Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps
- 3.1 Defining the Scope: What is a Right of Way?
- 3.2 Deciphering the Map: Components and Interpretation
- 3.3 The Importance of Right of Way Maps: A Multifaceted Impact
- 3.4 Common Applications: Navigating the Real World
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Navigating Right of Way Matters
- 3.7 Conclusion: Ensuring a Smooth Path Forward
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps
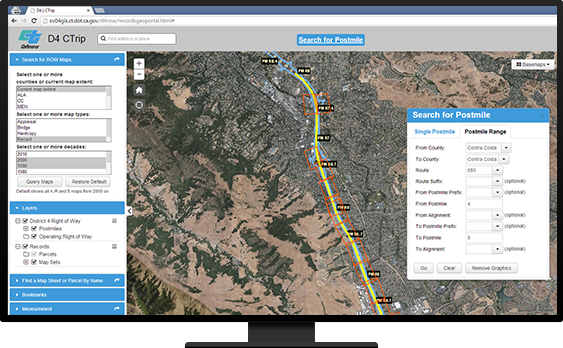
Right of way maps, often referred to as ROW maps, are essential tools in various sectors, particularly in land development, construction, and infrastructure projects. They provide a visual representation of legal access rights granted to entities, enabling them to utilize specific land areas for designated purposes. These maps serve as crucial reference points for navigating complex legal and physical terrains, ensuring projects are executed smoothly and within legal boundaries.
Defining the Scope: What is a Right of Way?
Before delving into the intricacies of right of way maps, it is crucial to understand the concept of right of way itself. In legal terms, right of way refers to the legal authority granted to an individual or entity to use a specific portion of land for a defined purpose. This right typically involves the ability to access, traverse, or utilize the land for activities such as:
- Construction and maintenance of utilities: Power lines, pipelines, telecommunication cables, and other essential infrastructure often require easements to traverse private property.
- Road and highway development: Road construction and maintenance necessitate rights of way to acquire land for roadbeds, shoulders, and other necessary features.
- Access to properties: Landlocked properties often rely on easements granted by neighboring landowners for vehicular or pedestrian access.
- Drainage and flood control: Construction of drainage ditches, culverts, and other flood control structures may require easements to cross private property.
- Public access: Parks, trails, and other recreational facilities often require easements for public access and enjoyment.
Deciphering the Map: Components and Interpretation
Right of way maps are meticulously crafted documents that convey a wealth of information. They typically include the following key elements:
- Property boundaries: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of the land parcels involved, highlighting the specific area where the right of way is granted.
- Right of way boundaries: The map defines the exact area covered by the right of way, outlining the permitted access zone for the designated purpose.
- Easement details: Specific information regarding the type of easement, its purpose, and any associated restrictions or limitations are clearly documented.
- Legal descriptions: The map incorporates legal descriptions of the property, including the lot and block numbers, providing a precise legal framework for the easement.
- Property ownership: The map identifies the owners of the property, both the entity granting the easement and the entity benefiting from it.
- Location details: The map clearly indicates the location of the right of way within the broader landscape, utilizing landmarks, coordinates, and other relevant reference points.
- Historical information: Maps may include historical details regarding previous easements or land use patterns, providing context for understanding the current right of way.
Interpreting these maps requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of legal terminology. While maps are visually intuitive, consulting with legal professionals or surveyors is often necessary to ensure accurate interpretation and compliance with legal requirements.
The Importance of Right of Way Maps: A Multifaceted Impact
Right of way maps play a critical role in various aspects of land development, construction, and infrastructure projects, contributing to:
- Legal clarity: Maps provide a clear and legally binding document outlining the rights and responsibilities associated with the right of way. This ensures compliance with land use regulations and minimizes potential disputes.
- Efficient planning: Maps facilitate informed planning by outlining the available access routes, potential limitations, and required infrastructure adjustments. This streamlines project execution and minimizes unforeseen challenges.
- Cost optimization: Clear understanding of the right of way boundaries and limitations allows for efficient utilization of resources, minimizing unnecessary land acquisition costs and construction delays.
- Environmental protection: Maps can incorporate environmental constraints and sensitive areas, ensuring projects are executed in a way that minimizes impact on the surrounding ecosystem.
- Public safety: Maps are essential for ensuring safe access and passage for pedestrians, vehicles, and utilities, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring public safety.
- Property value preservation: Maps help maintain the value of both the property granting the right of way and the property benefiting from it, by ensuring clear legal boundaries and mitigating potential disputes.
Common Applications: Navigating the Real World
Right of way maps are indispensable tools in various industries, including:
- Utilities: Power companies, gas companies, telecommunication providers, and other utility companies utilize right of way maps to plan and execute the installation and maintenance of their infrastructure.
- Transportation: Highway departments, municipalities, and private developers rely on these maps for road construction, bridge building, and other transportation infrastructure projects.
- Real estate development: Developers utilize right of way maps to navigate property access, plan infrastructure, and ensure compliance with zoning regulations.
- Environmental conservation: Conservation agencies use right of way maps to plan and manage access to protected areas, ensuring the preservation of natural resources and ecosystems.
- Emergency response: Emergency response agencies utilize right of way maps to understand access routes and potential hazards, ensuring efficient and effective response during disasters.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. What are the different types of easements?
Easements can be categorized based on their purpose and duration:
- Easement in gross: This type of easement grants access rights to a specific entity, regardless of land ownership. For example, a utility company may have an easement in gross to access a pipeline running through multiple properties.
- Easement appurtenant: This easement grants access rights to a specific property, allowing the owner to utilize adjacent land for a specific purpose. For example, an easement appurtenant might allow a property owner to access a public road through a neighboring property.
- Permanent easement: This type of easement grants access rights for an indefinite period, typically lasting as long as the property exists.
- Temporary easement: This easement grants access rights for a limited period, often for a specific construction project or activity.
2. How are right of way maps created?
Right of way maps are typically created by professional surveyors and land surveyors. The process involves:
- Site survey: A comprehensive survey of the land is conducted to determine the property boundaries, existing structures, and potential access routes.
- Legal research: Legal documents are reviewed to identify existing easements, property ownership, and relevant regulations.
- Map creation: The collected data is used to create a detailed map depicting the right of way boundaries, legal descriptions, and relevant information.
- Review and approval: The map is reviewed by legal professionals and relevant authorities to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal requirements.
3. How can I obtain a copy of a right of way map?
Obtaining a copy of a right of way map typically involves contacting the entity holding the easement or the relevant government agency. For example, you can request a copy of a utility easement map from the utility company, or a copy of a road easement map from the highway department.
4. What are the legal consequences of violating a right of way?
Violating a right of way can have serious legal consequences, including:
- Injunctions: Courts may issue injunctions prohibiting further violations of the easement.
- Damages: The entity holding the easement may seek monetary damages for any losses incurred due to the violation.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, violating a right of way may result in criminal charges, especially if it involves obstruction of access or damage to infrastructure.
5. How can I negotiate the terms of a right of way easement?
Negotiating the terms of an easement can be complex and requires careful consideration of legal and financial factors. It is highly recommended to consult with an attorney and a real estate professional to ensure your interests are protected.
Tips for Navigating Right of Way Matters
- Consult with professionals: Engage with legal professionals, surveyors, and other experts to ensure accurate interpretation of maps and compliance with legal requirements.
- Thorough research: Review existing records, maps, and legal documents to understand the history and scope of the right of way.
- Clear communication: Maintain open and transparent communication with all parties involved, including property owners, easement holders, and relevant authorities.
- Negotiate carefully: If necessary, negotiate the terms of the easement to ensure your interests are protected and the project remains feasible.
- Document everything: Maintain detailed records of all communications, negotiations, and agreements related to the right of way.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Smooth Path Forward
Right of way maps are essential tools for navigating the complexities of land development, construction, and infrastructure projects. They provide a clear visual representation of legal access rights, ensuring projects are executed within legal boundaries, minimizing disputes, and optimizing resources. By understanding the components of these maps, their importance, and their applications, individuals and organizations can navigate the legal and physical landscapes effectively, facilitating successful projects and safeguarding the interests of all stakeholders.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Right of Way Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!