The Enigmatic Landscape: Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia
Related Articles: The Enigmatic Landscape: Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enigmatic Landscape: Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigmatic Landscape: Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia

The map of Russia and Eurasia is a tapestry woven with threads of history, geography, and culture, revealing a vast and complex region that has captivated and challenged the world for centuries. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of this map, illuminating its significance and highlighting the multifaceted influences that shape its political, economic, and social landscape.
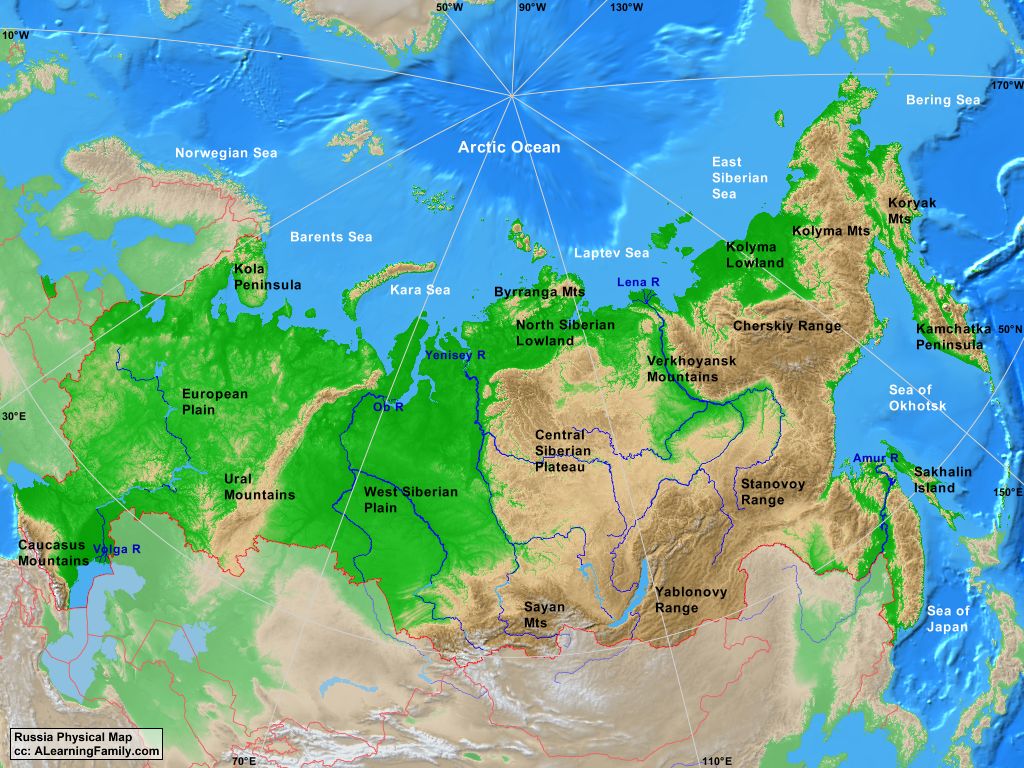
A Geographical Colossus: The Scale and Scope of Russia and Eurasia
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, sprawls across the northern expanse of Eurasia, its territory stretching from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. Eurasia, a term encompassing Europe and Asia, encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, climates, and ethnicities, making it a geographically and culturally vibrant region.
Understanding the Geography: Key Features and Their Influence
The geography of Russia and Eurasia plays a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and political landscape. Here are some key geographical features and their impact:
- Vastness and Diverse Landscapes: The sheer size of Russia and Eurasia is a defining characteristic. From the snow-capped mountains of the Caucasus to the vast steppes of Central Asia, from the tundra of Siberia to the fertile plains of the Black Sea region, the region boasts a diverse array of landscapes, each with its unique challenges and opportunities.
- Transcontinental Position: Russia’s unique transcontinental position, straddling both Europe and Asia, has historically been a source of both strength and complexity. This location grants Russia access to both Western and Eastern markets, while simultaneously placing it at the crossroads of different cultural and political spheres.
- Extensive Coastlines: Russia’s extensive coastlines, stretching along the Arctic Ocean, the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea, and the Pacific Ocean, provide access to vital shipping routes and marine resources. However, these coastlines also present challenges, particularly in terms of climate and infrastructure development.
- Rich Natural Resources: Russia and Eurasia are endowed with vast natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, timber, and fertile land. These resources have been instrumental in shaping the region’s economic development and geopolitical influence.
- Challenges of Climate: The region’s climate varies greatly, from the frigid Arctic north to the temperate south. This diversity presents both challenges and opportunities, influencing agriculture, transportation, and human settlement patterns.
The Historical Tapestry: A Journey Through Time
The map of Russia and Eurasia is a living testament to centuries of history, marked by both periods of peace and conflict. Understanding these historical events is crucial to comprehending the current political and social dynamics of the region:
- The Rise and Fall of Empires: The region has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the Mongol Empire, the Russian Empire, and the Soviet Union. These empires have shaped the political, cultural, and linguistic landscape of the region, leaving behind a legacy of both unity and division.
- The Legacy of the Soviet Union: The Soviet Union, a vast socialist state encompassing much of Eurasia, exerted a profound influence on the region. Its collapse in 1991 ushered in a period of political and economic transformation, with many former Soviet republics struggling to find their place in the new world order.
- National Identity and Independence: The dissolution of the Soviet Union paved the way for the emergence of independent nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and aspirations. This process has been marked by both progress and challenges, as these newly independent states navigate the complexities of nation-building and regional integration.
The Political Landscape: Navigating a Complex Web of Power
The map of Russia and Eurasia reflects a complex political landscape, shaped by historical legacies, geopolitical ambitions, and economic interests. Key aspects of this political landscape include:
- Russia’s Geopolitical Influence: Russia, as the largest country in the region, continues to exert significant geopolitical influence, particularly in its immediate neighborhood. Its military strength, vast natural resources, and strategic location make it a key player in international affairs.
- Regional Cooperation and Integration: Efforts to foster regional cooperation and integration have gained momentum in recent decades. Organizations like the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) aim to promote economic growth, security, and political stability within the region.
- Challenges to Stability: The region faces numerous challenges to its stability, including ethnic tensions, separatist movements, and external pressures. These challenges highlight the complexity of navigating the political landscape of Russia and Eurasia.
The Economic Landscape: Opportunities and Challenges
The map of Russia and Eurasia reveals a vast and diverse economic landscape, characterized by both opportunities and challenges:
- Resource-Rich Economies: Many countries in the region are resource-rich, with significant reserves of oil, gas, minerals, and timber. These resources have the potential to drive economic growth and development.
- Challenges of Diversification: The region’s economies are often heavily reliant on the extraction and export of natural resources. Diversifying these economies and developing other sectors is essential for long-term sustainability.
- Infrastructure Development: The region faces significant challenges in terms of infrastructure development, particularly in areas like transportation, energy, and communication. Investing in infrastructure is crucial for unlocking the region’s economic potential.
- Regional Integration and Trade: Efforts to foster regional integration and trade are underway, with the goal of creating a more interconnected and prosperous economic landscape. Initiatives like the EEU are aimed at promoting trade and investment within the region.
The Cultural Mosaic: A Tapestry of Diversity
The map of Russia and Eurasia reflects a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions. The region’s cultural diversity is a testament to its long and complex history:
- Ethnic Diversity: The region is home to a diverse array of ethnic groups, each with its own unique language, customs, and traditions. This diversity enriches the cultural landscape of the region.
- Religious Influences: Russia and Eurasia have been shaped by various religious influences, including Orthodox Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, and Judaism. These religions have played a significant role in shaping the region’s cultural identity.
- Art, Literature, and Music: The region boasts a rich artistic heritage, with contributions to literature, music, dance, and visual arts. From the works of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky to the music of Tchaikovsky and Stravinsky, the cultural legacy of Russia and Eurasia is vast and influential.
The Future of Russia and Eurasia: Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities
The map of Russia and Eurasia is not static; it is a dynamic landscape that is constantly evolving. The region faces a number of challenges, including:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical tensions between Russia and the West, particularly over Ukraine and the Arctic, continue to cast a shadow over the region.
- Economic Challenges: The region faces economic challenges, including a reliance on natural resources, limited diversification, and infrastructure gaps.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses significant challenges to the region, particularly in terms of permafrost thaw, coastal erosion, and extreme weather events.
However, the region also presents a number of opportunities:
- Economic Growth: The region has the potential for significant economic growth, driven by its vast natural resources, growing consumer markets, and increasing regional integration.
- Technological Development: The region is investing in technological development, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and space exploration.
- Cultural Exchange: The region’s cultural diversity offers opportunities for cultural exchange and understanding, fostering closer ties between different nations and communities.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Map of Russia and Eurasia
Q: What are the main challenges facing the region?
A: The region faces numerous challenges, including geopolitical tensions with the West, economic diversification challenges, infrastructure gaps, and the impacts of climate change.
Q: What are the main opportunities for the region?
A: The region has the potential for significant economic growth, driven by its vast natural resources, growing consumer markets, and increasing regional integration. It also has opportunities for technological development and cultural exchange.
Q: What are the key political actors in the region?
A: Key political actors in the region include Russia, China, the European Union, the United States, and various regional organizations such as the CIS and the EEU.
Q: How does the geography of the region influence its politics and economics?
A: The vast size, diverse landscapes, transcontinental position, and rich natural resources of Russia and Eurasia have a profound influence on its politics and economics. These factors shape trade routes, resource distribution, and geopolitical strategies.
Q: What is the significance of the Arctic region in the context of Russia and Eurasia?
A: The Arctic region holds significant geopolitical and economic importance, with its vast natural resources, potential shipping routes, and strategic location. The region is becoming increasingly contested as climate change opens up new opportunities for exploration and development.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia:
- Study the geography: Familiarize yourself with the region’s key geographical features, including its vastness, diverse landscapes, and transcontinental position.
- Explore historical events: Understand the region’s historical events, including the rise and fall of empires, the legacy of the Soviet Union, and the emergence of independent nations.
- Analyze the political landscape: Examine the region’s political dynamics, including Russia’s geopolitical influence, regional cooperation efforts, and challenges to stability.
- Investigate the economic landscape: Explore the region’s economic opportunities and challenges, including resource-rich economies, diversification efforts, infrastructure development, and regional integration initiatives.
- Appreciate the cultural mosaic: Recognize the region’s cultural diversity, including its ethnic groups, religious influences, and artistic heritage.
Conclusion: A Region of Complexity and Potential
The map of Russia and Eurasia reveals a complex and dynamic region, shaped by a confluence of history, geography, culture, and politics. While the region faces numerous challenges, it also holds immense potential for economic growth, technological development, and cultural exchange. Understanding the intricacies of this map is essential for navigating the complexities of this vast and influential region.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigmatic Landscape: Understanding the Map of Russia and Eurasia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!