Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping
Related Articles: Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping
- 3.1 What is Gut Mapping?
- 3.2 How Does Gut Mapping Work?
- 3.3 Benefits of Gut Mapping
- 3.4 Types of Gut Mapping Tests
- 3.5 Factors Influencing Gut Microbiome Composition
- 3.6 Gut Mapping FAQs
- 3.7 Gut Mapping Tips
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping
The human gut, a complex ecosystem teeming with trillions of microorganisms, plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being. This intricate world, known as the gut microbiome, is composed of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microscopic organisms that interact with our bodies in profound ways. Understanding the composition and function of this microbial community is crucial for maintaining optimal health, and this is where gut mapping comes into play.
What is Gut Mapping?
Gut mapping, also referred to as gut microbiome analysis or gut microbiome testing, is a process that provides a detailed snapshot of the microbial composition and activity within the digestive tract. It involves analyzing a stool sample, which contains a representative sample of the gut microbiome, to identify the different types of microorganisms present and their relative abundance.
How Does Gut Mapping Work?
Gut mapping utilizes advanced technologies, primarily next-generation sequencing (NGS), to analyze the DNA of the microorganisms present in the stool sample. This process involves extracting DNA from the sample, amplifying specific regions of the DNA, and sequencing the amplified DNA fragments. By comparing the sequences to a vast database of known microbial species, researchers can identify the different types of bacteria, fungi, and viruses present in the gut.
Benefits of Gut Mapping
The benefits of gut mapping extend beyond simply identifying the microorganisms residing within our gut. It offers valuable insights into various aspects of our health, including:
1. Identifying Dysbiosis:
Gut mapping can identify imbalances in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, which can contribute to a range of health issues. By analyzing the relative abundance of different microbial species, researchers can determine if certain beneficial bacteria are depleted or if harmful bacteria are overrepresented.
2. Tailoring Nutritional Strategies:
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Gut mapping can identify specific deficiencies or imbalances in microbial activity that may affect nutrient utilization. This information can be used to tailor dietary recommendations to optimize nutrient absorption and overall health.
3. Assessing Risk Factors for Diseases:
Emerging research suggests a strong link between the gut microbiome and various chronic diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), obesity, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Gut mapping can help identify individuals at risk for these conditions and guide personalized interventions to mitigate these risks.
4. Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness:
Gut mapping can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for various gut-related conditions, such as antibiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). By analyzing the microbial composition before and after treatment, researchers can assess the impact of the intervention on the gut microbiome and its potential contribution to improved health outcomes.
5. Personalized Probiotic Recommendations:
Gut mapping can identify specific strains of bacteria that are depleted in an individual’s gut. This information can be used to recommend personalized probiotic supplements that target specific microbial imbalances and promote gut health.
Types of Gut Mapping Tests
Several types of gut mapping tests are available, each with its own strengths and limitations:
1. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing:
This method focuses on a specific gene (16S rRNA) found in bacteria, which is highly conserved across different species. By analyzing the 16S rRNA gene sequences, researchers can identify the different bacterial species present in the gut. This approach is cost-effective and provides a good overview of the bacterial composition.
2. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing (WGS):
WGS analyzes the entire genome of all microorganisms present in the stool sample, providing a comprehensive view of the microbial community, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This approach offers a more detailed analysis but is more expensive than 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
3. Metabolite Analysis:
This method analyzes the metabolites produced by the gut microbiome, providing insights into the metabolic activity of the microbial community. Metabolite analysis can identify potential imbalances in nutrient metabolism and provide insights into the overall health of the gut microbiome.
Factors Influencing Gut Microbiome Composition
The composition and function of the gut microbiome are influenced by a variety of factors, including:
1. Genetics:
Genetics plays a role in shaping the initial composition of the gut microbiome during early childhood. However, the microbiome is highly dynamic and can be influenced by environmental factors throughout life.
2. Diet:
Diet is a major determinant of gut microbiome composition. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, while a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the microbial balance.
3. Lifestyle:
Lifestyle factors, such as exercise, sleep, stress levels, and exposure to environmental toxins, can also influence the gut microbiome. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins can contribute to a healthier gut microbiome.
4. Medications:
Antibiotics, particularly broad-spectrum antibiotics, can have a significant impact on the gut microbiome, disrupting the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria. Other medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also affect the gut microbiome.
5. Age:
The gut microbiome changes throughout life, with significant shifts occurring during infancy, adolescence, and aging. These changes can influence susceptibility to certain diseases and health outcomes.
Gut Mapping FAQs
1. Is gut mapping safe?
Gut mapping is generally considered safe, as it involves analyzing a stool sample, which is a non-invasive procedure. However, it is important to choose a reputable laboratory with proper safety protocols and quality control measures.
2. Who should consider gut mapping?
Individuals with digestive issues, chronic diseases, or a family history of certain health conditions may benefit from gut mapping. Those interested in optimizing their health, improving their dietary habits, or understanding the impact of lifestyle factors on their gut microbiome may also find it beneficial.
3. How often should I get a gut map done?
The frequency of gut mapping depends on individual needs and goals. Some individuals may benefit from a single test to gain a baseline understanding of their gut microbiome, while others may require repeat testing to monitor the effectiveness of interventions or track changes over time.
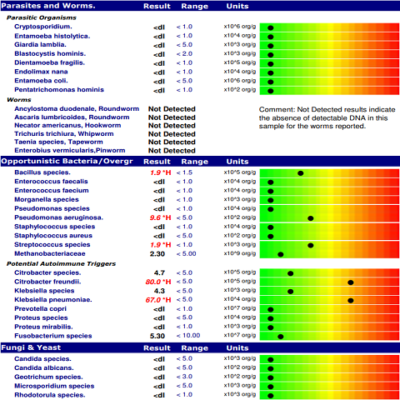
4. How do I interpret the results of a gut map?
Interpreting gut mapping results requires specialized expertise. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified practitioner who can provide personalized guidance based on the specific findings.
5. What are the limitations of gut mapping?
Gut mapping is a powerful tool, but it has limitations. It provides a snapshot of the gut microbiome at a specific point in time, and it may not capture the full complexity of the microbial ecosystem. Additionally, the interpretation of results can be complex and requires careful consideration of individual factors.
Gut Mapping Tips
1. Choose a Reputable Laboratory:
Select a laboratory with a proven track record of accuracy, reliability, and adherence to industry standards.
2. Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
Discuss your reasons for considering gut mapping with a healthcare professional to determine if it is appropriate for your individual needs and goals.
3. Follow Sample Collection Instructions Carefully:
Follow the laboratory’s instructions for collecting and storing the stool sample to ensure accurate results.
4. Consider Lifestyle Modifications:
After receiving your gut mapping results, work with a healthcare professional or a qualified practitioner to develop personalized recommendations for dietary and lifestyle modifications to improve gut health.
5. Be Patient and Consistent:
Improving gut health requires time and consistent effort. Be patient with the process and focus on making sustainable changes to your diet and lifestyle.
Conclusion
Gut mapping offers a valuable tool for understanding the complex ecosystem of the human gut microbiome. By providing insights into the composition and function of this microbial community, it can help identify dysbiosis, tailor nutritional strategies, assess risk factors for diseases, monitor treatment effectiveness, and guide personalized probiotic recommendations. However, it is important to approach gut mapping with a balanced perspective, understanding its limitations and seeking guidance from qualified healthcare professionals. By embracing a holistic approach to gut health, encompassing diet, lifestyle, and personalized interventions, we can unlock the potential of our gut microbiome and cultivate a healthier and more vibrant life.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Guide to Gut Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!