Navigating Boston: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Tram Network
Related Articles: Navigating Boston: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Tram Network
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Boston: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Tram Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Boston: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Tram Network
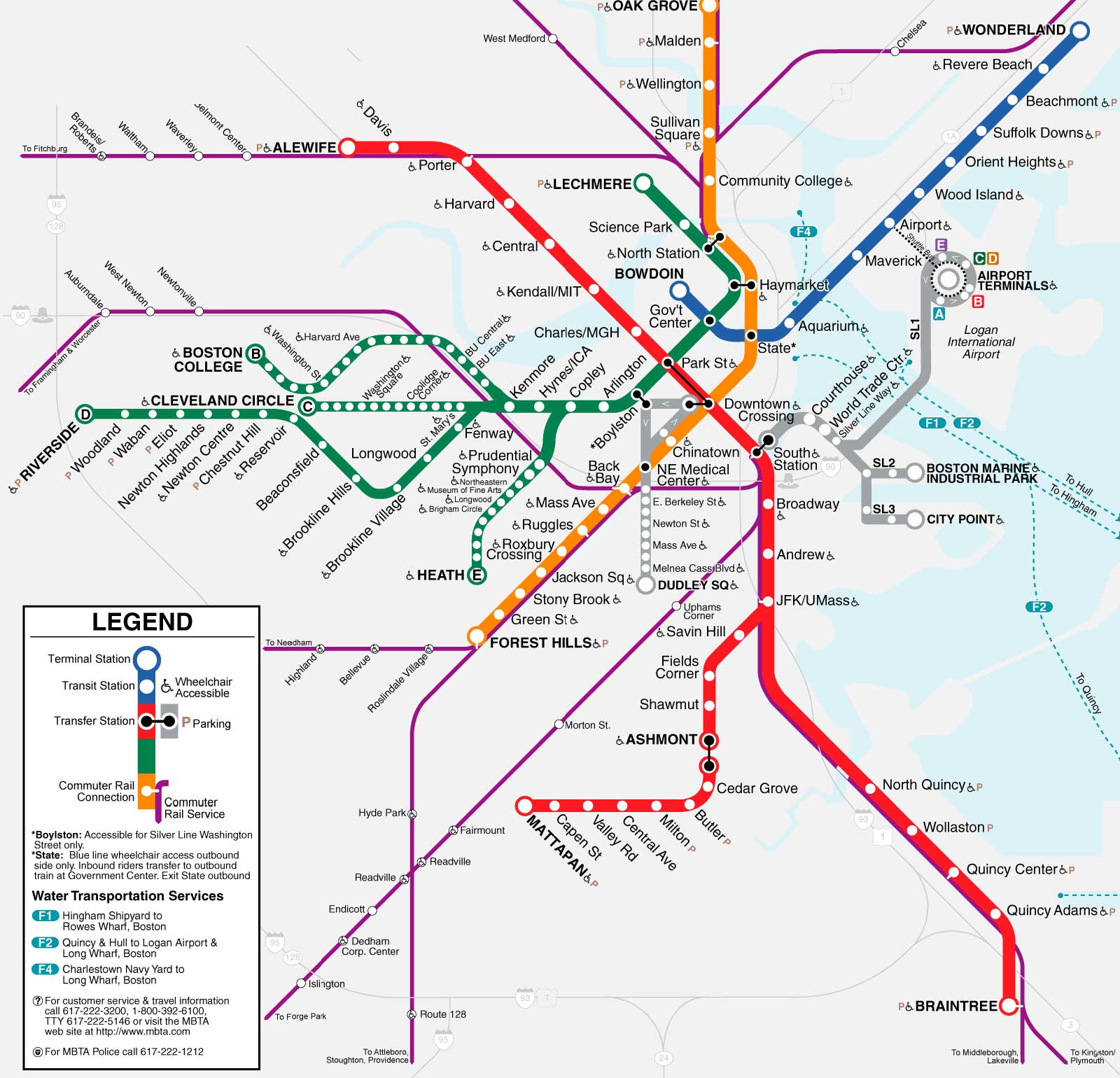
Boston, a city steeped in history and vibrant culture, offers a diverse transportation network that caters to the needs of its residents and visitors. Among these options, the city’s tram system, commonly known as the "T", stands out as a reliable and efficient mode of public transportation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Boston’s tram network, exploring its history, routes, fares, and benefits, providing a clear understanding of its importance in the city’s infrastructure.
A Historical Journey: The Evolution of Boston’s Tram System
The origins of Boston’s tram system can be traced back to the late 19th century, with the introduction of horse-drawn streetcars. The first electric streetcar line commenced operation in 1889, ushering in a new era of urban transportation. Over the years, the system underwent significant expansions and transformations, evolving into the modern-day "T" we know today.
In 1967, the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) was established to oversee the operations of the city’s public transportation system, including the tram network. The MBTA has played a crucial role in modernizing the system, introducing new lines, and upgrading existing infrastructure.
Understanding the "T": A Network of Lines and Routes
Boston’s tram network comprises multiple lines, each serving specific areas of the city and its surrounding suburbs. The most prominent lines include:
- Green Line: The Green Line, a sprawling network with three branches (B, C, D, E), is the longest tram line in the United States. It traverses the city from east to west, connecting downtown Boston with neighborhoods like Brookline, Newton, and Cambridge.
- Red Line: The Red Line is a vital artery connecting the northern suburbs with downtown Boston, passing through popular areas like Harvard Square and Park Street.
- Orange Line: The Orange Line runs through the city from north to south, connecting downtown Boston with areas like Jamaica Plain and Oak Grove.
- Blue Line: The Blue Line serves the northern waterfront, connecting downtown Boston with areas like Revere and Wonderland.
Navigating the "T": A Guide to Fares, Stations, and Transfers
To utilize the "T", passengers require a CharlieCard, a contactless fare card that can be purchased at designated stations. The fare structure is based on a zone system, with different fares for different zones. For those planning multiple trips, the CharlieTicket offers unlimited travel within a specific time frame.
The "T" boasts an extensive network of stations, strategically located throughout the city and its suburbs. Each station provides clear signage and information displays to guide passengers. Transfers between different lines are seamlessly facilitated at designated stations, allowing for convenient travel across the city.
Beyond Transportation: The Significance of Boston’s Tram Network
Boston’s tram network extends far beyond a mere transportation system; it plays a pivotal role in shaping the city’s landscape and influencing its social and economic fabric.
- Reducing Congestion: The "T" serves as a vital alternative to private vehicles, alleviating traffic congestion on the city’s streets. This reduction in congestion contributes to improved air quality and reduced travel times for all road users.
- Enhancing Accessibility: The "T" provides accessible transportation for individuals with disabilities, with dedicated wheelchair-accessible trains and stations. This ensures inclusivity and promotes equal access to opportunities for all members of the community.
- Economic Growth: The "T" fosters economic growth by connecting residents and businesses across the city, facilitating commerce and job opportunities. It enhances the efficiency of transportation for workers and commuters, boosting productivity and economic activity.
- Environmental Sustainability: By encouraging public transportation, the "T" contributes to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable urban development. This aligns with the city’s commitment to environmental responsibility and combatting climate change.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Boston’s Tram Network
Q: What are the operating hours of the "T" ?
A: The "T" operates 24 hours a day, seven days a week, with varying frequency depending on the time of day and line.
Q: How can I obtain a CharlieCard?
A: CharlieCards can be purchased at designated vending machines located at stations or online through the MBTA website.
Q: Are there any discounts available for seniors or students?
A: Yes, the MBTA offers discounted fares for seniors (65 and older) and students with valid identification.
Q: What are the safety measures in place on the "T"?
A: The MBTA prioritizes passenger safety and employs a range of measures, including security personnel, surveillance cameras, and emergency response protocols.
Q: How can I stay updated on service disruptions or delays?
A: The MBTA provides real-time updates on service disruptions and delays through its website, mobile app, and social media channels.
Tips for Navigating Boston’s Tram Network
- Plan Your Trip: Before embarking on your journey, consult the MBTA website or mobile app to plan your route and check for any service disruptions.
- Allow Ample Time: Factor in potential delays or unexpected circumstances when planning your travel time.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Stay alert and be mindful of your belongings, especially during peak hours or in crowded areas.
- Use the "T" App: The MBTA’s mobile app provides real-time information on train locations, arrival times, and service disruptions.
- Follow Safety Guidelines: Adhere to all safety guidelines posted at stations and on trains, including respecting personal space and avoiding distractions.
Conclusion: Boston’s Tram Network – A Vital Component of Urban Life
Boston’s tram network, the "T", stands as a testament to the city’s commitment to efficient and accessible public transportation. Its extensive network, reliable service, and dedication to safety and sustainability make it an integral part of urban life in Boston. From connecting residents to their workplaces to facilitating tourism and cultural exploration, the "T" plays a vital role in shaping the city’s dynamism and fostering a sense of community. As Boston continues to grow and evolve, the "T" remains a vital infrastructure, ensuring the city’s continued success and progress.


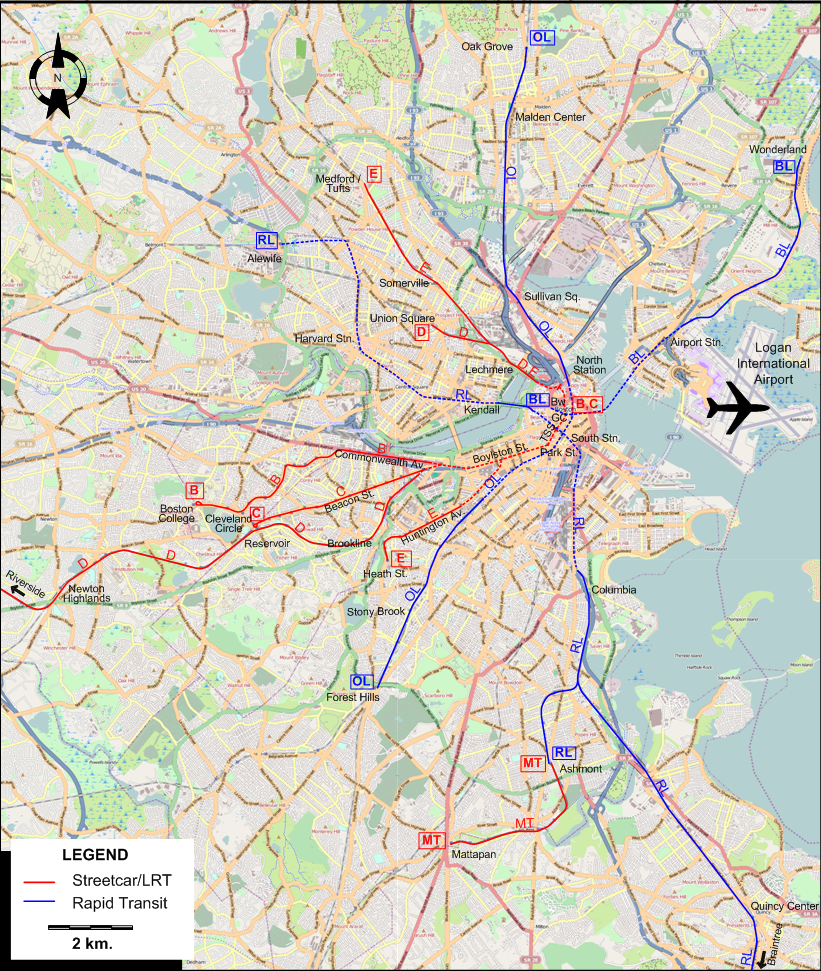

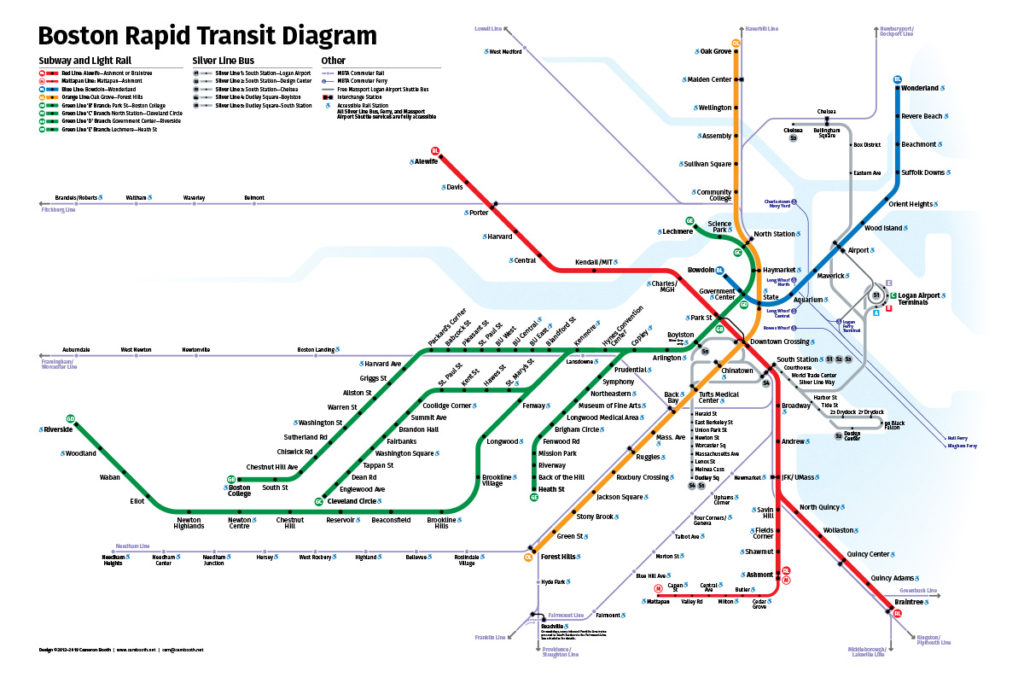



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Boston: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Tram Network. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!