to the east, the Gaza Strip is densely populated and faces significant economic and humanitarian challenges.
- It has been subject to Israeli military control and blockade since 2007.
Implications of the Location:
- Strategic Importance: Palestine’s location at the heart of the Middle East places it at a critical juncture of trade routes and energy pipelines, making it strategically important for regional stability.
- Resource Scarcity: The Palestinian territories face significant water scarcity due to limited natural resources and the ongoing conflict.
- Political and Economic Constraints: The Israeli occupation and the lack of a sovereign state have severely hampered Palestinian economic development and political autonomy.
Exploring the Importance of Palestine’s Location:
1. A Global Focal Point:
Palestine’s location, with its historical and religious significance, has transformed it into a global focal point. The ongoing conflict draws international attention and humanitarian efforts, highlighting the urgency for a peaceful resolution.
2. A Bridge Between Cultures:
The convergence of cultures and religions within Palestine has created a unique and vibrant society. Despite the challenges, Palestinian culture reflects a rich tapestry of traditions, art, and literature, embodying a spirit of resilience and hope.
3. A Symbol of Struggle for Self-Determination:
The Palestinian struggle for independence and self-determination resonates with people around the world who champion human rights and justice. The fight for Palestinian statehood symbolizes the broader struggle for equality and freedom for marginalized communities.
FAQs about Palestine’s Location:
1. What is the capital of Palestine?
The capital of Palestine is officially Jerusalem, although this claim is contested by Israel. Currently, the Palestinian government operates from Ramallah in the West Bank.
2. Why is Palestine located in such a politically sensitive region?
Palestine’s location is at the heart of a complex geopolitical landscape, with historical claims and competing interests from multiple parties. The region has witnessed centuries of conflict and power struggles, contributing to the ongoing tensions.
3. How does the Israeli-Palestinian conflict impact the region?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has had a profound impact on the entire Middle East, leading to political instability, economic hardship, and humanitarian crises. It has also fueled regional tensions and international interventions.
4. What is the significance of the Palestinian territories to the world?
Palestine’s location and its historical, religious, and cultural significance make it a crucial part of the global landscape. The ongoing conflict and the struggle for Palestinian statehood raise important questions about human rights, international law, and the pursuit of peace.
Tips for Understanding Palestine’s Location:
- Study Historical Maps: Examining historical maps can provide valuable insights into the evolution of the region’s boundaries and the historical claims of different parties.
- Engage with Palestinian Voices: Reading Palestinian literature, watching Palestinian films, and listening to Palestinian perspectives can offer a deeper understanding of their experiences and aspirations.
- Follow News and Analysis: Stay informed about current events and developments in the region through reputable news sources and think tanks that provide in-depth analysis.
Conclusion:
Understanding Palestine’s location on the world map is essential for comprehending the complexities of the region and the ongoing conflict. Its strategic importance, historical significance, and the struggle for Palestinian self-determination all contribute to the region’s intricate geopolitical landscape. By engaging with the historical context, understanding the contemporary challenges, and recognizing the human cost of the conflict, we can foster a more informed and compassionate approach towards achieving a just and lasting peace in the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Landscape of Palestine: A Look at its Location on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!