The Ethnic Tapestry of Sudan: A Complex and Diverse Landscape
Related Articles: The Ethnic Tapestry of Sudan: A Complex and Diverse Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Ethnic Tapestry of Sudan: A Complex and Diverse Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ethnic Tapestry of Sudan: A Complex and Diverse Landscape

Sudan, a nation in Northeast Africa, is renowned for its vast expanse and rich cultural heritage. This heritage is intricately woven with a diverse tapestry of ethnic groups, each contributing to the nation’s unique identity. Understanding the ethnic map of Sudan is crucial for comprehending the country’s history, social dynamics, and ongoing challenges.
A Mosaic of Cultures:
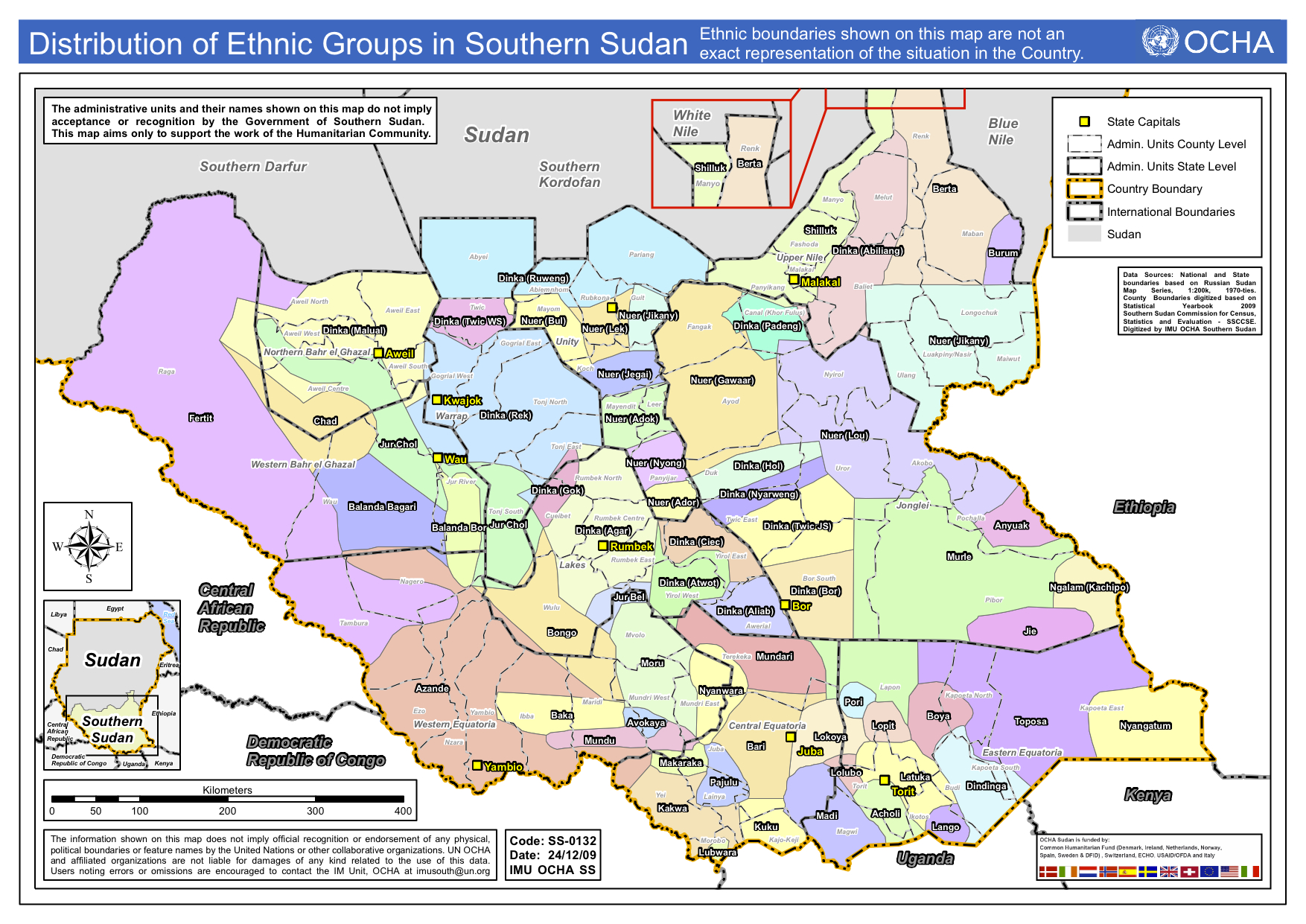
Sudan’s ethnic landscape is characterized by a remarkable variety of groups, each with distinct languages, traditions, and cultural practices. While precise numbers are difficult to ascertain, estimates suggest over 100 distinct ethnic groups residing within Sudan’s borders. These groups can be broadly categorized into four major clusters:
-
Arab Tribes: The Arab population, concentrated in the north and east, comprises various tribes with a shared linguistic and cultural heritage. These tribes, including the Jaalin, the Baggara, and the Shukriya, have historically played a prominent role in Sudan’s political and social life.
-
Nilotic Groups: The Nilotic tribes, primarily found in the south and central regions, are known for their pastoralist traditions and close ties to the Nile River. This diverse group includes the Dinka, the Nuer, the Shilluk, and the Anuak, each with unique cultural practices and traditions.
-
Fur and Related Groups: The Fur, along with related ethnicities like the Masalit and the Zaghawa, reside predominantly in the western region of Darfur. Their distinct languages and cultural practices contribute to the region’s unique identity.
-
Beja and Related Groups: The Beja, residing in the Red Sea Hills region, are known for their nomadic lifestyle and close ties to the sea. This group, which also includes the Hadendowa and the Bisharin, has long been associated with trade and livestock herding.
The Historical Context:
The ethnic map of Sudan is a product of centuries of migrations, interactions, and historical events. The Arab tribes, migrating from the Arabian Peninsula, gradually established their presence in the north and east, while the Nilotic groups, originating from the south, moved northward along the Nile Valley. The Fur and related groups, originating in the Sahel region, settled in Darfur, while the Beja, originating from the Horn of Africa, established themselves in the Red Sea Hills.
The Impact of Colonialism:
The British colonial period in Sudan (1899-1956) had a significant impact on the ethnic landscape. The colonial administration introduced policies that favored the Arab population in the north, leading to tensions and conflicts with the Nilotic and other groups in the south. This legacy of colonial policies continues to influence the dynamics between different ethnic groups in Sudan.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The ethnic map of Sudan is a complex and dynamic landscape, with ongoing challenges and opportunities for development. The country has experienced periods of instability and conflict, often fueled by ethnic tensions and grievances. However, Sudan also possesses immense potential for unity and progress, based on the rich cultural diversity and shared history of its people.
Understanding the Importance:
Understanding the ethnic map of Sudan is crucial for several reasons:
- Policy Formulation: Recognizing the diverse needs and aspirations of different ethnic groups is essential for developing effective policies that promote peace, development, and social cohesion.
- Conflict Resolution: Understanding the historical context and root causes of ethnic conflicts is crucial for developing sustainable solutions and fostering dialogue and reconciliation.
- Cultural Preservation: Recognizing and celebrating the diverse cultural heritage of Sudan’s ethnic groups is vital for preserving the nation’s rich history and identity.
Moving Forward:
The future of Sudan hinges on its ability to harness the potential of its diverse ethnic tapestry. This requires promoting dialogue, understanding, and respect among different communities. It also necessitates policies that address the historical injustices, promote inclusive governance, and ensure equitable distribution of resources and opportunities.
FAQs
1. What are the major ethnic groups in Sudan?
The major ethnic groups in Sudan include the Arab tribes, the Nilotic groups, the Fur and related groups, and the Beja and related groups.
2. How many ethnic groups are there in Sudan?
Estimates suggest over 100 distinct ethnic groups residing in Sudan, although precise numbers are difficult to ascertain.
3. What are the main challenges associated with Sudan’s ethnic diversity?
Challenges include historical grievances, economic disparities, political marginalization, and the potential for conflict fueled by ethnic tensions.
4. How can Sudan promote unity and progress amidst its ethnic diversity?
Promoting dialogue, understanding, and respect among different communities, addressing historical injustices, fostering inclusive governance, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources and opportunities are crucial steps towards unity and progress.
Tips
- Embrace cultural exchange: Encourage interaction and exchange between different ethnic groups to foster understanding and appreciation for diverse cultures.
- Promote inclusive education: Implement educational programs that highlight the contributions of all ethnic groups to Sudan’s history and culture.
- Support community development: Invest in programs that empower marginalized communities and promote economic opportunities for all ethnic groups.
- Strengthen interfaith dialogue: Encourage dialogue and cooperation between different religious groups to foster interfaith harmony and understanding.
Conclusion
The ethnic map of Sudan is a testament to the country’s rich cultural heritage and the diversity of its people. While challenges exist, there is also immense potential for unity and progress based on the shared history and cultural tapestry of the nation. By promoting dialogue, understanding, and inclusive governance, Sudan can harness the power of its diverse ethnic groups to build a more prosperous and peaceful future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ethnic Tapestry of Sudan: A Complex and Diverse Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!