Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Georgia’s Railway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Georgia’s Railway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Georgia’s Railway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Georgia’s Railway Network
Georgia’s extensive railway network plays a vital role in the state’s economy, facilitating the transportation of goods and people across diverse landscapes. Understanding the intricate web of tracks and their connections is crucial for businesses, travelers, and anyone interested in the state’s transportation infrastructure. This guide delves into the key aspects of Georgia’s railway system, providing a comprehensive overview of its history, current state, and future prospects.
A Historical Journey: Tracing the Roots of Georgia’s Railroads
The story of Georgia’s railroads begins in the 19th century, with the construction of the first line connecting Savannah to Augusta in 1836. This marked the dawn of a new era, enabling faster and more efficient transportation of goods and people across the state. The subsequent decades witnessed a rapid expansion of the railway network, with lines extending to major cities like Atlanta, Macon, and Columbus.
The development of railroads had a profound impact on Georgia’s economy, fostering growth in agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. The network facilitated the transportation of cotton, timber, and other commodities, connecting rural areas to urban markets and contributing to the state’s economic prosperity.
The Modern Network: A Vital Backbone for Georgia’s Economy
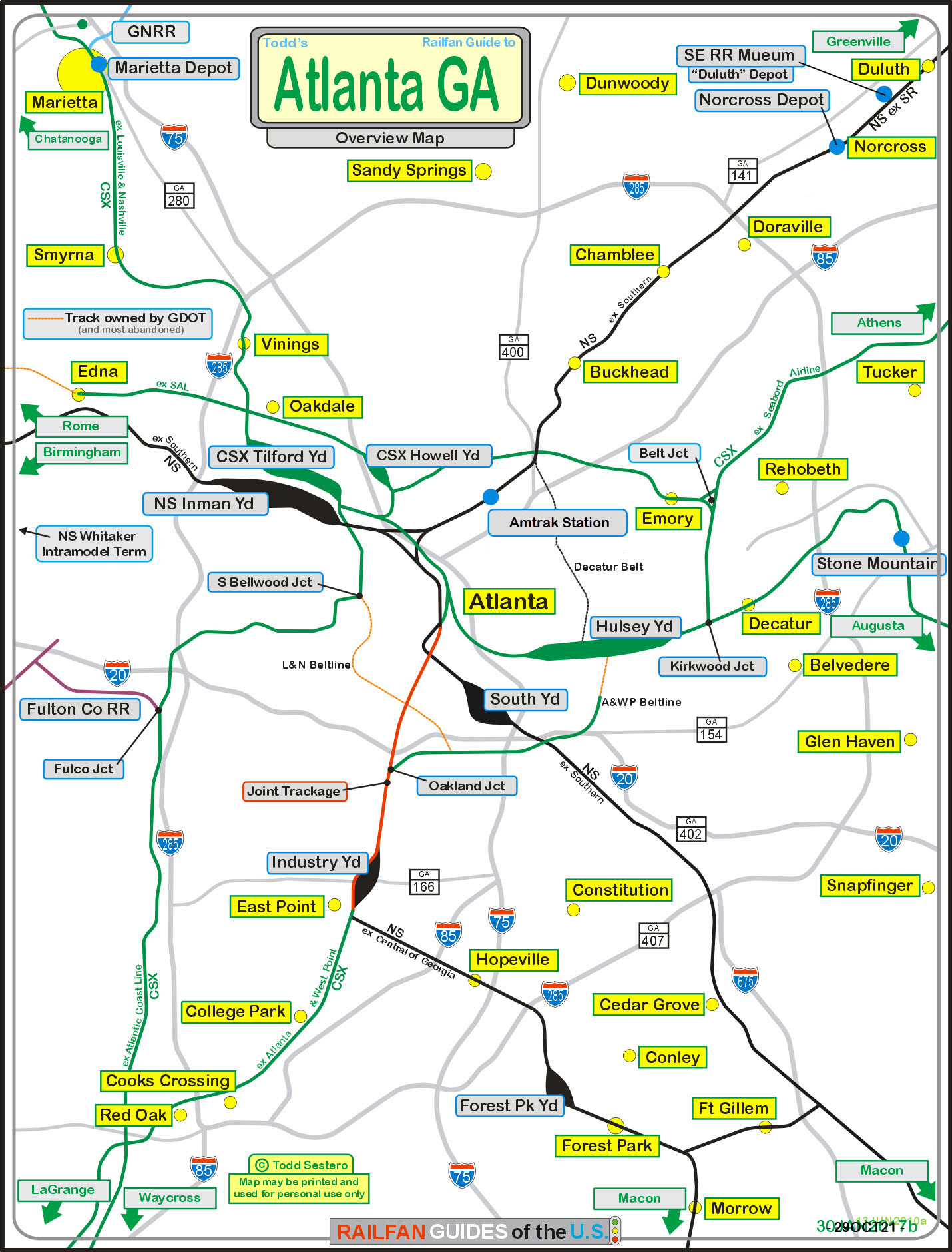
Today, Georgia boasts a robust railway network, spanning over 5,000 miles and connecting major cities and industrial centers across the state. The network is primarily comprised of freight lines, serving as a critical artery for the transportation of goods, including agricultural products, manufactured goods, and raw materials. Major freight carriers like CSX, Norfolk Southern, and Georgia Ports Authority operate extensive lines across the state, facilitating the movement of goods to and from major ports and industrial hubs.
Passenger Rail: Connecting Communities and Promoting Tourism
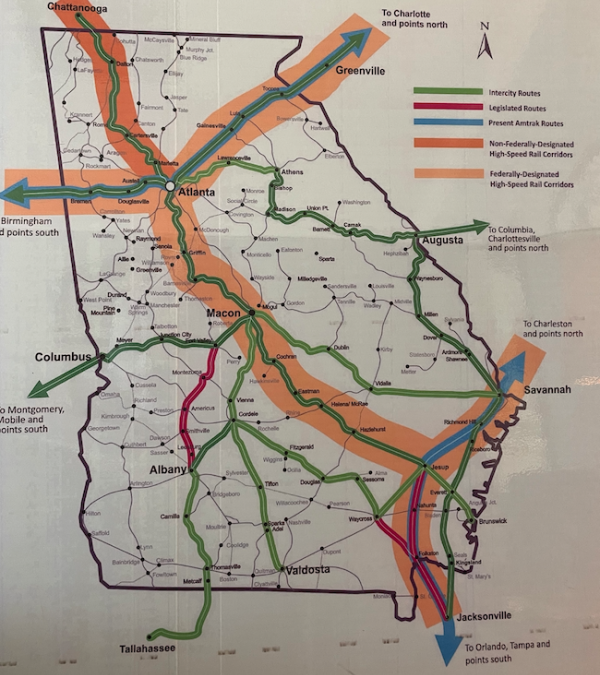
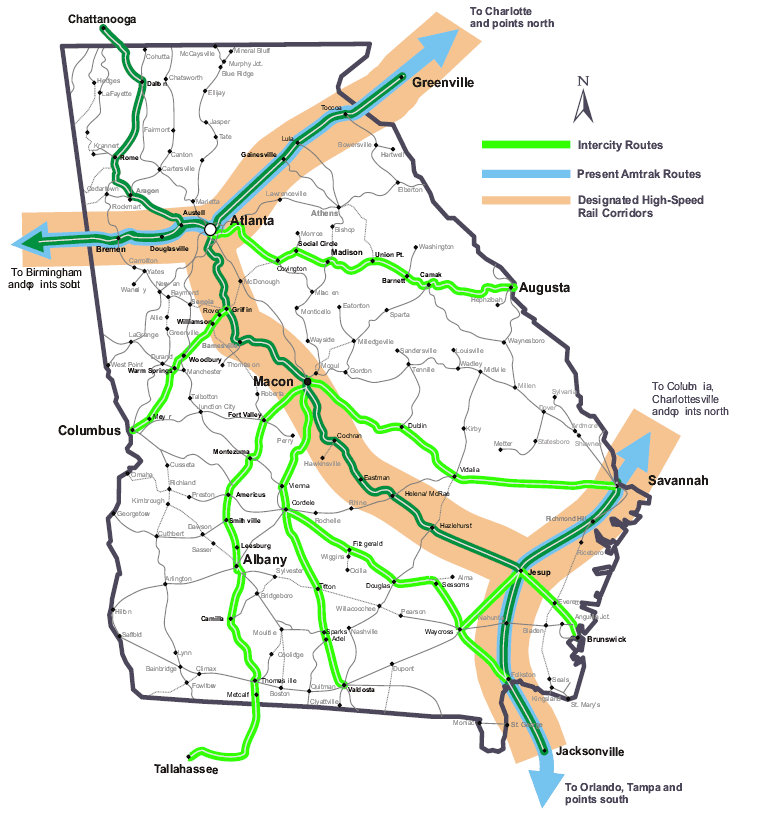
While freight transportation remains the dominant mode of operation, Georgia’s railway network also plays a significant role in passenger transportation. Amtrak operates a passenger rail service connecting major cities like Atlanta, Savannah, and Jacksonville, providing a convenient and cost-effective alternative to road travel.
The state government is also actively exploring opportunities to expand passenger rail services, recognizing its potential to reduce traffic congestion, promote tourism, and provide a more sustainable mode of transportation.
Key Components of Georgia’s Railway Network
Understanding the key components of Georgia’s railway network is crucial for appreciating its complexity and significance. These components include:
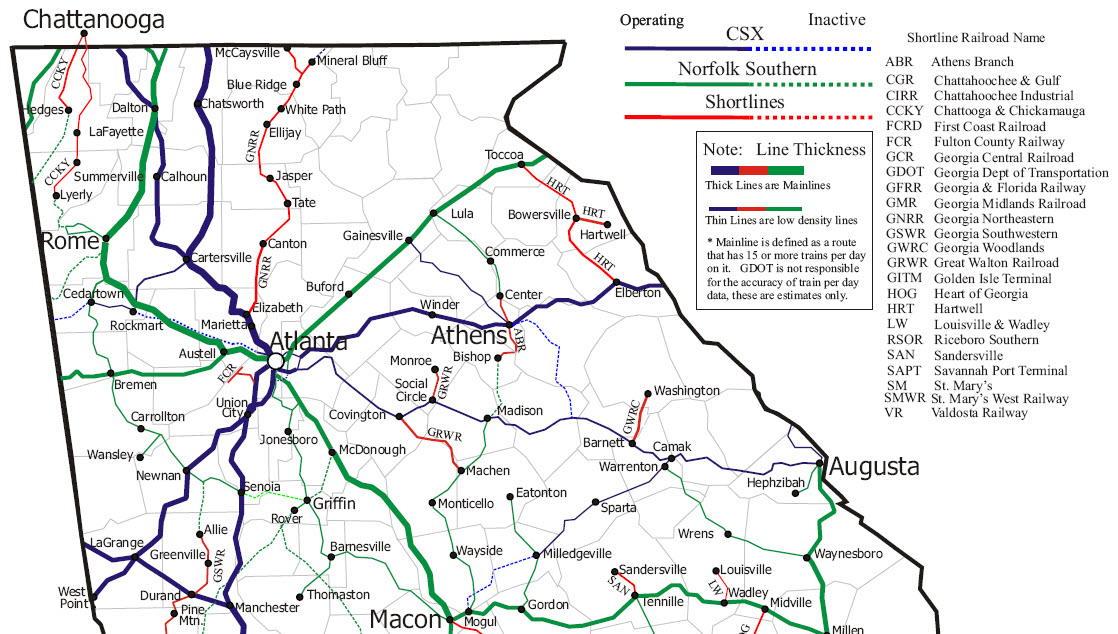
- Major Freight Lines: CSX and Norfolk Southern are the two primary freight carriers operating in Georgia, with extensive networks connecting major cities and industrial centers.
- Passenger Rail Lines: Amtrak’s lines connect major cities like Atlanta, Savannah, and Jacksonville, offering a convenient travel option.
- Short Line Railroads: These smaller lines connect local industries and businesses to major freight lines, playing a vital role in facilitating regional trade.
- Intermodal Facilities: These facilities connect different modes of transportation, such as rail, road, and water, facilitating the efficient transfer of goods between different networks.
Benefits of Georgia’s Railway Network
Georgia’s railway network delivers numerous benefits to the state, contributing to its economic growth, environmental sustainability, and overall well-being. These benefits include:
- Economic Growth: The network facilitates the efficient transportation of goods, supporting industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, driving economic growth and job creation.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: Passenger rail services provide a viable alternative to road travel, reducing traffic congestion on highways and improving overall mobility.
- Environmental Sustainability: Rail transportation is a more environmentally friendly option compared to road transport, emitting fewer greenhouse gases and reducing air pollution.
- Improved Connectivity: The network connects major cities and towns, facilitating trade, tourism, and social interaction, fostering a sense of connectedness across the state.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its importance, Georgia’s railway network faces challenges, including:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many lines require upgrades and modernization to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Competition from Road Transport: The dominance of road transport poses a challenge to the rail industry, requiring innovative strategies to attract more freight and passenger traffic.
- Funding Constraints: Limited funding for infrastructure improvements and expansion can hinder the growth and modernization of the network.
These challenges also present opportunities for growth and innovation. Investing in infrastructure upgrades, promoting passenger rail services, and exploring new technologies can enhance the network’s efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Looking Ahead: Shaping the Future of Georgia’s Railway Network
Georgia’s railway network is poised for growth and modernization. The state government is investing in infrastructure improvements, expanding passenger rail services, and promoting the use of rail for freight transportation. Initiatives like the development of high-speed rail lines and the integration of new technologies can further enhance the network’s efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
FAQs about Georgia’s Railway Network
Q: What are the major freight carriers operating in Georgia?
A: The two primary freight carriers operating in Georgia are CSX and Norfolk Southern.
Q: What are the major passenger rail lines in Georgia?
A: Amtrak operates a passenger rail service connecting major cities like Atlanta, Savannah, and Jacksonville.
Q: How does Georgia’s railway network contribute to the state’s economy?
A: The network facilitates the efficient transportation of goods, supporting industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, driving economic growth and job creation.
Q: What are the challenges facing Georgia’s railway network?
A: Challenges include aging infrastructure, competition from road transport, and funding constraints.
Q: What are the future prospects for Georgia’s railway network?
A: The network is poised for growth and modernization, with investments in infrastructure improvements, expansion of passenger rail services, and the exploration of new technologies.
Tips for Using Georgia’s Railway Network
- Plan Ahead: Research schedules and routes in advance to ensure a smooth journey.
- Check for Updates: Stay informed about any service disruptions or delays.
- Purchase Tickets in Advance: Secure your tickets in advance, especially during peak travel times.
- Consider Intermodal Options: Explore the possibility of using intermodal facilities to combine rail and road transportation.
- Explore Local Lines: Discover the unique charm of short line railroads and their connections to local businesses and communities.
Conclusion
Georgia’s railway network stands as a testament to the state’s rich history and its commitment to innovation and progress. Its extensive network of tracks connects major cities, industries, and communities, facilitating trade, travel, and economic growth. As the state continues to invest in infrastructure improvements and explore new technologies, its railway network is poised to play an even more vital role in shaping Georgia’s future. By understanding its history, current state, and future prospects, we can appreciate the significance of this vital transportation infrastructure and its contribution to the state’s overall well-being.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Georgia’s Railway Network. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
