Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Analysis
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Analysis

Weather, a force of nature that shapes our lives, is a constant subject of curiosity and concern. From planning outdoor activities to preparing for potential storms, understanding weather patterns is crucial. While technology provides us with instant weather updates, the ability to interpret weather maps remains an invaluable skill, offering a deeper understanding of the forces at play and empowering informed decision-making.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of analyzing weather maps, focusing on the essential elements that reveal the story behind the forecast.
Understanding the Basics: A Visual Language of Weather
Weather maps, often referred to as synoptic charts, are visual representations of meteorological data collected across a specific region at a given time. They serve as a snapshot of atmospheric conditions, providing insights into temperature, pressure, wind, precipitation, and other key factors influencing weather patterns.
Key Elements of Weather Maps:
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines reveal areas of high pressure (anticyclones) and low pressure (cyclones), which are fundamental to understanding weather patterns.
- Isotherms: Lines connecting points of equal temperature. These lines provide a visual representation of temperature variations across the map, highlighting areas of warmth and cold.
- Fronts: Boundaries between different air masses. These lines indicate areas of potential instability and weather changes, such as thunderstorms, precipitation, and shifts in temperature.
- Wind Barbs: Symbols depicting wind speed and direction. These barbs provide information about the movement of air, which can influence temperature, precipitation, and cloud formation.
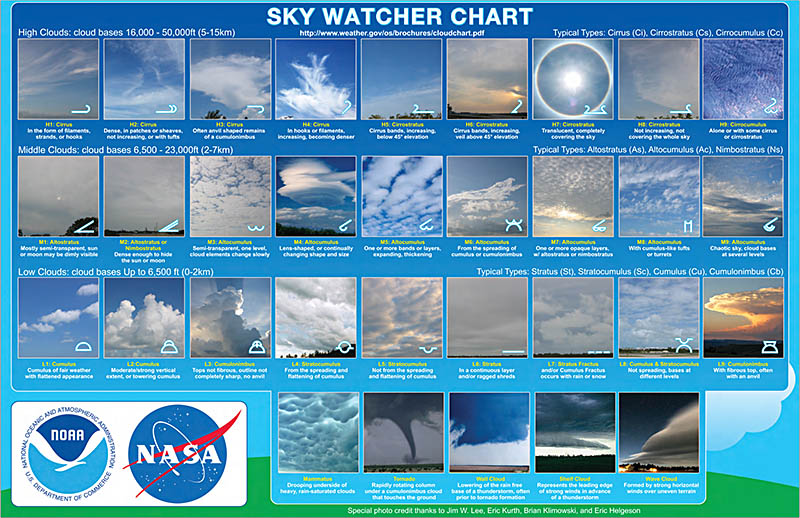
- Symbols: Icons representing various weather phenomena, such as precipitation, cloud cover, and visibility. These symbols provide additional context for interpreting the overall weather situation.
Decoding the Message: A Step-by-Step Guide to Weather Map Analysis
-
Identify the Date and Time: The first step in analyzing a weather map is to note the date and time of the data collection. This information is crucial for understanding the current weather conditions and predicting potential changes.
-
Analyze Pressure Systems: Identify high and low-pressure areas by observing the isobars. High-pressure systems are associated with clear skies, calm conditions, and descending air. Conversely, low-pressure systems bring unsettled weather, including clouds, precipitation, and rising air.
-
Locate Fronts: Identify the location and type of fronts on the map. Cold fronts are characterized by a sharp temperature drop, strong winds, and potential for thunderstorms. Warm fronts bring gradual warming, increasing humidity, and light precipitation. Stationary fronts represent a boundary between two air masses that are not moving.
-
Interpret Wind Patterns: Observe the direction and speed of the wind using wind barbs. Wind direction indicates the direction from which the wind is blowing, while wind speed is represented by the length and number of barbs.
-
Examine Weather Symbols: Analyze the various symbols on the map to understand the current weather conditions. These symbols provide information on precipitation type, cloud cover, visibility, and other relevant factors.
The Importance of Understanding Weather Maps:
- Informed Decision-Making: By analyzing weather maps, individuals can make informed decisions regarding outdoor activities, travel plans, and preparedness for potential weather events.
- Enhanced Safety: Understanding weather patterns can help individuals take necessary precautions to ensure safety during severe weather events, such as thunderstorms, tornadoes, or hurricanes.
- Improved Agricultural Practices: Farmers rely on weather maps to optimize crop planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules, ensuring optimal yields and minimizing potential losses.
- Effective Resource Management: Weather maps are essential for managing water resources, planning power generation, and mitigating the impact of extreme weather events on infrastructure.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Weather Map Analysis
Q: What is the difference between a surface weather map and an upper-level weather map?
A: Surface weather maps depict conditions at ground level, providing information on temperature, pressure, wind, and precipitation. Upper-level weather maps show atmospheric conditions at higher altitudes, offering insights into jet streams, air masses, and potential for severe weather events.
Q: How can I access weather maps?
A: Weather maps are readily available through various sources, including:
- National Weather Service Websites: The National Weather Service (NWS) provides detailed weather maps and forecasts for the United States.
- Weather Apps: Numerous weather apps, such as AccuWeather, The Weather Channel, and Weather Underground, offer interactive weather maps and forecasts.
- Online Weather Resources: Websites like Weather.com, NOAA, and Environment Canada provide access to various weather maps and data.
Q: What are some tips for interpreting weather maps?
A:
- Focus on the Key Elements: Pay attention to isobars, isotherms, fronts, wind barbs, and weather symbols to gain a comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
- Consider the Context: Analyze weather maps within the broader context of geographical location, season, and historical weather patterns.
- Utilize Multiple Sources: Refer to multiple weather maps and forecasts from different sources to obtain a more complete picture of the weather situation.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice analyzing weather maps, the more proficient you will become in interpreting their information.
Conclusion: Mastering the Language of the Skies
Weather maps are powerful tools that provide a window into the complex and dynamic world of meteorology. By understanding the key elements and interpreting the information presented, individuals can gain valuable insights into current weather conditions and potential future changes. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making, enhances safety, and contributes to a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the atmosphere. As we continue to rely on weather forecasts for a wide range of activities, mastering the language of weather maps remains an invaluable skill for navigating the ever-changing forces of nature.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sky-cover_key-58b740215f9b5880804caa18.png)



![[44+] Weather Map With Cold And Warm Fronts](http://lakeeriewx.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Figure_01.gif)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!