Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map
- 3.1 The Importance of the FIRM: A Foundation for Informed Decisions
- 3.2 Deciphering the FIRM: A Look at Flood Zones
- 3.3 Understanding the FIRM: Key Considerations
- 3.4 Navigating the FIRM: Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.5 Navigating the FIRM: Tips for Homeowners
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Guide to Informed Decisions
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map

The New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM), a critical tool for understanding flood risk, plays a vital role in shaping insurance premiums and guiding responsible development practices. This comprehensive map, developed and maintained by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provides a detailed visual representation of flood zones across New Jersey, categorizing areas based on their susceptibility to flooding.
The Importance of the FIRM: A Foundation for Informed Decisions
The FIRM serves as a cornerstone for informed decision-making, influencing various aspects of life in New Jersey:
1. Flood Insurance Premiums: The FIRM forms the basis for calculating flood insurance premiums. Properties located in high-risk flood zones typically face higher premiums due to their increased vulnerability. Conversely, properties in lower-risk zones may benefit from lower premiums.
2. Building and Development Regulations: The FIRM guides local governments in establishing building codes and zoning regulations. Areas identified as high-risk zones may require stricter building standards to minimize flood damage and ensure public safety.
3. Mortgage Lending: Lenders often use the FIRM to assess the risk associated with properties and determine loan eligibility. Properties located in high-risk flood zones may face stricter lending criteria or higher interest rates.
4. Community Planning and Development: The FIRM provides crucial data for planning and development initiatives, enabling communities to make informed decisions regarding infrastructure development, flood mitigation measures, and land use planning.
5. Emergency Response Planning: The FIRM helps emergency responders understand flood risk areas, enabling them to develop effective response plans and prioritize resources during flood events.
Deciphering the FIRM: A Look at Flood Zones
The FIRM categorizes flood zones into different categories, each representing a distinct level of flood risk:
1. Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs): These areas are defined as having a 1% annual chance of flooding, or a 26% chance of flooding over a 30-year period. Properties within SFHAs are typically required to purchase flood insurance if they have a federally-backed mortgage.
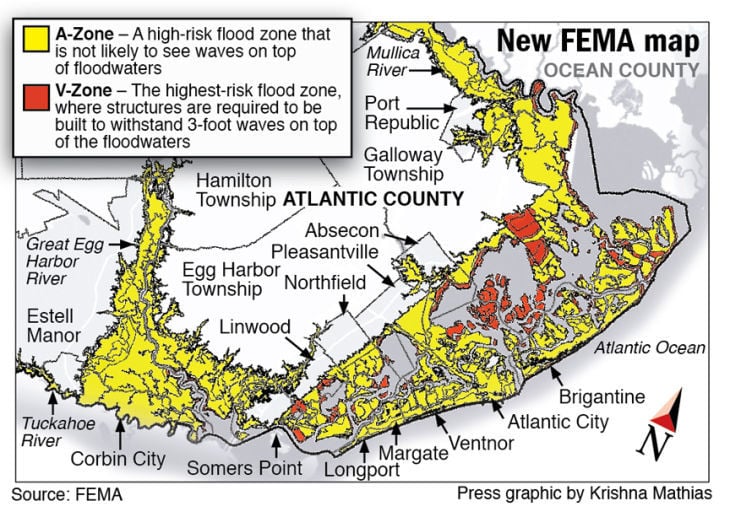
2. Zone A: These areas are subject to flooding from a 100-year flood event, but the specific flood risk is not precisely determined.
3. Zone AE: Similar to Zone A, these areas are also subject to flooding from a 100-year flood event, but the flood risk is more precisely determined based on elevation data.
4. Zone AO: These areas are subject to flooding from a 100-year flood event and are characterized by shallow flooding depths.
5. Zone AH: These areas are subject to flooding from a 100-year flood event and are characterized by deeper flooding depths.
6. Zone X: These areas are considered to have a low risk of flooding and are not typically subject to flood insurance requirements.
7. Zone D: These areas have been identified as areas with a potential flood risk, but they are not classified as SFHAs.
Understanding the FIRM: Key Considerations
1. Elevation: The FIRM considers elevation as a key factor in determining flood risk. Properties situated at higher elevations are typically less prone to flooding.
2. Topography: The FIRM analyzes the topography of an area, considering factors like slopes, drainage patterns, and proximity to water bodies.
3. Flood History: Historical flood data plays a crucial role in determining flood risk. Areas with a history of frequent or severe flooding are more likely to be classified as high-risk zones.
4. Development and Infrastructure: The FIRM accounts for the impact of development and infrastructure on flood risk. For example, the construction of roads, buildings, and drainage systems can alter flood patterns.
5. Climate Change: The FIRM acknowledges the potential impact of climate change on flood risk, recognizing the increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events.
Navigating the FIRM: Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can I find my flood zone on the FIRM?
The FIRM is publicly available through the FEMA website (www.fema.gov). You can search for your property address on the website to determine its flood zone classification.
2. What if my property is in a flood zone, but I have never experienced flooding?
Even if you have not experienced flooding in the past, properties located in flood zones are still at risk. The FIRM is based on statistical analysis and considers the potential for flooding, not just historical events.
3. Do I need flood insurance if my property is in a low-risk zone?
While flood insurance is not mandatory for properties in low-risk zones, it is still recommended. Flood events can occur even in areas with low risk, and insurance can provide financial protection in case of unexpected damage.
4. What is the difference between flood insurance and homeowners insurance?
Homeowners insurance typically does not cover flood damage. Flood insurance is a separate policy that specifically covers damage caused by flooding.
5. How can I reduce my flood risk?
There are various measures you can take to reduce your flood risk, including elevating your property, installing flood barriers, and improving drainage around your home.
6. What if the FIRM changes?
The FIRM is periodically updated to reflect changes in flood risk. If the FIRM changes and your property is reclassified to a higher-risk zone, your flood insurance premiums may increase.
Navigating the FIRM: Tips for Homeowners
1. Understand your flood risk: Consult the FIRM to determine your property’s flood zone classification.
2. Purchase flood insurance: If your property is located in a high-risk flood zone, consider purchasing flood insurance to protect yourself financially.
3. Implement flood mitigation measures: Take steps to reduce your flood risk, such as elevating your home, installing flood barriers, and improving drainage.
4. Stay informed: Keep abreast of any updates or changes to the FIRM.
5. Contact your insurance agent: Discuss your flood insurance options and coverage with your insurance agent.
Conclusion: A Guide to Informed Decisions
The New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map is a vital tool for understanding flood risk and making informed decisions. By understanding the FIRM’s classification system, its underlying factors, and its implications, homeowners, developers, and communities can take proactive steps to mitigate flood risk and protect themselves from financial hardship. The FIRM serves as a guide to navigating the waters of risk, enabling responsible development, informed planning, and effective disaster preparedness.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters of Risk: Understanding the New Jersey Flood Insurance Rate Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
