A Comparative Look at Alabama and Louisiana: A Geographic and Cultural Journey
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at Alabama and Louisiana: A Geographic and Cultural Journey
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at Alabama and Louisiana: A Geographic and Cultural Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at Alabama and Louisiana: A Geographic and Cultural Journey

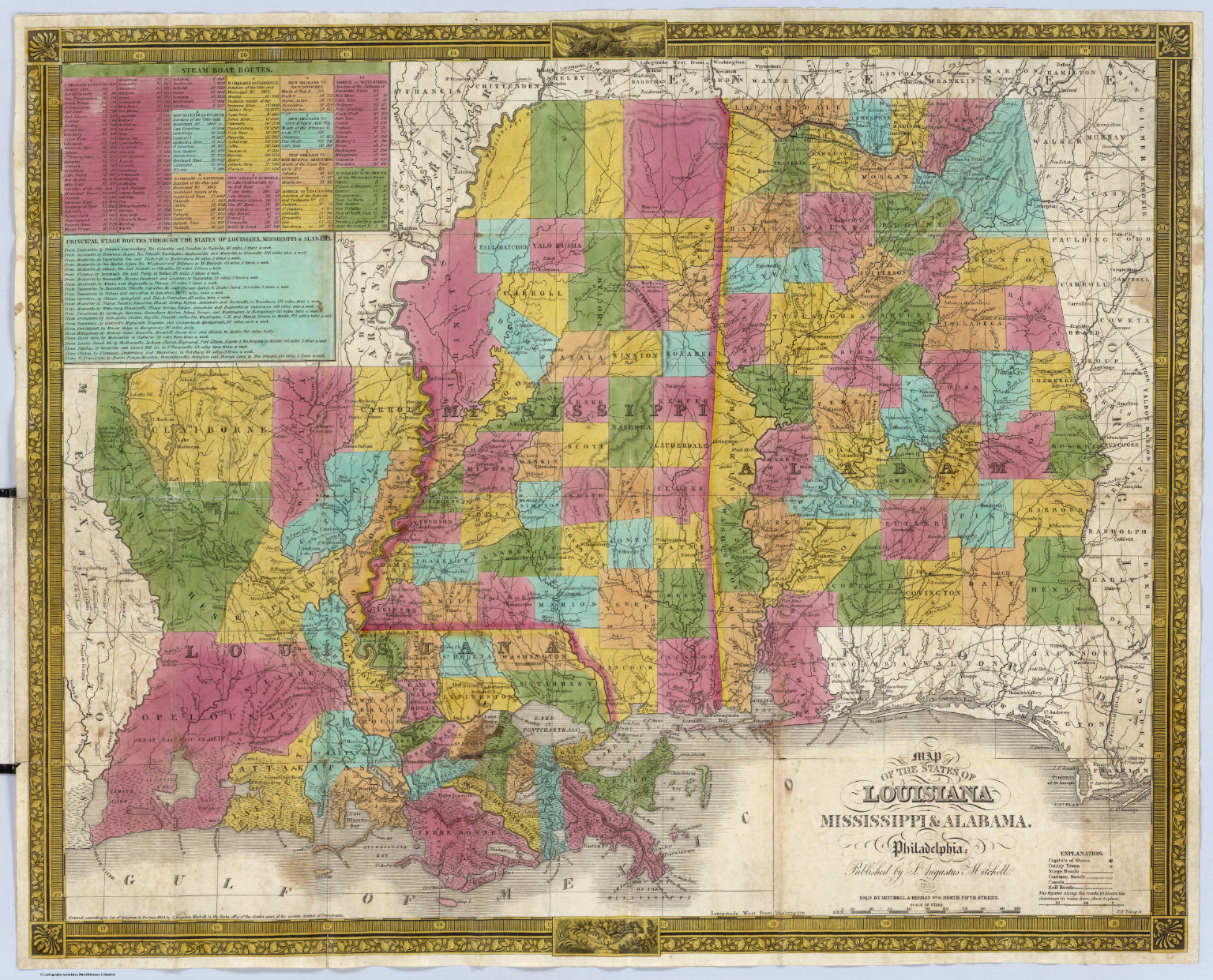
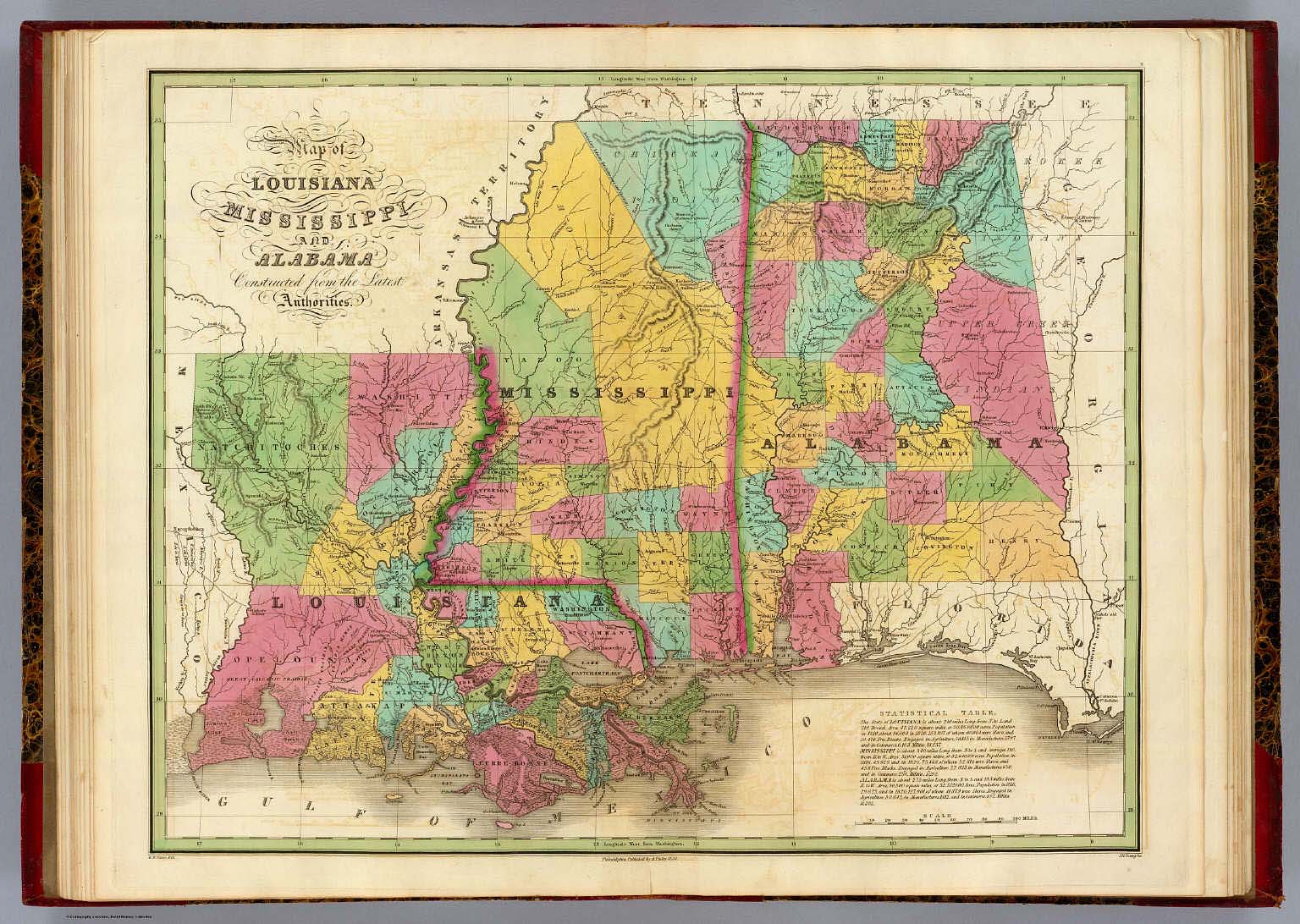
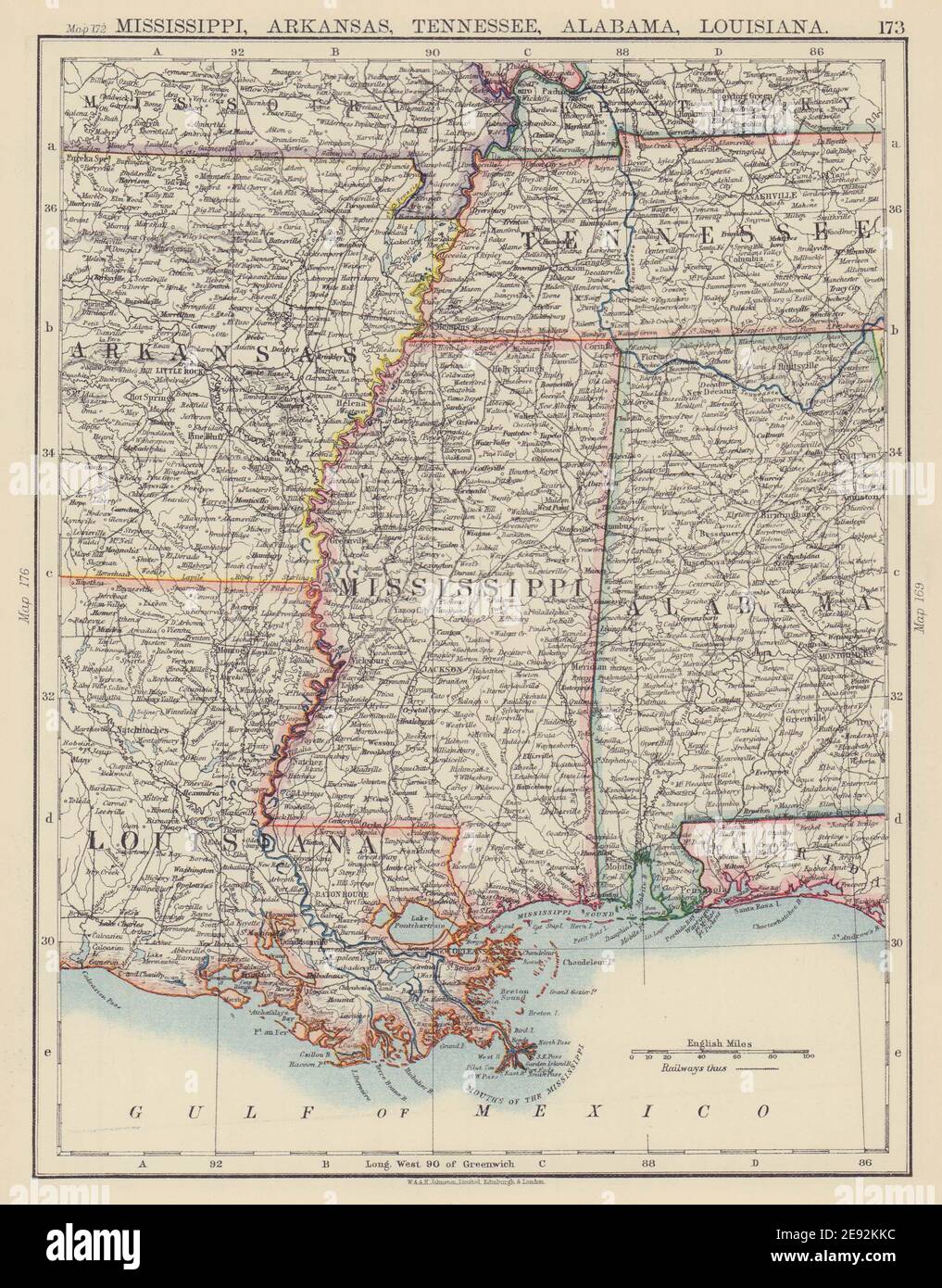
The southeastern United States holds a tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich histories, and vibrant cultures. Two states that embody this diversity are Alabama and Louisiana, each offering unique geographic features and cultural experiences. This exploration delves into the maps of these states, examining their geographical characteristics, historical influences, and cultural expressions, highlighting the distinct identities that make them fascinating destinations.
Alabama: The Heart of the South
Alabama, often referred to as the "Yellowhammer State," occupies a central position in the southeastern United States. Its map reveals a state characterized by rolling hills, fertile plains, and a significant coastline along the Gulf of Mexico.
Geographic Features:
- The Appalachian Mountains: The northern portion of Alabama is home to the southernmost reaches of the Appalachian Mountains, creating a rugged and scenic landscape. This region is known for its diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic Appalachian Trail that passes through the state.
- The Piedmont Plateau: Transitioning from the mountains to the coastal plains, the Piedmont Plateau of Alabama is characterized by gently rolling hills and fertile soils. This region is a significant agricultural hub, producing crops such as cotton, soybeans, and peanuts.
- The Coastal Plain: The southern and southwestern portion of Alabama is dominated by the Coastal Plain, a flat, low-lying region that extends to the Gulf of Mexico. This area is known for its sandy beaches, vast swamps, and abundant wildlife, including alligators, deer, and numerous bird species.
- The Black Belt: A distinctive feature of Alabama’s map is the Black Belt, a narrow band of fertile, dark-colored soil that stretches across the central portion of the state. This region was historically known for its cotton plantations and played a significant role in the state’s agricultural development.
Historical Influences:
Alabama’s history is intertwined with the broader narrative of the American South. The state was a key player in the development of the cotton industry, leading to the establishment of large plantations and a complex social structure. The Civil War significantly impacted Alabama, leaving lasting scars on its social and economic landscape. The state’s history is also marked by the Civil Rights Movement, with Birmingham becoming a focal point for activism and change.
Cultural Expressions:
Alabama’s cultural identity is deeply rooted in its Southern heritage. The state is renowned for its traditional music, including blues, gospel, and country, as well as its vibrant culinary scene, featuring dishes like fried chicken, barbecue, and sweet tea. The state’s arts and crafts tradition is also strong, with renowned artists specializing in pottery, quilting, and woodworking.
Louisiana: The Pelican State
Louisiana, known as the "Pelican State," occupies a unique position on the southeastern coast, sharing a border with the Gulf of Mexico and the Mississippi River. Its map reveals a state characterized by diverse landscapes, ranging from swampy wetlands to rolling hills.
Geographic Features:
- The Mississippi River Delta: The most prominent feature on Louisiana’s map is the Mississippi River Delta, a vast, fertile region formed by the deposition of sediment from the river. This area is a critical ecosystem, supporting a rich biodiversity of plant and animal life, including the state’s iconic alligators.
- The Atchafalaya Basin: The Atchafalaya Basin, the largest swamp in the United States, is a significant geographic feature of Louisiana. This vast wetland area is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life, including cypress trees, alligators, and numerous bird species.
- The Coastal Marshes: Louisiana’s coastline is characterized by extensive coastal marshes, a critical habitat for a wide range of wildlife. These marshes are under threat from rising sea levels and erosion, highlighting the state’s vulnerability to climate change.
- The Upland Regions: The northern and western portions of Louisiana are characterized by rolling hills and forested areas. This region is home to numerous state parks and offers opportunities for hiking, camping, and outdoor recreation.
Historical Influences:
Louisiana’s history is deeply intertwined with its unique geographic location. The state’s proximity to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico made it a vital trade route and a strategic location for European colonization. French influence is deeply embedded in Louisiana’s culture and history, evident in its language, cuisine, and architecture. The state also played a significant role in the development of the American West, serving as a gateway for westward expansion.
Cultural Expressions:
Louisiana’s culture is a vibrant blend of French, African, and American influences. The state is renowned for its vibrant music scene, including Cajun and Zydeco music, as well as its rich culinary tradition, featuring dishes like gumbo, jambalaya, and beignets. The state’s unique festivals and celebrations, such as Mardi Gras, showcase its diverse cultural heritage.
Comparing Alabama and Louisiana: A Tale of Two States
While both Alabama and Louisiana share a common Southern heritage, their maps reveal distinct geographic features and cultural expressions. Alabama’s landscape is characterized by a mix of rolling hills, fertile plains, and a significant coastline, while Louisiana’s map is dominated by the Mississippi River Delta and vast wetlands.
Cultural Differences:
The cultural differences between Alabama and Louisiana are equally pronounced. Alabama’s culture is deeply rooted in its Southern traditions, while Louisiana’s culture is a vibrant fusion of French, African, and American influences. This difference is reflected in their music, cuisine, and festivals.
Economic Differences:
Alabama’s economy is more diversified, with significant contributions from agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. Louisiana’s economy is heavily reliant on the oil and gas industry, making it more vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy markets.
Conclusion: A Rich Tapestry of Geography and Culture
The maps of Alabama and Louisiana provide a fascinating glimpse into the diverse landscapes, rich histories, and vibrant cultures of these two southeastern states. From the rolling hills of Alabama to the vast wetlands of Louisiana, these states offer unique experiences for travelers and residents alike. Understanding the geographical and cultural nuances of these states allows for a deeper appreciation of the rich tapestry of the American South.
FAQs
1. What are the major cities in Alabama and Louisiana?
- Alabama: Birmingham, Huntsville, Mobile, Montgomery
- Louisiana: Baton Rouge, New Orleans, Shreveport, Lafayette
2. What are the main industries in Alabama and Louisiana?
- Alabama: Agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, aerospace, automotive
- Louisiana: Oil and gas, tourism, agriculture, seafood, manufacturing
3. What are some popular tourist attractions in Alabama and Louisiana?
- Alabama: Gulf Shores, Birmingham Botanical Gardens, Huntsville Space & Rocket Center, Montgomery’s Civil Rights Memorial, Oak Mountain State Park
- Louisiana: New Orleans French Quarter, Cajun Country, Atchafalaya Basin, Louisiana State Capitol, French Market
4. What are the climate differences between Alabama and Louisiana?
- Alabama: Alabama has a humid subtropical climate with hot, humid summers and mild winters.
- Louisiana: Louisiana also has a humid subtropical climate with hot, humid summers and mild winters. However, Louisiana’s proximity to the Gulf of Mexico makes it more susceptible to hurricanes.
5. What are the main languages spoken in Alabama and Louisiana?
- Alabama: English is the primary language spoken in Alabama.
- Louisiana: English is the primary language spoken in Louisiana. However, French, particularly Cajun French, is also spoken in certain areas.
Tips for Visiting Alabama and Louisiana
-
Alabama:
- Visit the Gulf Shores for pristine beaches and seafood.
- Explore the historical sites in Montgomery, the state capital.
- Attend a college football game in Tuscaloosa, home to the University of Alabama.
-
Louisiana:
- Experience the vibrant culture of New Orleans, including its music, cuisine, and festivals.
- Visit Cajun Country to learn about the region’s unique heritage and cuisine.
- Take a swamp tour to see the iconic alligators and other wildlife.
Conclusion:
The maps of Alabama and Louisiana serve as gateways to understanding the unique character of these two southeastern states. Their diverse landscapes, rich histories, and vibrant cultures invite exploration and discovery, offering a rich tapestry of experiences for travelers and residents alike. The differences between these states, both geographical and cultural, contribute to the vibrant mosaic of the American South, making them fascinating destinations for those seeking a deeper understanding of this region’s history and identity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at Alabama and Louisiana: A Geographic and Cultural Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!