Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding FEMA Flood Map Changes
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding FEMA Flood Map Changes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding FEMA Flood Map Changes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding FEMA Flood Map Changes

The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) plays a crucial role in mitigating flood risk across the United States. One of its primary tools is the Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM), a detailed cartographic representation of flood hazard areas. These maps are instrumental in guiding flood insurance policies, development decisions, and community planning. However, the dynamic nature of our environment necessitates periodic updates to these maps, reflecting evolving flood risks.
The Evolution of Flood Risk: A Dynamic Process
Flood risk is not static; it is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, altered precipitation patterns, and increased intensity of storms are all contributing to heightened flood risk in many areas.
- Land Use Changes: Urbanization, deforestation, and other land-use modifications can alter drainage patterns and increase flood vulnerability.
- Infrastructure Improvements: New flood control structures, levees, and drainage systems can reduce flood risk in some areas while potentially shifting it to others.
- Improved Data and Modeling: Advancements in scientific understanding, data collection, and modeling techniques allow for more accurate assessments of flood hazards.
These factors necessitate regular updates to FEMA flood maps to ensure they accurately reflect current and projected flood risks.
Understanding FEMA Flood Map Updates: A Guide to the Process
FEMA undertakes a multi-step process to update its flood maps, ensuring accuracy and transparency:
- Data Collection: This involves gathering data from various sources, including aerial imagery, topographic surveys, historical flood records, and hydrological modeling.
- Flood Hazard Analysis: This phase involves analyzing the collected data to determine flood risk zones, flood depths, and flood frequencies for different areas.
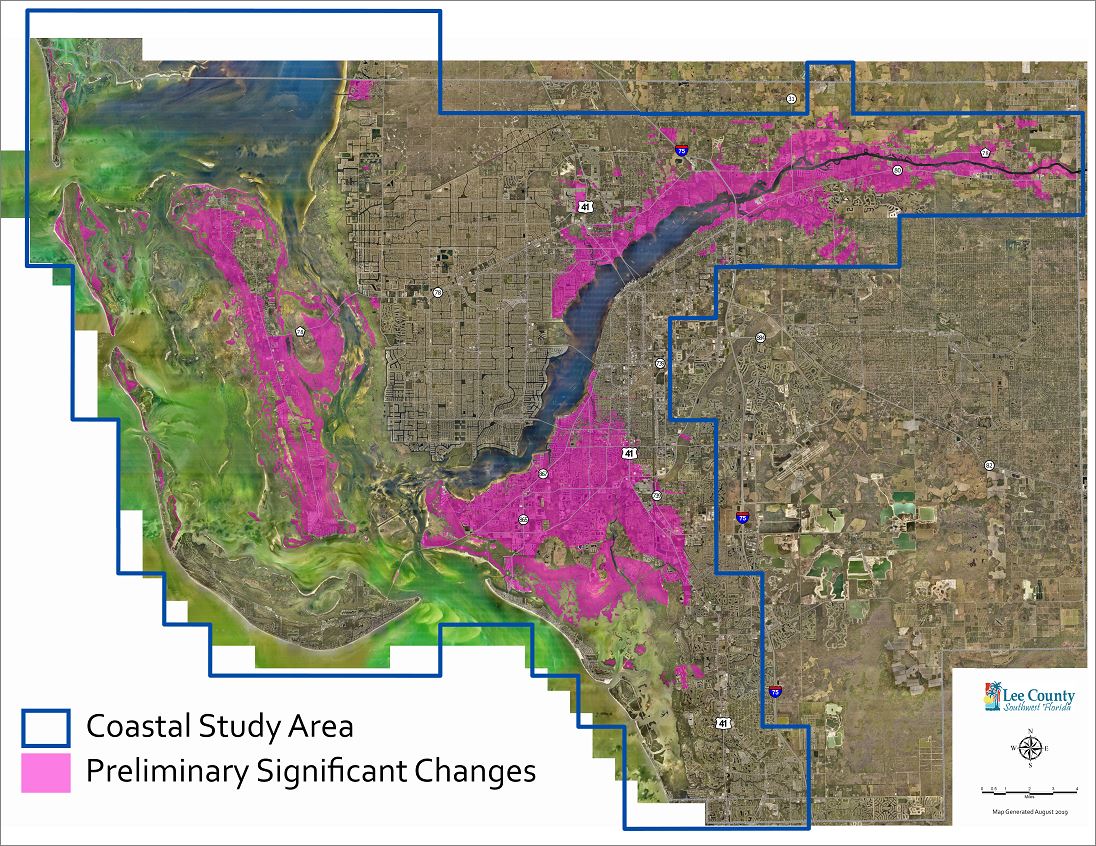
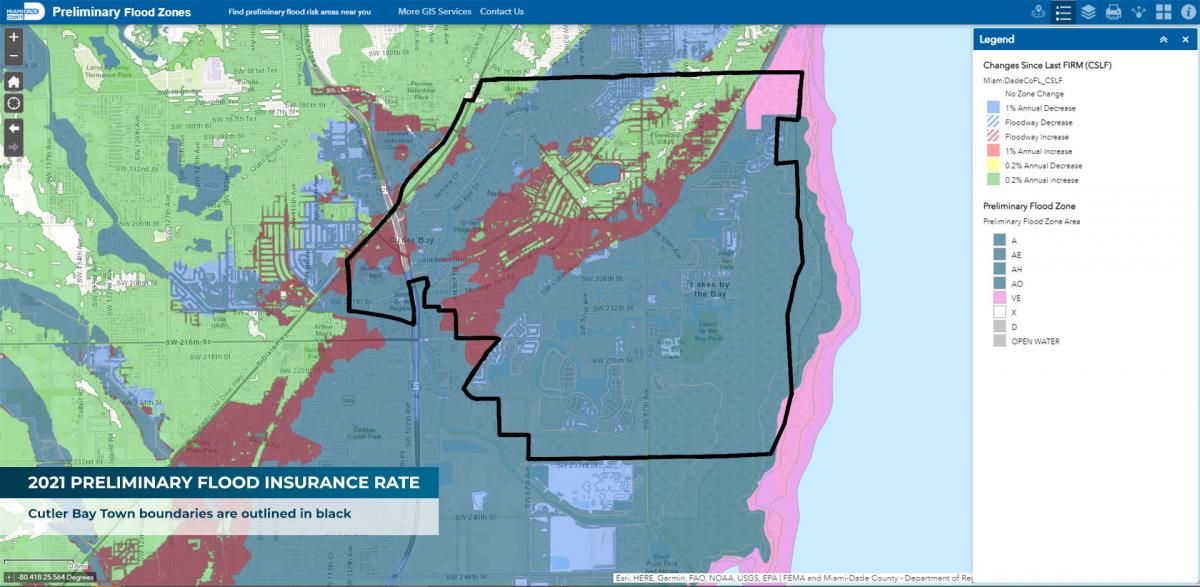
- Map Revision: Based on the hazard analysis, FEMA revises the existing flood maps, incorporating new information and delineating updated flood hazard areas.
- Public Review and Comment: FEMA encourages public participation in the map update process by providing opportunities for stakeholders to review the proposed changes and submit comments.
- Final Map Adoption: After considering public feedback, FEMA finalizes the revised flood maps, making them legally binding for flood insurance purposes.
The Impact of FEMA Flood Map Changes: Implications for Individuals and Communities
FEMA flood map changes can have significant implications for individuals, businesses, and communities:
- Flood Insurance Premiums: Property owners located in newly designated flood hazard areas may see an increase in their flood insurance premiums. Conversely, those whose properties are removed from high-risk areas may experience a reduction in premiums.
- Development Restrictions: New development within newly designated flood hazard areas may be subject to stricter building codes and regulations designed to minimize flood damage.
- Community Planning: FEMA flood maps serve as a vital tool for local governments and planning agencies to develop flood mitigation strategies, prioritize infrastructure investments, and guide land-use decisions.
- Disaster Preparedness: Updated flood maps provide crucial information for emergency responders, enabling them to better prepare for and respond to flood events.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About FEMA Flood Map Changes
Q: How often are FEMA flood maps updated?
A: FEMA updates flood maps on a cyclical basis, typically every 5-10 years, with the frequency varying depending on the region’s flood risk profile and the availability of new data. However, FEMA may also conduct more frequent updates in areas with significant changes in flood risk.
Q: How do I know if my property is located in a flood hazard area?
A: You can access FEMA’s online flood map viewer at FEMA’s website to check your property’s flood risk. You can also contact your local building department or floodplain administrator for assistance.
Q: What if I disagree with the flood map changes affecting my property?
A: FEMA provides opportunities for public review and comment during the map update process. If you disagree with the proposed changes, you can submit your concerns to FEMA. You may also have the option to appeal the map changes through a formal process.
Q: How can I prepare for potential flood risks?
A: Regardless of your property’s location on the flood map, taking proactive measures to prepare for potential floods is essential. This includes:
- Elevating valuables: Moving essential belongings to higher floors or storing them in waterproof containers.
- Installing flood barriers: Implementing measures like sandbags, flood doors, or flood vents to protect your property from floodwaters.
- Developing a flood evacuation plan: Identifying safe evacuation routes and assembling an emergency kit.
Tips for Navigating FEMA Flood Map Changes
- Stay Informed: Regularly check FEMA’s website and local news sources for updates on flood map changes.
- Engage in Public Comment: Participate in the public review process by submitting comments and attending public meetings.
- Consult with Experts: Seek advice from qualified professionals, such as floodplain managers, engineers, or insurance agents, regarding the implications of flood map changes.
- Consider Flood Insurance: Even if your property is not located in a high-risk area, flood insurance can provide valuable protection against potential flood damage.
Conclusion: Embracing a Future of Resilience
FEMA flood map changes are a reflection of our evolving understanding of flood risk and the need to adapt to a changing environment. By embracing these changes and incorporating them into our planning and decision-making processes, we can enhance our resilience to floods and build communities that are better prepared for the challenges of a dynamic future.
It is crucial to remember that FEMA flood maps are not static. They are living documents that evolve with our understanding of flood hazards and our ability to model and predict them. Staying informed about these changes and taking proactive steps to mitigate flood risk are essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals, businesses, and communities across the nation.
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/PPDIZXNFAZGWVNYCGLLF6Z6ZHQ.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding FEMA Flood Map Changes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!