A Comprehensive Look at Europe’s Resource Map: Unveiling the Continent’s Wealth and Challenges
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Europe’s Resource Map: Unveiling the Continent’s Wealth and Challenges
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Europe’s Resource Map: Unveiling the Continent’s Wealth and Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Europe’s Resource Map: Unveiling the Continent’s Wealth and Challenges
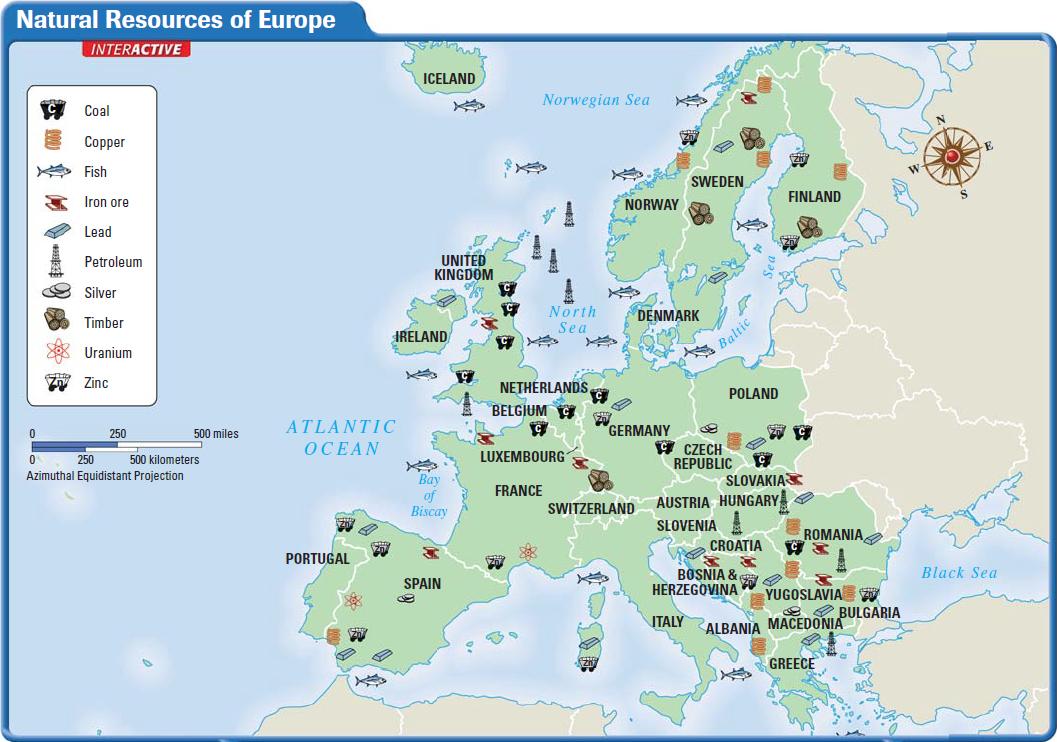
Europe, a continent renowned for its rich history, diverse cultures, and vibrant economies, also boasts a complex and varied resource landscape. Understanding the distribution and utilization of resources within Europe is crucial for comprehending the continent’s economic development, environmental sustainability, and geopolitical influence. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Europe’s resource map, exploring the key resources, their distribution, and the challenges and opportunities associated with their management.
I. Key Resources of Europe
Europe’s resource map is characterized by a diverse array of resources, ranging from abundant renewable energy sources to significant reserves of fossil fuels, minerals, and agricultural products.
A. Energy Resources:
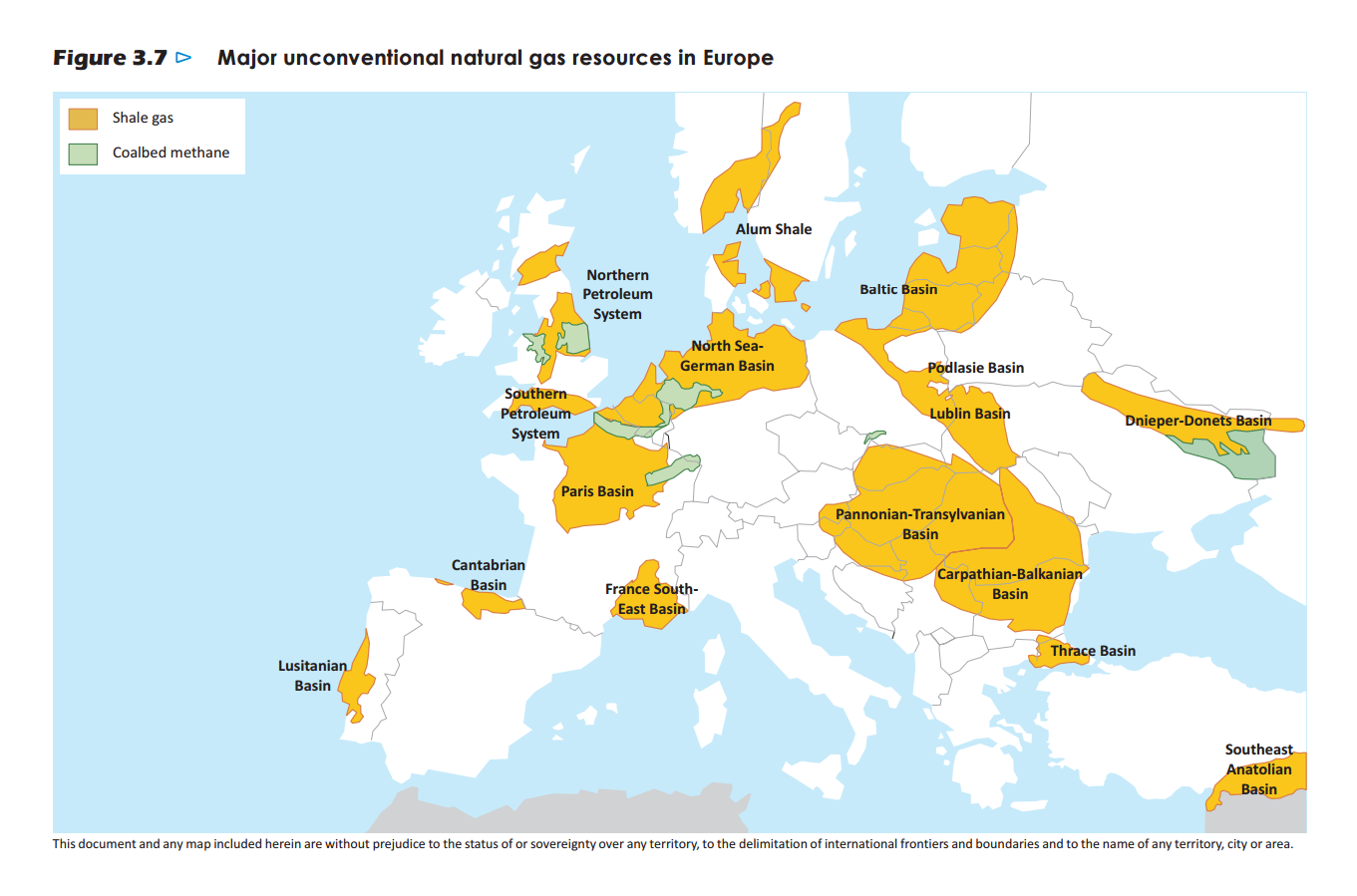
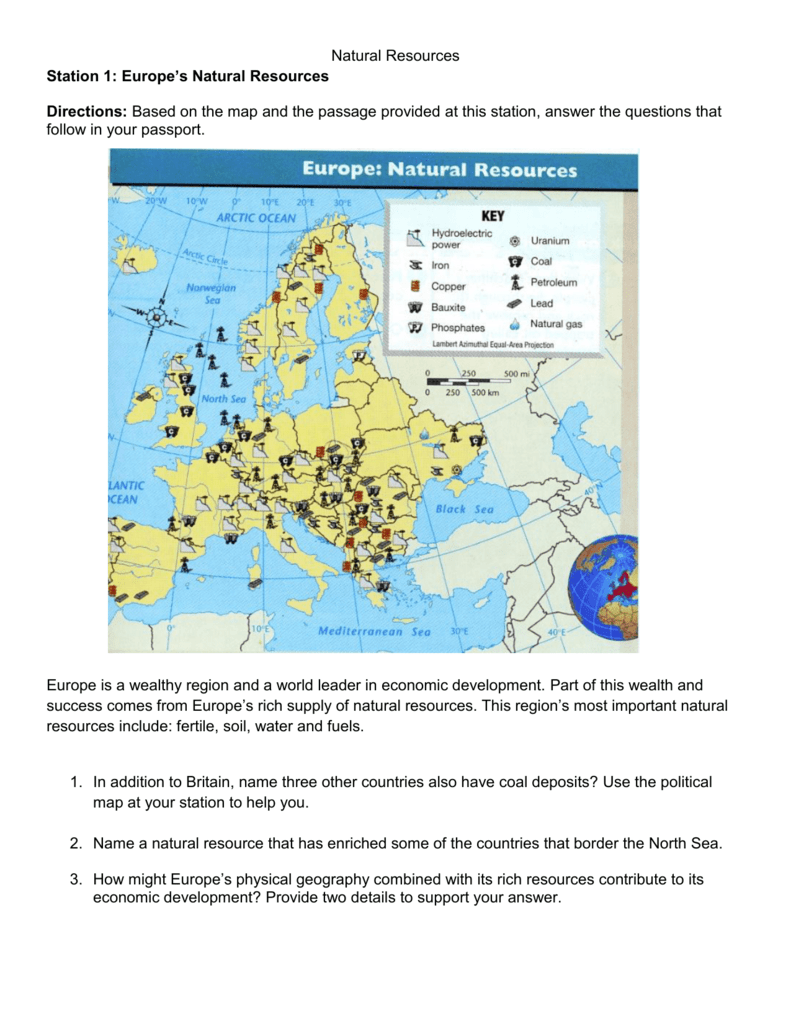
- Fossil Fuels: While Europe’s reliance on fossil fuels is declining, they remain crucial energy sources. The continent holds significant reserves of natural gas, particularly in the North Sea and Russia. Coal, primarily found in Germany, Poland, and the Czech Republic, is also a significant energy source, albeit facing environmental concerns.
- Renewable Energy: Europe is a global leader in renewable energy development, driven by ambitious climate targets. Wind energy is abundant in northern and western Europe, while solar energy potential is high in southern regions. Hydropower is also significant, particularly in the Alps and Scandinavia. Geothermal energy, while less prevalent, is being explored in Iceland and other countries.
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear power remains a significant energy source in several European countries, notably France, which derives a large proportion of its electricity from nuclear plants. However, concerns over nuclear safety and waste disposal have led to a decline in new nuclear projects.
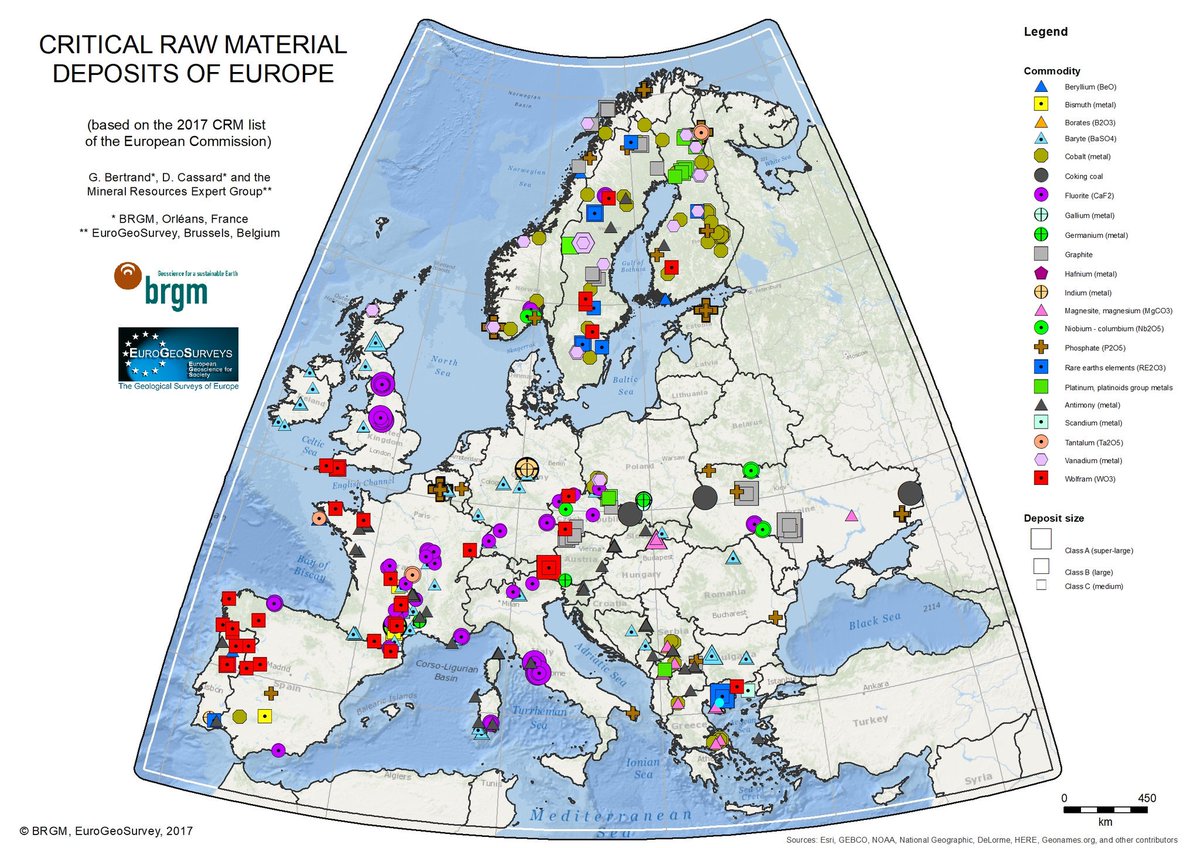
B. Mineral Resources:
Europe possesses significant mineral resources, essential for various industries.
- Iron Ore: The continent holds substantial iron ore deposits, primarily in Sweden, France, and Ukraine. These deposits are crucial for steel production, a cornerstone of European manufacturing.
- Aluminum: Bauxite, the raw material for aluminum production, is found in significant quantities in Hungary, Greece, and Romania. Aluminum is vital for various industries, from transportation to construction.
- Copper: Europe possesses copper reserves, particularly in Poland, Romania, and Spain. Copper is essential for electrical wiring, plumbing, and various industrial applications.
- Other Minerals: Europe also has deposits of other minerals, including zinc, lead, nickel, and gold, which are essential for various industries.
C. Agricultural Resources:
Europe’s fertile soils and temperate climate support a diverse agricultural sector.
- Cereals: Wheat, barley, and maize are major crops grown across Europe, providing food security and supporting animal feed production.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Europe is a major producer of fruits and vegetables, with significant production of grapes, apples, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes, and onions.
- Dairy Products: Europe is a major dairy producer, with significant production of milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Meat Production: The continent is a major producer of beef, pork, and poultry, contributing significantly to global meat markets.
II. Distribution of Resources: A Geographical Perspective
Europe’s resource distribution is uneven, with significant regional variations.
- Western Europe: This region is characterized by abundant renewable energy resources, particularly wind and solar power. It also holds significant reserves of natural gas in the North Sea and substantial mineral resources, including iron ore, aluminum, and copper.
- Eastern Europe: This region is rich in fossil fuels, particularly natural gas and coal, with significant reserves in Russia and Ukraine. It also holds substantial mineral resources, including iron ore and aluminum.
- Southern Europe: This region is renowned for its agricultural production, particularly fruits, vegetables, and olive oil. It also has significant potential for solar energy.
- Northern Europe: This region is rich in renewable energy resources, particularly wind and hydropower. It also holds significant reserves of iron ore and timber.
III. Challenges and Opportunities
While Europe boasts a diverse resource base, several challenges and opportunities arise from its management.
A. Challenges:
- Resource Depletion: The continued extraction of non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, raises concerns about resource depletion and environmental sustainability.
- Environmental Concerns: The extraction and utilization of resources often lead to environmental degradation, including pollution, deforestation, and habitat loss.
- Resource Security: Europe’s dependence on external sources for certain resources, such as oil and gas, poses risks to its energy security.
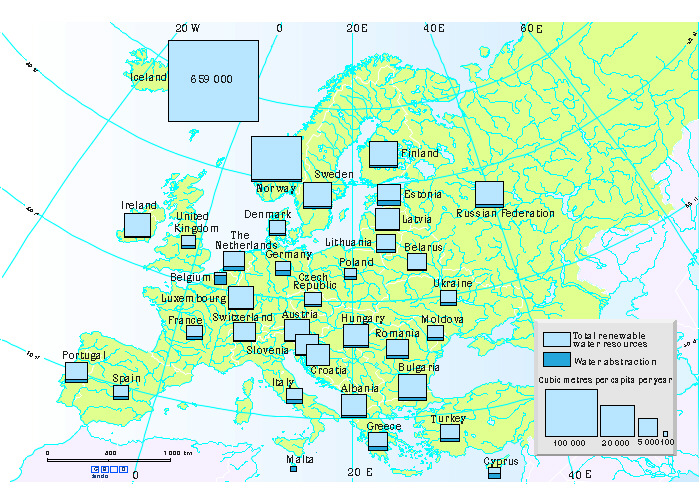
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting resource availability and utilization, leading to water scarcity, extreme weather events, and changes in agricultural yields.
B. Opportunities:
- Renewable Energy Development: Europe has the potential to become a global leader in renewable energy, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
- Resource Efficiency: Improving resource efficiency through innovation and technological advancements can minimize waste and reduce environmental impact.
- Circular Economy: Transitioning to a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled, can reduce dependence on virgin materials and minimize environmental footprint.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts with other countries can address resource scarcity, enhance energy security, and promote sustainable resource management.
IV. The Importance of Europe’s Resource Map
Understanding Europe’s resource map is vital for several reasons:
- Economic Development: The availability and utilization of resources are crucial for economic growth, supporting various industries and creating employment opportunities.
- Environmental Sustainability: Sustainable resource management is essential for protecting the environment, mitigating climate change, and ensuring the long-term well-being of future generations.
- Geopolitical Influence: Europe’s resource wealth and dependence on external sources influence its geopolitical relationships with other countries.
- Energy Security: Ensuring access to reliable and sustainable energy sources is critical for Europe’s economic stability and national security.
V. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the most important resources in Europe?
A: Europe possesses a wide range of resources, but key ones include fossil fuels (natural gas, coal), renewable energy (wind, solar, hydropower), minerals (iron ore, aluminum, copper), and agricultural products (cereals, fruits, vegetables, dairy).
Q2: How is Europe’s resource distribution uneven?
A: Europe’s resource distribution is uneven, with Western Europe possessing abundant renewable energy and mineral resources, Eastern Europe rich in fossil fuels, Southern Europe known for its agricultural production, and Northern Europe abundant in wind and hydropower.
Q3: What are the main challenges associated with Europe’s resource management?
A: Challenges include resource depletion, environmental concerns, resource security, and the impact of climate change on resource availability and utilization.
Q4: What opportunities exist for sustainable resource management in Europe?
A: Opportunities include renewable energy development, resource efficiency improvements, transition to a circular economy, and international cooperation for resource security and sustainable management.
Q5: Why is understanding Europe’s resource map important?
A: Understanding the continent’s resource map is crucial for economic development, environmental sustainability, geopolitical influence, and energy security.
VI. Tips for Understanding Europe’s Resource Map
- Consult reliable sources: Utilize reputable organizations like the European Commission, the International Energy Agency, and the World Bank for accurate data and analysis.
- Explore regional differences: Analyze the resource distribution and utilization patterns across different regions of Europe to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Consider environmental impacts: Evaluate the environmental consequences of resource extraction and utilization, including pollution, deforestation, and habitat loss.
- Track policy developments: Stay informed about European Union policies and regulations related to resource management, energy transition, and environmental protection.
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze the challenges and opportunities associated with resource management in Europe, considering both economic and environmental aspects.
VII. Conclusion
Europe’s resource map is a complex and dynamic landscape, reflecting the continent’s economic, environmental, and geopolitical realities. Understanding the distribution, utilization, and management of resources is crucial for ensuring sustainable development, mitigating environmental challenges, and fostering economic prosperity. By embracing innovation, promoting international cooperation, and implementing effective policies, Europe can harness its resource potential while safeguarding its environment for future generations.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Europe’s Resource Map: Unveiling the Continent’s Wealth and Challenges. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!